Question: TOPIC 1: Triangle Inequalities EXPLORE: ACTIVITY NO.1: LABELLING EXERCISES Direction: Identify which congruence postulate or theorem justifies that two triangles are congruent. Label it as
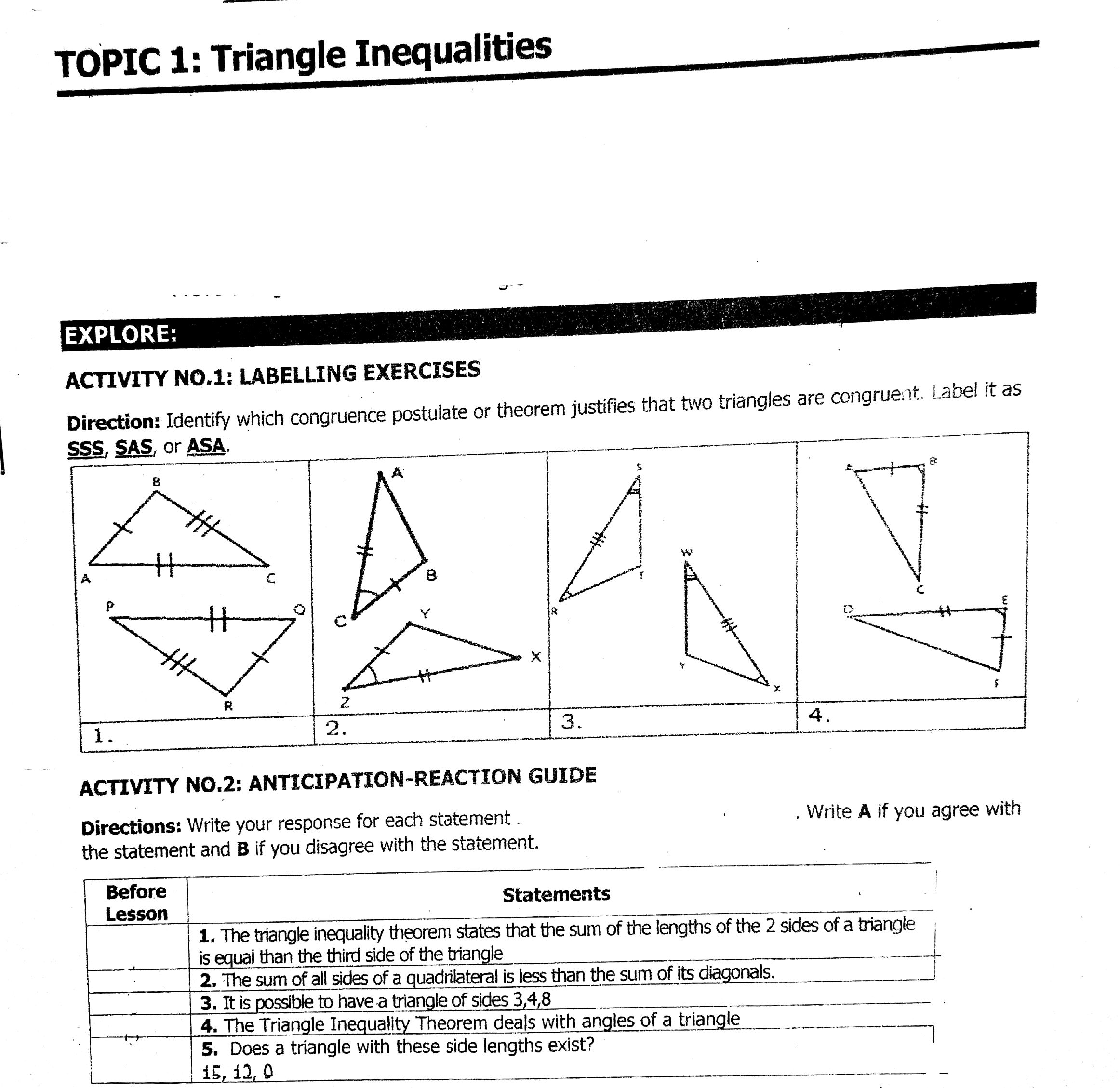
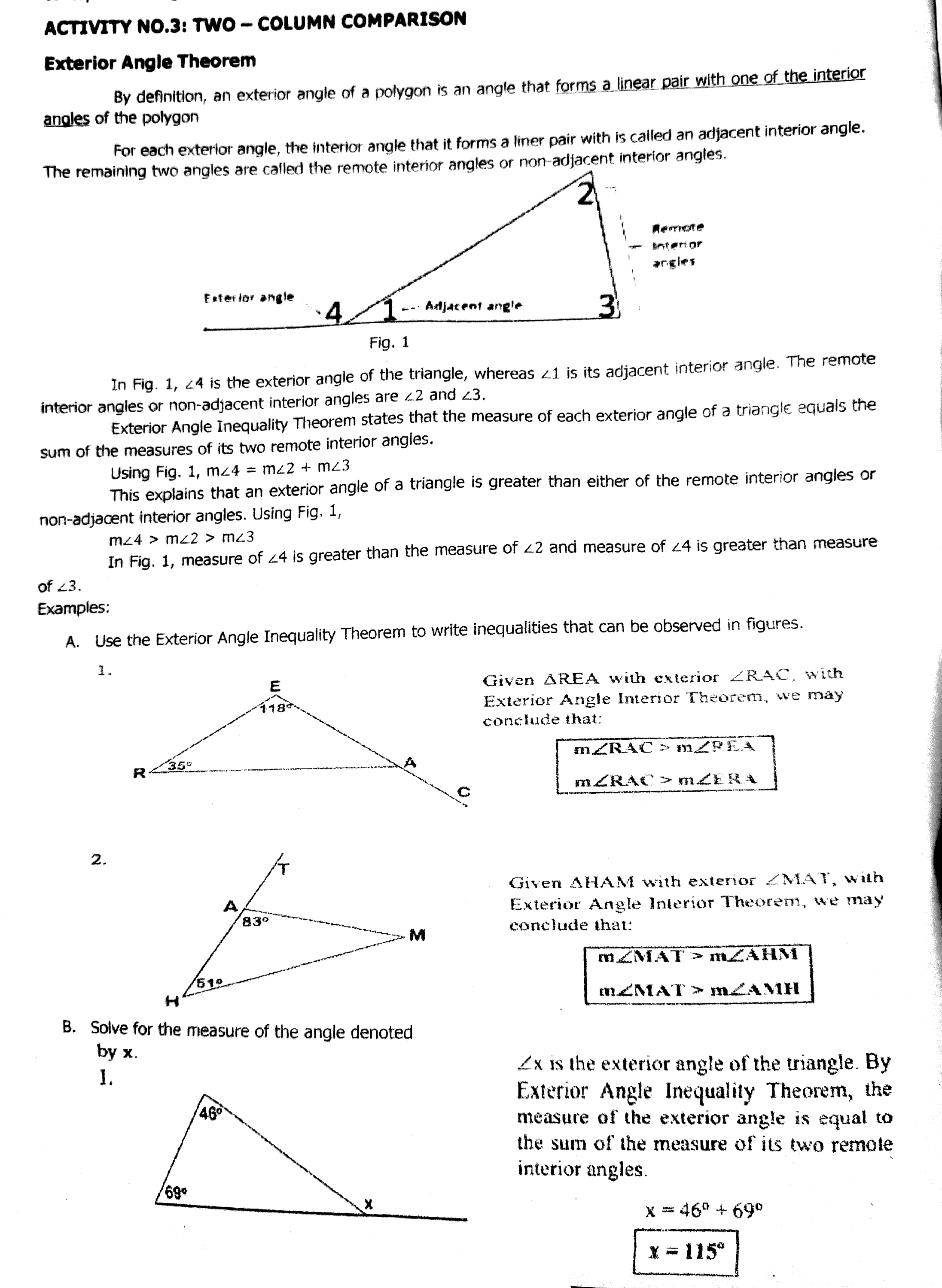
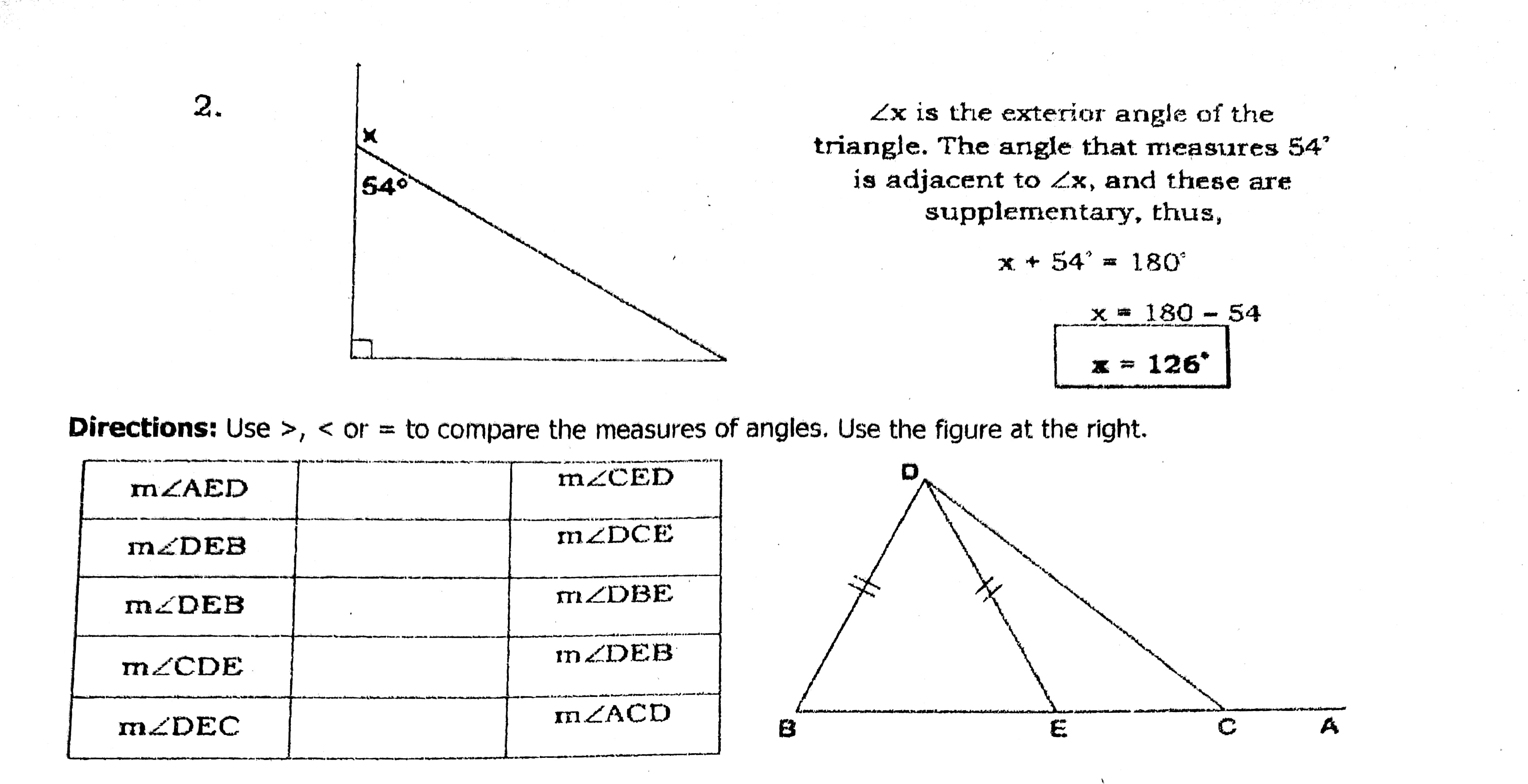
TOPIC 1: Triangle Inequalities EXPLORE: ACTIVITY NO.1: LABELLING EXERCISES Direction: Identify which congruence postulate or theorem justifies that two triangles are congruent. Label it as SSS, SAS, or ASA. X 1 2. 3. 4 ACTIVITY NO.2: ANTICIPATION-REACTION GUIDE Directions: Write your response for each statement Write A if you agree with the statement and B if you disagree with the statement. Before Statements Lesson 1. The triangle inequality theorem states that the sum of the lengths of the 2 sides of a triangle is equal than the third side of the triangle 2. The sum of all sides of a quadrilateral is less than the sum of its diagonals. 