Question: This question applies to parts ( mathbf{1 - 1 0} ). It contains drop-down multiple choice and numerical questions. Consider a world in which there
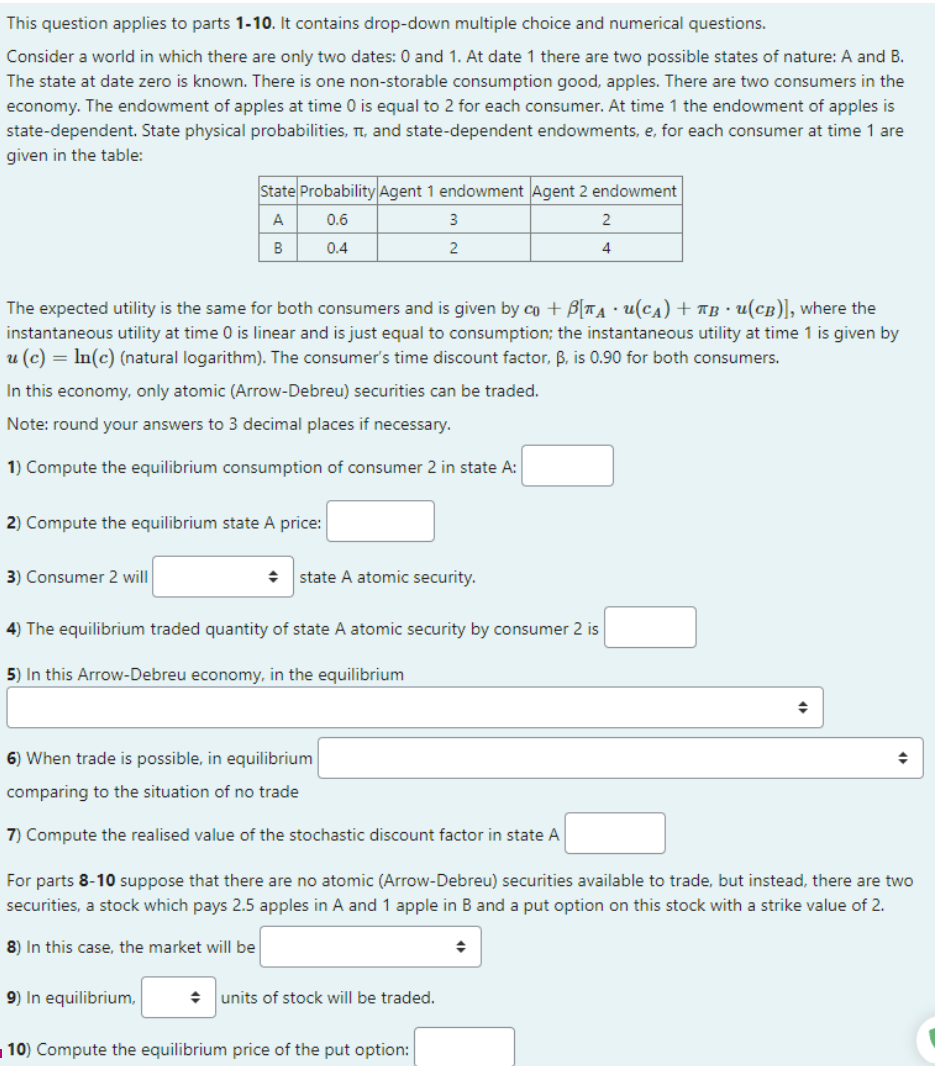
This question applies to parts \\( \\mathbf{1 - 1 0} \\). It contains drop-down multiple choice and numerical questions. Consider a world in which there are only two dates: 0 and 1 . At date 1 there are two possible states of nature: \\( A \\) and \\( B \\). The state at date zero is known. There is one non-storable consumption good, apples. There are two consumers in the economy. The endowment of apples at time 0 is equal to 2 for each consumer. At time 1 the endowment of apples is state-dependent. State physical probabilities, \\( \\pi \\), and state-dependent endowments, \\( e \\), for each consumer at time 1 are given in the table: The expected utility is the same for both consumers and is given by \\( c_{0}+\\beta\\left[\\pi_{A} \\cdot u\\left(c_{A}\ ight)+\\pi_{B} \\cdot u\\left(c_{B}\ ight)\ ight] \\), where the instantaneous utility at time 0 is linear and is just equal to consumption; the instantaneous utility at time 1 is given by \\( u(c)=\\ln (c) \\) (natural logarithm). The consumer's time discount factor, \\( \\beta \\), is 0.90 for both consumers. In this economy, only atomic (Arrow-Debreu) securities can be traded. Note: round your answers to 3 decimal places if necessary. 1) Compute the equilibrium consumption of consumer 2 in state \\( A: \\) 2) Compute the equilibrium state A price: 3) Consumer 2 will state \\( \\mathrm{A} \\) atomic security. 4) The equilibrium traded quantity of state \\( A \\) atomic security by consumer 2 is 5) In this Arrow-Debreu economv, in the equilibrium 6) When trade is possible, in equilibrium comparing to the situation of no trade 7) Compute the realised value of the stochastic discount factor in state A For parts 8-10 suppose that there are no atomic (Arrow-Debreu) securities available to trade, but instead, there are two securities, a stock which pays 2.5 apples in \\( A \\) and 1 apple in B and a put option on this stock with a strike value of 2. 8) In this case, the market will be 9) In equilibrium, units of stock will be traded. 10) Compute the equilibrium price of the put option
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


