Question: this question is related to material science. mircostructure evolution and control in metallic materials Q3. Understanding and controlling microstructure formation in metallic alloys upon solidification
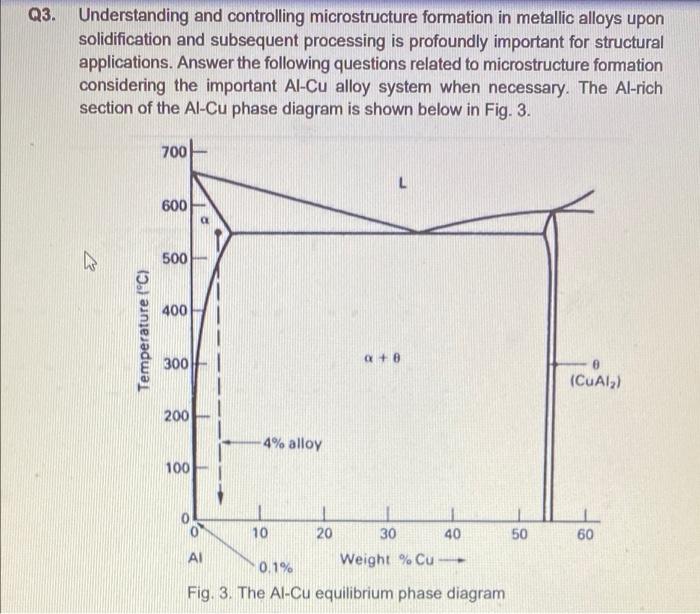


Q3. Understanding and controlling microstructure formation in metallic alloys upon solidification and subsequent processing is profoundly important for structural applications. Answer the following questions related to microstructure formation considering the important Al-Cu alloy system when necessary. The Al-rich section of the Al-Cu phase diagram is shown below in Fig. 3. 700 600 IN 500 400 Temperature (C) 3001 Q+8 0 (CUAI) 200 4% alloy 100 60 10 20 30 40 50 AI 0.1% Weight % Cu -- Fig. 3. The Al-Cu equilibrium phase diagram (a) State the reasons why attaining a fine equiaxed polycrystalline grain structure during solidification is desirable. [5 marks] (b) Al-Cu alloys are inoculated using Al-5Ti-1B (compositions expressed in wt%) grain refiner where the TiB2 particles present in the refiner promote Al-grain nucleation. Explain why the refiner uses Ti concentration significantly higher than 2.2wt.% required for the stoichiometric ratio in TiB2. [4 marks] (c) Al-4wt%Cu sheets are produced from solidified ingots by rolling. What strategy would you suggest for refining the grain structure during manufacturing? (6 marks] (d) Age hardening of Al-4wt%Cu alloy significantly increases its strength properties. Artificially aging the solution treated alloy at different temperatures leads to considerable variation in the peak attainable strength. Explain why this happens. [5 marks] (e) In relation to microstructure formation during the processing of metallic materials, state if the following statements are 'True' or 'False'. I i) Dendrites observed during solidification of pure metals develop due to constitutional undercooling. ii) Low substrate-solid interfacial energy leads to low contact angle for spherical cap nuclei. iii) Low melt-superheat can lead to grain refinement during solidification. iv) Stored energy of cold work provides driving force for grain growth during annealing v) During age hardening, precipitation is prevented at the grain boundaries. (5 marks] Q3. Understanding and controlling microstructure formation in metallic alloys upon solidification and subsequent processing is profoundly important for structural applications. Answer the following questions related to microstructure formation considering the important Al-Cu alloy system when necessary. The Al-rich section of the Al-Cu phase diagram is shown below in Fig. 3. 700 600 IN 500 400 Temperature (C) 3001 Q+8 0 (CUAI) 200 4% alloy 100 60 10 20 30 40 50 AI 0.1% Weight % Cu -- Fig. 3. The Al-Cu equilibrium phase diagram (a) State the reasons why attaining a fine equiaxed polycrystalline grain structure during solidification is desirable. [5 marks] (b) Al-Cu alloys are inoculated using Al-5Ti-1B (compositions expressed in wt%) grain refiner where the TiB2 particles present in the refiner promote Al-grain nucleation. Explain why the refiner uses Ti concentration significantly higher than 2.2wt.% required for the stoichiometric ratio in TiB2. [4 marks] (c) Al-4wt%Cu sheets are produced from solidified ingots by rolling. What strategy would you suggest for refining the grain structure during manufacturing? (6 marks] (d) Age hardening of Al-4wt%Cu alloy significantly increases its strength properties. Artificially aging the solution treated alloy at different temperatures leads to considerable variation in the peak attainable strength. Explain why this happens. [5 marks] (e) In relation to microstructure formation during the processing of metallic materials, state if the following statements are 'True' or 'False'. I i) Dendrites observed during solidification of pure metals develop due to constitutional undercooling. ii) Low substrate-solid interfacial energy leads to low contact angle for spherical cap nuclei. iii) Low melt-superheat can lead to grain refinement during solidification. iv) Stored energy of cold work provides driving force for grain growth during annealing v) During age hardening, precipitation is prevented at the grain boundaries. (5 marks]
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