3. It is possible to have a triangle of sides 3,4,8 + + 4. The Triangle Inequality Theorem deals with angles of a triangle 5. Does a triangle with these side lengths exist? 15, 12, 0ACTIVITY NO.3: TWO - COLUMN COMPARISON Exterior Angle Theorem By definition, an exterior angle of a polygon is an angle that forms a linear pair with one of the interior angles of the polygon For each exterior angle, the interior angle that it forms a liner pair with is called an adjacent interior angle. The remaining two angles are called the remote interior angles or non-adjacent interior angles. Remote Entertor angies Exterior angle - -. Adjacent angle Fig. 1 In Fig. 1, 24 is the exterior angle of the triangle, whereas 41 is its adjacent interior angle. The remote interior angles or non-adjacent interior angles are 42 and 23. Exterior Angle Inequality Theorem states that the measure of each exterior angle of a triangle equals the sum of the measures of its two remote interior angles. Using Fig. 1, mz4 = mc2 + m43 This explains that an exterior angle of a triangle is greater than either of the remote interior angles or non-adjacent interior angles. Using Fig. 1, m24 > mc2 > mc3 In Fig. 1, measure of 44 is greater than the measure of 42 and measure of 24 is greater than measure of 23. Examples: A. Use the Exterior Angle Inequality Theorem to write inequalities that can be observed in figures. 1 . Given AREA with exterior ZRAC, with Exterior Angle Interior Theorem, we may conclude that: R MEERA 2. T Given AHAM with exterior /MAT, with Exterior Angle Interior Theorem, we may conclude that: myMAT > mZAHN 510 H' meMAT > MZAMH B. Solve for the measure of the angle denoted by x. 1. Ex is the exterior angle of the triangle. By AGO Exterior Angle Inequality Theorem, the measure of the exterior angle is equal to the sum of the measure of its two remote interior angles. 69 x = 460 + 690 * = 11502. X Zx is the exterior angle of the triangle. The angle that measures 54' 640 is adjacent to Zx, and these are supplementary, thus, x. + 54" = 180 x = 180 - 54 x = 126* Directions: Use >,
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


