Question: To be coded fully and working properly in MATLAB The figure below shows a cross-section of a double-pane window with argon gas between the glass.
To be coded fully and working properly in MATLAB
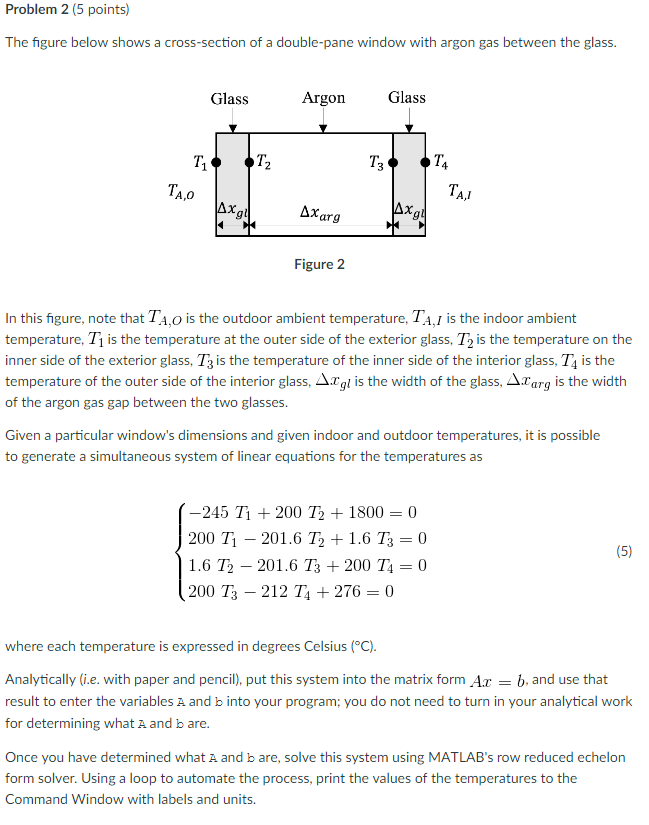
The figure below shows a cross-section of a double-pane window with argon gas between the glass. In this figure, note that T_A, O is the outdoor ambient temperature T_A, I is the indoor ambient temperature, T_1 is the temperature at the outer side of the exterior glass, T_2 is the temperature on the inner side of the exterior glass, T_3 is the temperature of the inner side of the interior glass, T_4 is the temperature of the outer side of the interior glass. Delta x_gl is the width of the glass, delta x_arg is the width of the argon gas gap between the two glasses. Given a particular window's dimensions and given indoor and outdoor temperatures, it is possible to generate a simultaneous system of linear equations for the temperatures as {-245 T_1 + 200 T_2 + 1800 = 0 200 T_1 -201.6 T_2 + 1.6 T_3 = 0 1.6 T_2 -201.6 T_3 + 200 T_4 = 0 200 T_3 -212 T_4 + 276 = 0 where each temperature is expressed in degrees Celsius (degree C). Analytically (i.e. with paper and pencil), put this system into the matrix form Ax = b, and use that result to enter the variables A and b into your program; you do not need to turn in your analytical work for determining what A and b are. Once you have determined what A and b are, solve this system using MATLAB's row reduced echelon form solver. Using a loop to automate the process, print the values of the temperatures to the Command Window with labels and units
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


