Question: This project must be completed by writing a computer program using the language of your choice, but NOT Excel. The 1-D steady state diffusion for
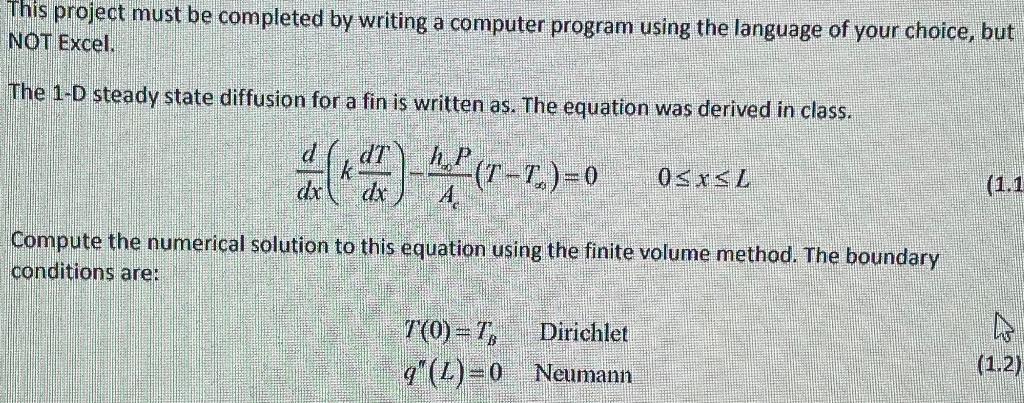

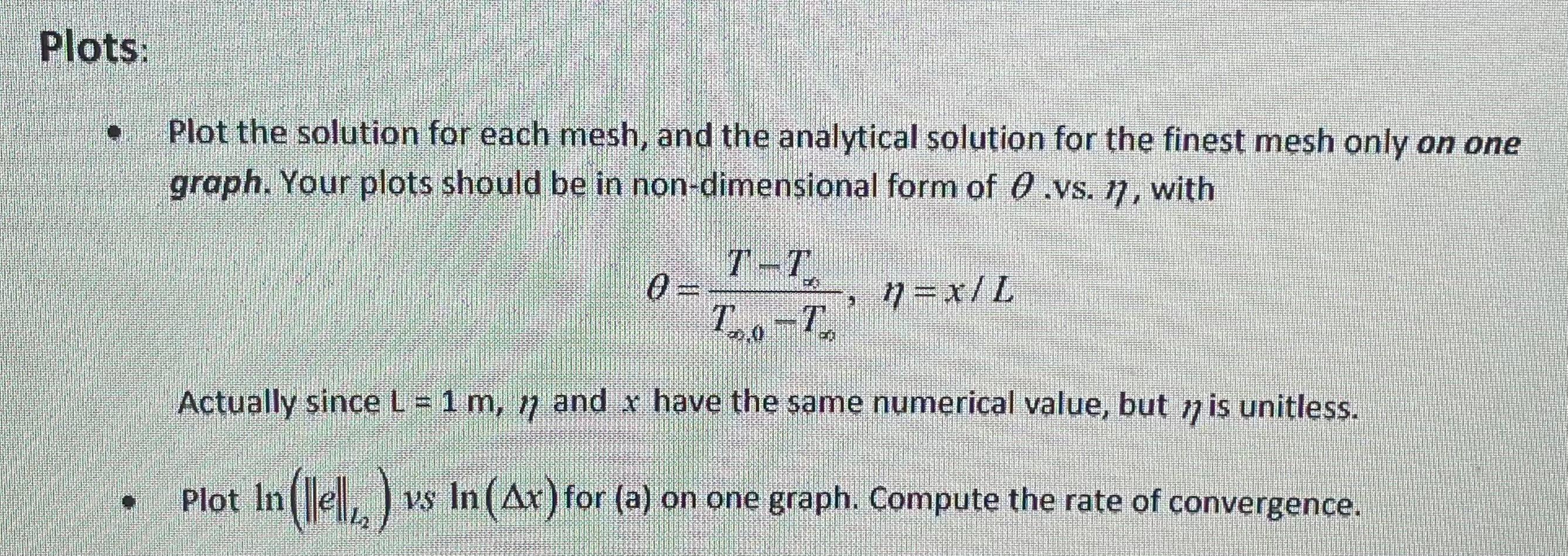

This project must be completed by writing a computer program using the language of your choice, but NOT Excel. The 1-D steady state diffusion for a fin is written as. The equation was derived in class. k h.P (T -Tv)=0 osrs Compute the numerical solution to this equation using the finite volume method. The boundary conditions are: Dirichlet T(0)=T, q" (2)=0 Neumann (1.2) With the following constants. To = 200C (Dirichlet, for all) 7. = 100C = 200C (Robin, for graduate students) L la (1.3) The fin is circular with a diameter, d=8cm k = 100 W/m-K, h = 50 W/m2-K. Use the Dirichlet boundary condition approximation. The tridiagonal coefficients are given by Eqns. 7.24, 7.29, and 7.56 for the interior, and left and right boundaries, respectively. See Example 3 in Chapter 7 for guidance. Assume constant mesh spacing for all calculations. Obtain solutions for 20, 40, 80, 120, and 360 cell meshes. The analytical solution is given by Eqn. 7.50. Plots: Plot the solution for each mesh, and the analytical solution for the finest mesh only on one graph. Your plots should be in non-dimensional form of 8 .vs. 17, with FO , 12=x/L TE Actually since L = 1 m, n and x have the same numerical value, but n is unitless. Plot In ||ell,,) vs In (Ax) for (a) on one graph. Compute the rate of convergence. Report: In your own words and equations (not cut and paste equations). 1. Present equations and boundary conditions. 2. Present tridiagonal coefficients. 3. Present results. 4. Discuss results. Number and reference every figure and/or table you put in your report
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


