Question: thx for help DISTRIBUTION FUNCTION OF THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION The function tabulated is +() = e- du 0.02 0.03 0.01 0.07 0.09 0.0 0.5000 0.5040
thx for help
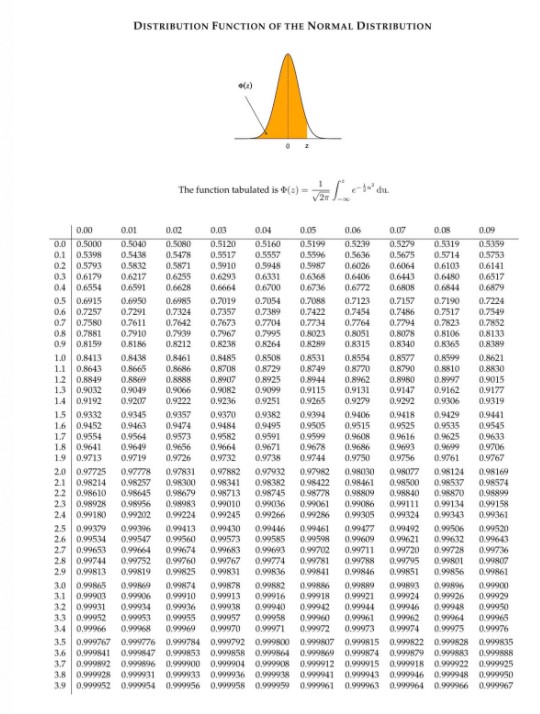

DISTRIBUTION FUNCTION OF THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION The function tabulated is +() = e- du 0.02 0.03 0.01 0.07 0.09 0.0 0.5000 0.5040 0.5080 0.5120 0.5160 05199 0.5239 0.5279 0.5019 0.5359 0.1 0.5398 0.5438 0.5478 0.5617 0.5557 0.5596 0.5636 0.5675 0.5714 0.5753 0.2 0.5793 0.58.12 0.5571 0.5910 0.5945 0.5947 0.6026 0.6064 0.6103 0.6141 03 0.6179 0.6217 0.6255 0.6293 0.6331 0.6365 0.6-406 0,6443 0.6480 0.6517 04 0.6554 0.6591 0.6628 0.6664 0.6700 0.6736 0.6772 0.680S 0.6844 0.6879 0.5 0.6915 0.6950 0.6985 0.7019 0.7054 0.7048 0.7123 0.7157 0.7190 0.7224 0.6 0.7257 0.7291 0.7324 0.7357 0.7369 0.7422 0.7454 0.7486 0.7517 0.75-49 0.7 0.7580 0.7611 0.76-42 0.7673 0.7704 0.7734 0.7764 0.7794 0.7823 0.7852 0.8 0.7861 0.7910 0.7939 0,7967 0.7995 0.5023 0.8051 0,8078 0.8106 0.8133 0.9 D.8159 0.8186 0.8212 0.8238 0.6264 0.8289 0.8315 0.8340 0.8365 0.8389 1.0 0.8413 0.8438 0.8461 0.8485 0.8508 0.8531 0.8554 0.8577 0.8599 0.8621 1.1. 0.8643 0.8665 0.8686 0.8708 0.6729 0.8749 0.8770 0.8790 0.8810 0.8830 1.2 0.6849 0.6869 0.8858 0.8907 0.8925 0.8944 0.8962 0.8960 0.8997 0.9015 1.3 0.9032 0.9049 0.9066 0.9082 0.9099 0.9115 0.9131 0.9147 0.9162 0.9177 1.4 0.9192 0.9207 0.9222 0.9236 0.9251 0.9265 0.9279 0.9292 0.9306 0.9319 1.5 0.9332 0.9345 0.9357 0.9370 0.9382 0.9394 0.9406 0.9418 0.9429 0.94-41 16 0.9452 0.9463 0.9474 0.9484 0.9495 0.9505 0.9515 0.9525 0.9535 0.9545 17 0.9554 0.9564 0.9573 0.9582 0.9591 0.9599 0.9608 0.9616 0.9625 0.9633 1.H 0.9641 0.9649 0.9656 0.9664 0.9671 0.9678 0.9686 0.9693 0.9649 0.9706 0.9713 0.9719 0.9726 0.9732 0.9735 0.9744 0.9750 0.9756 0.9761 0.9767 2.0 0.97725 0.97778 0.97831 0.97882 0.97932 0.97962 0.98030 0.98077 0.98124 0.98169 2.1 0.98214 0.98257 0.98300 0.98341 0.98382 0.98422 0.98-461 0,98500 0.98537 0.98574 2.2 0.98610 0.98645 0.98679 0.98713 0.98745 0.96778 0.98809 0.98840 0.93870 0.98899 2.3 0.98928 0.98956 0.98983 0.99010 0.99036 0.99061 0.99086 0,99111 0.99134 0.99158 2.4 0.99180 0.99202 0.99224 0.99245 0.99266 0.99286 0.99305 0.99324 0.993-43 0.99361 2.5 0.99379 0.99396 0.90413 0.99430 0.994 46 0.99461 0.99477 0,99492 0.99506 0.99520 2.6 0.99534 0.99547 0.99560 0,99573 0.99585 0.99598 0.99609 0,99621 0.99632 0.99643 17 0.99654 0.99664 0.99674 0,99683 0.99693 0.99702 0.99711 0,99720 0.99728 0.99736 2.8 0.99744 0.99752 0.99760 0.99767 0.99774 199761 0.99788 0.99795 0.99801 0.99807 20 0.99813 0.99819 0.9982 0.99831 0.99836 0.99841 0.99846 0.99851 0.99856 0.99861 3.01 0.99865 0.99869 0.99874 0,99878 0.99682 0.99856 0,99:889 0,99693 0.99896 0.99900 3.1 0.99903 0.90906 0.94910 0,99913 0.99916 0.99918 0.99921 0,99924 0.99926 0.99929 3.1 0.99931 0.99934 0.99936 0.99938 0,999 40 0.999.12 0.99944 0,999 46 0.999-48 0.99950 3.1 0.99952 0.90953 0.99957 0.99958 0.99960 0.99961 0.99962 0.99964 0.99915 3.4 0.99066 0.99969 0.99970 0.99971 0.99972 0.99973 0,99974 0.99975 0.99976 3.5 0.999767 0.999776 0.999784 0.999792 0.999500 0.999817 0.999815 0,999822 0.999828 0.999835 0.999841 0.999847 0.999853 0.999858 0.999564 0.999569 0.999874 0,999879 0.999683 0.999838 1.7 0.999692 0.999896 0.999900 0.999904 0.999908 0.999912 0.999915 0,999918 0.999922 0.999925 0.999925 0.999931 0.999933 0.999936 0.999938 0.999941 0.999943 0,999946 0.999948 0.999950 0,999953 0.999954 0.939956 0.999958 0.999959 0.999961 0.999963 0,999964 0.999966 0.999967A firm has a telephone and it receives numbers of calls that follow a Poisson distribution with a mean of 4 in a period of half an hour. (i) Write down the p.m.f. of the number of calls received by this telephone in a period of 2 hours. (ii) Compute the probability of receiving at least 4 calls in a period of 1 hour. (iii) Suppose that this firm has another telephone and it also receives numbers of calls that follow a Poisson distribution with a mean of 3 in a period of half an hour. Meanwhile, it receives calls independently of the other telephone. Let X be the total number of calls received by these two telephones in 1 hour. What is the distribution of X? and why
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


