Question: This question considers a system with two processing units. There are two types of requests that can arrive at this system: The Type 1 requests
This question considers a system with two processing units. There are two types of requests that can arrive at this system:
The Type requests require only one processing unit. These requests arrive according
to a Poisson distribution with a mean rate of lambda These requests require a processing
time which is exponentially distributed with a mean processing time of
Each Type request requires two processing units simultaneously. By simultaneously we mean that a Type request can only be admitted into the two processing
units when both processing units are available. If admitted, both processing units will
start to work on the admitted request at the same time and they will complete the
request at the same time.
Type requests arrive at the system according to a Poisson distribution with a mean
rate of lambda The above description says that a Type request requires the same amount
of processing time at each processing unit. The processing time required by a Type
request at each processing unit is exponentially distributed with a mean processing
time of
The four interarrival and service time distributions are assumed to be independent.
The system has two queueing slots. One slot is reserved for Type requests only and it
has a capacity to hold exactly one Type request. The other slot can only be used to hold
Type requests and it has a capacity to hold exactly one Type request.
The rules here are:
If the Type queueing slot is empty and there is a request at the Type queueing slot,
then the Type request is admitted to the processing units if both units are available;
otherwise, the request remains in the Type queueing slot.
If there is a request in the Type queueing slot, then this request will be admitted into
a newly available processing unit.
Note that the second rule above covers the case when both Type and Type queueing
slots have a request each. In that case, the request in Type queueing slot will be admitted
because the second rule above gives the priority to the Type request. Note also that the
Type request in the queue will not be admitted because there will not be two processing
units available; the Type request will remain in the queue.
Note that the above rules imply that:
If there is a Type request is in the queue, then it is not possible to have any idle
processing unit.
If there is a Type request in the queue, then it is not possible to have two idle
processing units. It is possible to have an empty Type queue, an occupied Type queue and one idle
processing unit.
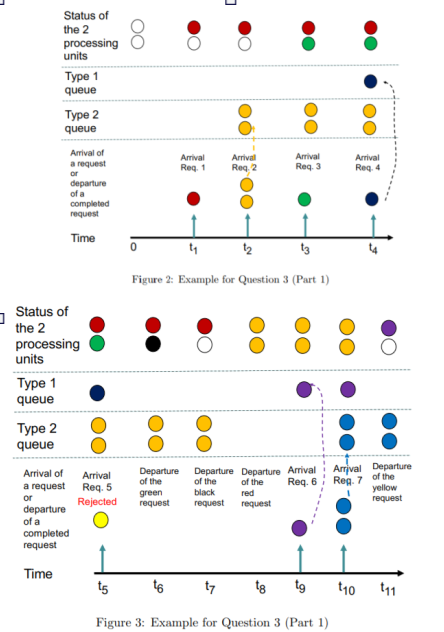
We now describe what happens when a Type request arrives. These are the possible
scenarios:
If the Type queueing slot is occupied, then this request is rejected.
If the Type queueing slot is not occupied, then:
If at least one processing unit is idle, then this request will be admitted to an idle
processing unit and its processing will begin.
If both processing units are occupied, then this request will be admitted into the
Type queueing slot.
Finally, we describe what happens when a Type request arrives. These are the possible
scenarios:
If the Type queueing slot is occupied, then this request is rejected.
If the Type queueing slot is not occupied, then:
If both processing units are idle, then this request will be admitted to both processing units and its processing will begin.
If at least one processing unit is occupied, then this request will be admitted into
the Type queueing slot.
We will now use an example to illustrate the operation of the system.
Answer the following questions:
a Formulate a continuoustime Markov chain for the system using the following tuple
as the state:
number of Type requests in the processing units,
number of Type requests in the processing units,
number of requests in the Type queueing slot,
number of requests in the Type queueing slot
Your formulation should include a list of all possible states and the transition rates
between states. The transition rates should be expressed in terms lambda lambda and b Assuming that lambda lambda and All these four parameters
have the unit of number of queries per some given unit time.
i Determine the steady state probabilities of the state of the continuoustime Markov
chain that you have specified in Part a
ii Determine the probability that an arriving Type request will be rejected.
iii Determine the mean waiting time of Type requests.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


