Question: This problem investigates the derivative of the absolute value function. Recall that we define the absolute value as: |x| { (a) In the space
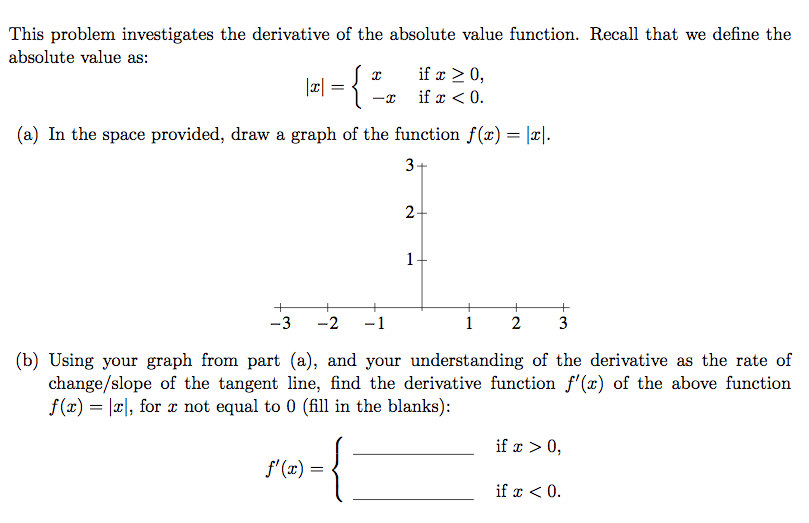

This problem investigates the derivative of the absolute value function. Recall that we define the absolute value as: |x| { (a) In the space provided, draw a graph of the function f(x) = |x|. 3- = x f'(x) = -I + -3 -2 1 if x 0, if x < 0. 2- 1. + 1 2 3 (b) Using your graph from part (a), and your understanding of the derivative as the rate of change/slope of the tangent line, find the derivative function f'(x) of the above function f(x)= x, for r not equal to 0 (fill in the blanks): if x > 0, if x < 0. (c) But what about f'(0)? It is not so clear from the picture even how to draw a tangent line to the function at the origin. So let's try to compute f'(0) by first looking at the corresponding lefthand and righthand limits of the difference quotient. i. Compute limh0+ f(0+h)-f(0). Hint: use the piecewise definition of f(x) given above. h ii. Compute limh0- (0+h)-f(0) iii. What do your answers to parts (i) and (ii) tell you about f'(0)? Please explain.
Step by Step Solution
3.33 Rating (153 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


