Question: This lab is about a very well known implementation: Linked Lists. Last week notes discussed what a linked list is, if you already forgot please
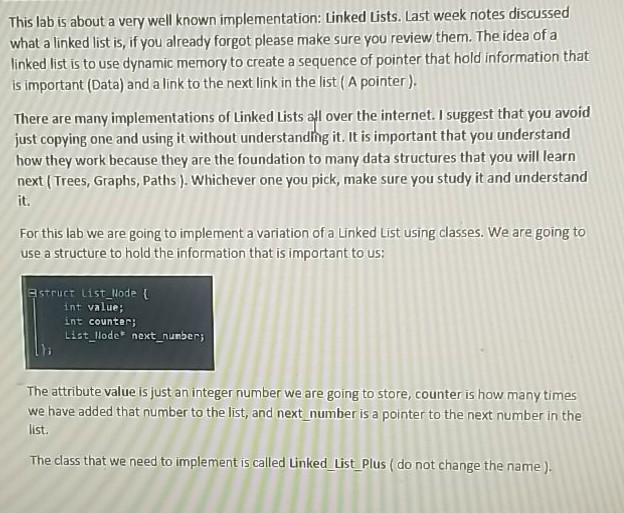
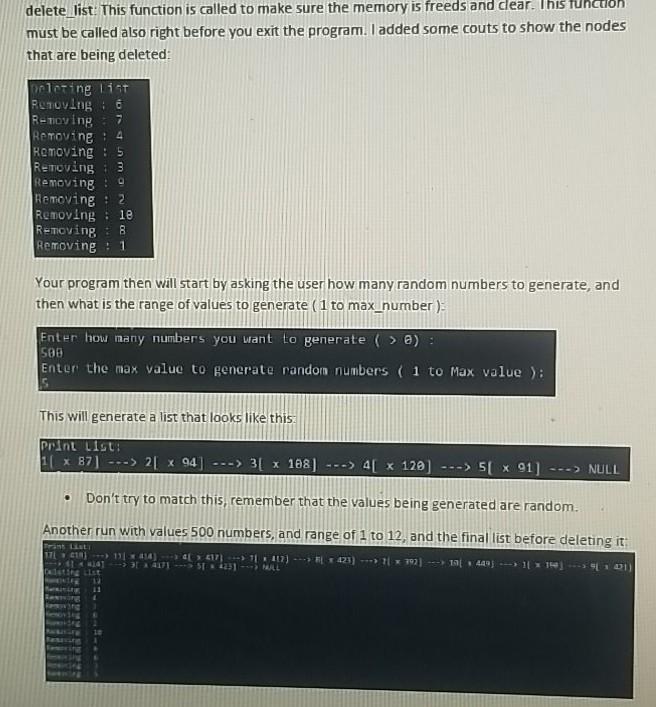
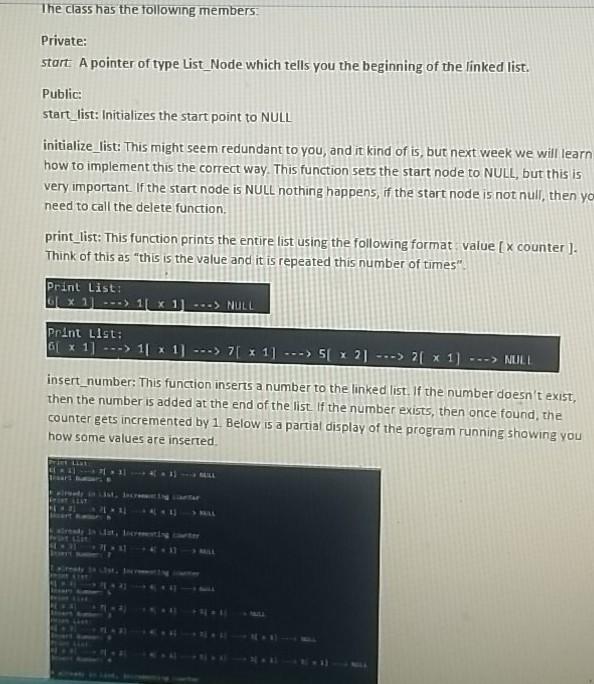
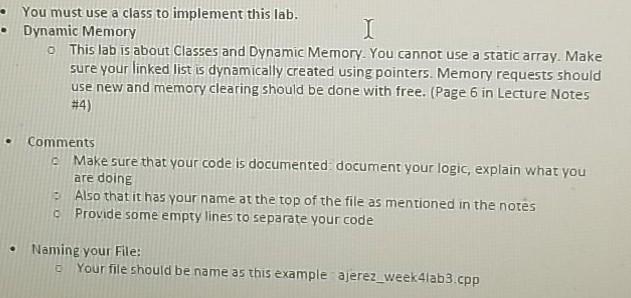
This lab is about a very well known implementation: Linked Lists. Last week notes discussed what a linked list is, if you already forgot please make sure you review them. The idea of a linked list is to use dynamic memory to create a sequence of pointer that hold information that is important (Data) and a link to the next link in the list (A pointer), There are many implementations of Linked Lists all over the internet. I suggest that you avoid just copying one and using it without understanding it. It is important that you understand how they work because they are the foundation to many data structures that you will learn next (Trees, Graphs, Paths). Whichever one you pick, make sure you study it and understand it. For this lab we are going to implement a variation of a Linked List using classes. We are going to use a structure to hold the information that is important to us: struct List_Model int value; int counter List_llode next_number; The attribute value is just an integer number we are going to store, counter is how many times we have added that number to the list, and next_number is a pointer to the next number in the list. The class that we need to implement is called Linked List Plus ( do not change the name). delete list: This function is called to make sure the memory is freeds and dear. This function must be called also right before you exit the program. I added some couts to show the nodes that are being deleted: 7 proting list Removing Removing Removine: 4 Removing: 5 Removing 3 Removing : 9 Removing : 2 Removing : 18 Removing 8 Removine: 1 Your program then will start by asking the user how many random numbers to generate, and then what is the range of values to generate (1 to max_number) Enter how many numbers you want to generate ( > ): 500 Enter the max value to generate randon numbers ( 1 to Max value): This