Question: Three different assembly methods have been proposed for a new product. A completely randomized experimental design was chosen to determine which assembly method results in
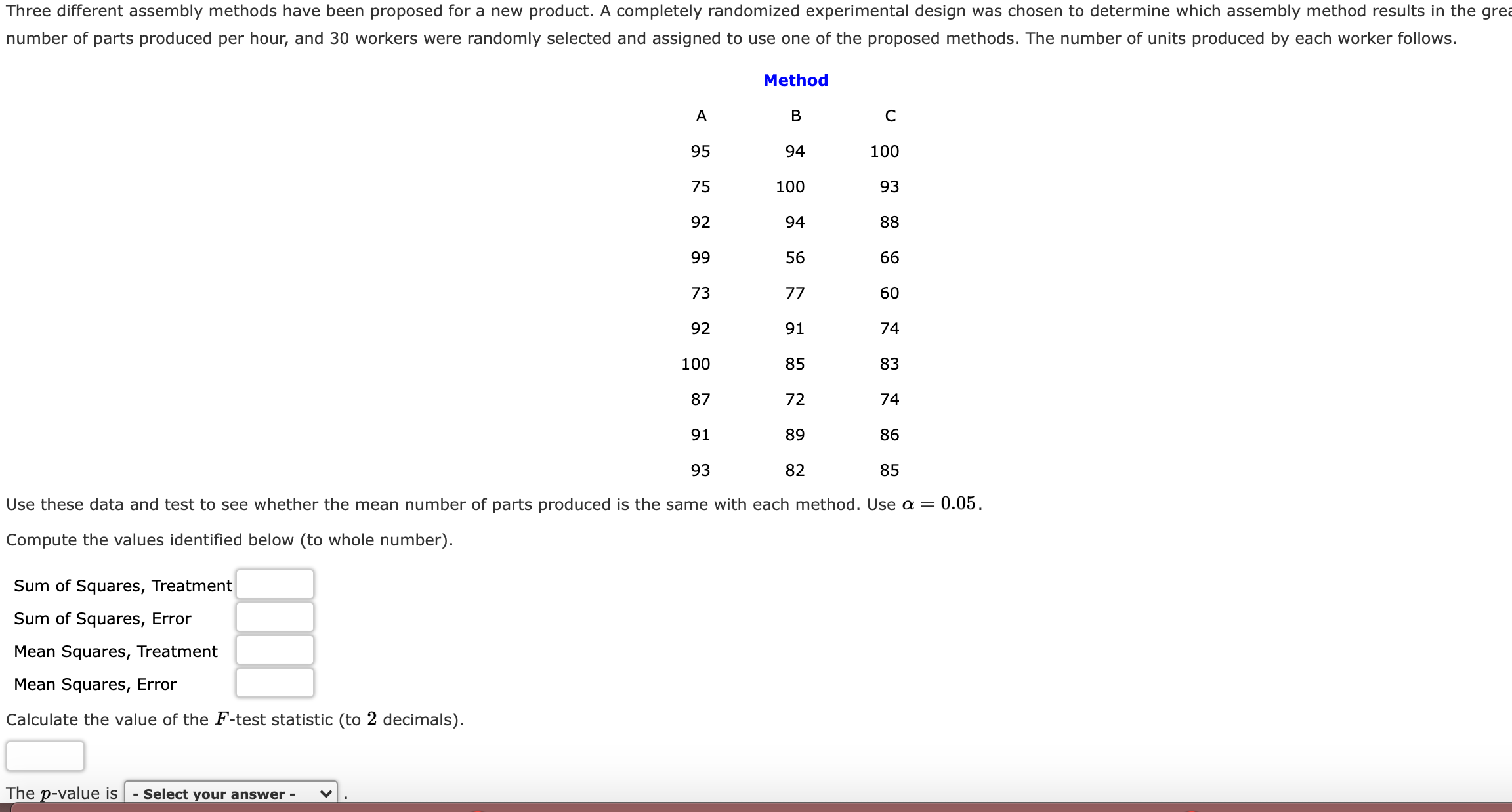

Three different assembly methods have been proposed for a new product. A completely randomized experimental design was chosen to determine which assembly method results in the grez number of parts produced per hour, and 30 workers were randomly selected and assigned to use one of the proposed methods. The number of units produced by each worker follows. Method A B C 95 94 100 75 100 93 92 94 88 99 56 66 73 77 60 92 91 74 100 85 83 87 72 74 91 89 86 93 82 85 Use these data and test to see whether the mean number of parts produced is the same with each method. Use a = 0.05. Compute the values identified below (to whole number). Sum of Squares, Treatment Sum of Squares, Error Mean Squares, Treatment Mean Squares, Error Calculate the value of the F-test statistic (to 2 decimals). The -value is - Select yo nswer - . 95 94 100 75 100 93 92 94 88 99 56 66 73 77 60 92 91 74 100 85 83 87 72 74 91 89 86 93 82 85 Use these data and test to see whether the mean number of parts produced is the same with each method. Use 0: = 0.05. Compute the values identified below (to whole number). Sum of Squares, Treatment Sum of Squares, Error Mean Squares, Treatment Mean Squares, Error Calculate the value of the Ftest statistic (to 2 decimals). The p-value is - Select your answer - v . What is your conclusion? - Select your answer - v that the means are not equal
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


