Question: This problem concerns the electric circuit shown in the figure below. figure of a circuit with a capacitor, inductor and resistor in series. A charged
This problem concerns the electric circuit shown in the figure below. figure of a circuit with a capacitor, inductor and resistor in series. A charged capacitor connected to an inductor causes a current to flow through the inductor until the capacitor is fully discharged. The current in the inductor, in turn, charges up the capacitor until the capacitor is fully charged again. If Q(t) Q ( t ) is the charge on the capacitor at time t t , and I I is the current, then I=dQdt. I = d Q d t . If the circuit resistance is zero, then the charge Q Q and the current I I in the circuit satisfy the differential equation LdIdt+QC=0, L d I d t + Q C = 0 , where C C is the capacitance and L L is the inductance, so Ld2Qdt2+QC=0. L d 2 Q d t 2 + Q C = 0. Then, just as as a spring can have a damping force which affects its motion, so can a circuit; this is introduced by the resistor, so that if the resistance of the resistor is R R , Ld2Qdt2+RdQdt+1CQ=0. L d 2 Q d t 2 + R d Q d t + 1 C Q = 0. If L=1 L = 1 henry, R=1 R = 1 ohm, and C=4 C = 4 farads, find a formula for the charge when (a) Q(0)=0 Q ( 0 ) = 0 and Q′(0)=4 Q ′ ( 0 ) = 4 : Q(t)= Q ( t ) = (b) Q(0)=4 Q ( 0 ) = 4 and Q′(0)=0 Q ′ ( 0 ) = 0 : Q(t)= Q ( t ) =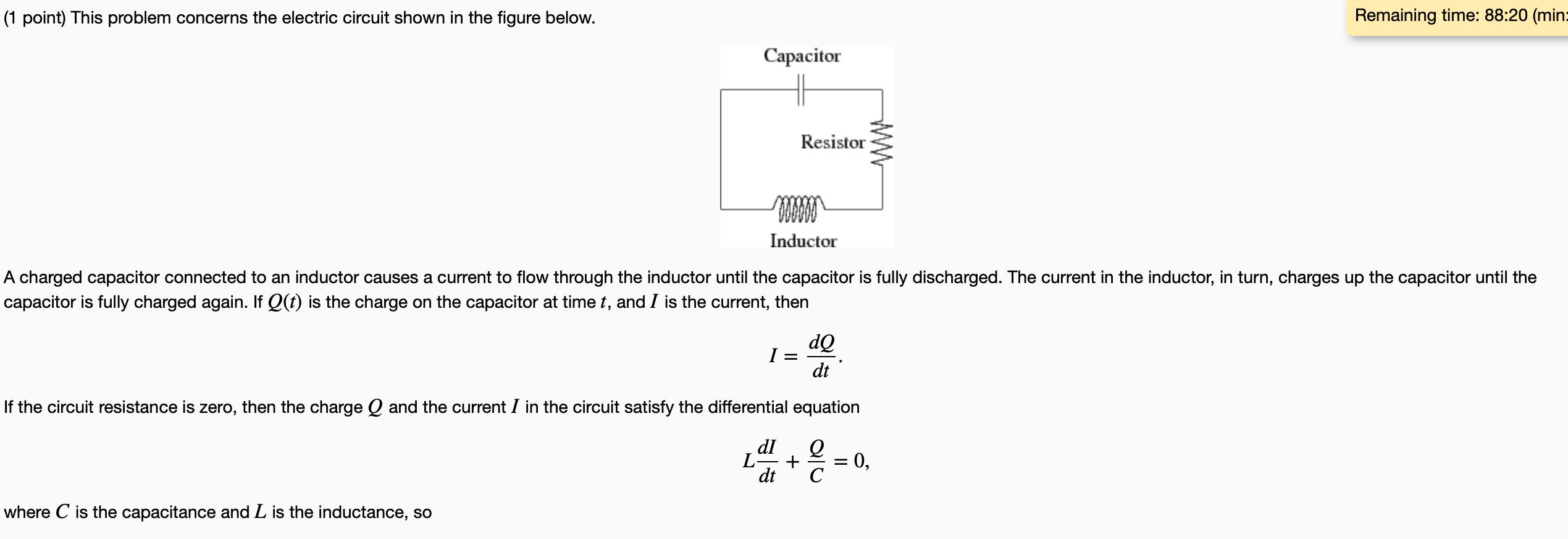
(1 point) This problem concerns the electric circuit shown in the figure below. Capacitor where C is the capacitance and L is the inductance, so Resistor mooooo Inductor A charged capacitor connected to an inductor causes a current to flow through the inductor until the capacitor is fully discharged. The current in the inductor, in turn, charges up the capacitor until the capacitor is fully charged again. If Q(t) is the charge on the capacitor at time t, and I is the current, then dQ dt If the circuit resistance is zero, then the charge and the current I in the circuit satisfy the differential equation I = dI L4 + 2 = dt C Remaining time: 88:20 (min: 0,
Step by Step Solution
3.42 Rating (152 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
given a b differential Equation LdQ Since Now dt NOW da ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