will generate a list that looks like this. Princ LIGUE 11 x B7] ---> 21 x 94 -> 3 x 188) ---> 4[ x 120) ---> 5 x 91] ---> NULL Don't try to match this, remember that the values being generated are random. Another run with values 500 numbers, and range of 1 to 12, and the final list before deleting it 121) 1114) *417) -> 11 412) ---> 423) -> 11192) ---> 191 449---> 1119] [101) OLAF.SSE 4251 - MALL The class has the following members Private: start A pointer of type List_Node which tells you the beginning of the linked list. Public: start_list: Initializes the start point to NULL initialize_list: This might seem redundant to you, and it kind of is, but next week we will learn how to implement this the correct way. This function sets the start node to NULL, but this is very important. If the start node is NULL nothing happens, if the start node is not null, then yo need to call the delete function. print_list: This function prints the entire list using the following format value [x counter ). Think of this as "this is the value and it is repeated this number of times". Print List: * ... 1 NULL Print List: 61 * 1] ---> 1[1] ---> 71 : 1] ---> 5 1 2] ---> 21 x 1) ---> NULL insert_number: This function inserts a number to the linked list. If the number doesn't exist, then the number is added at the end of the list. If the number exists, then once found the counter gets incremented by 1 Below is a partial display of the program running showing you how some values are inserted ser are You must use a class to implement this lab. Dynamic Memory I o This lab is about Classes and Dynamic Memory. You cannot use a static array. Make sure your linked list is dynamically created using pointers. Memory requests should use new and memory clearing should be done with free. (Page 6 in Lecture Notes #4) Comments Make sure that your code is documented document your logic, explain what you are doing Also that it has your name at the top of the file as mentioned in the notes Provide some empty lines to separate your code Naming your File: Your file should be name as this example ajerez_week4lab3.cpp
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


