Question: Topic Design from Failure Prevention Principle (Fatigue Loading Analysis) A power transmission shaft ABCD subjected to fatigue loading is to be designed with components

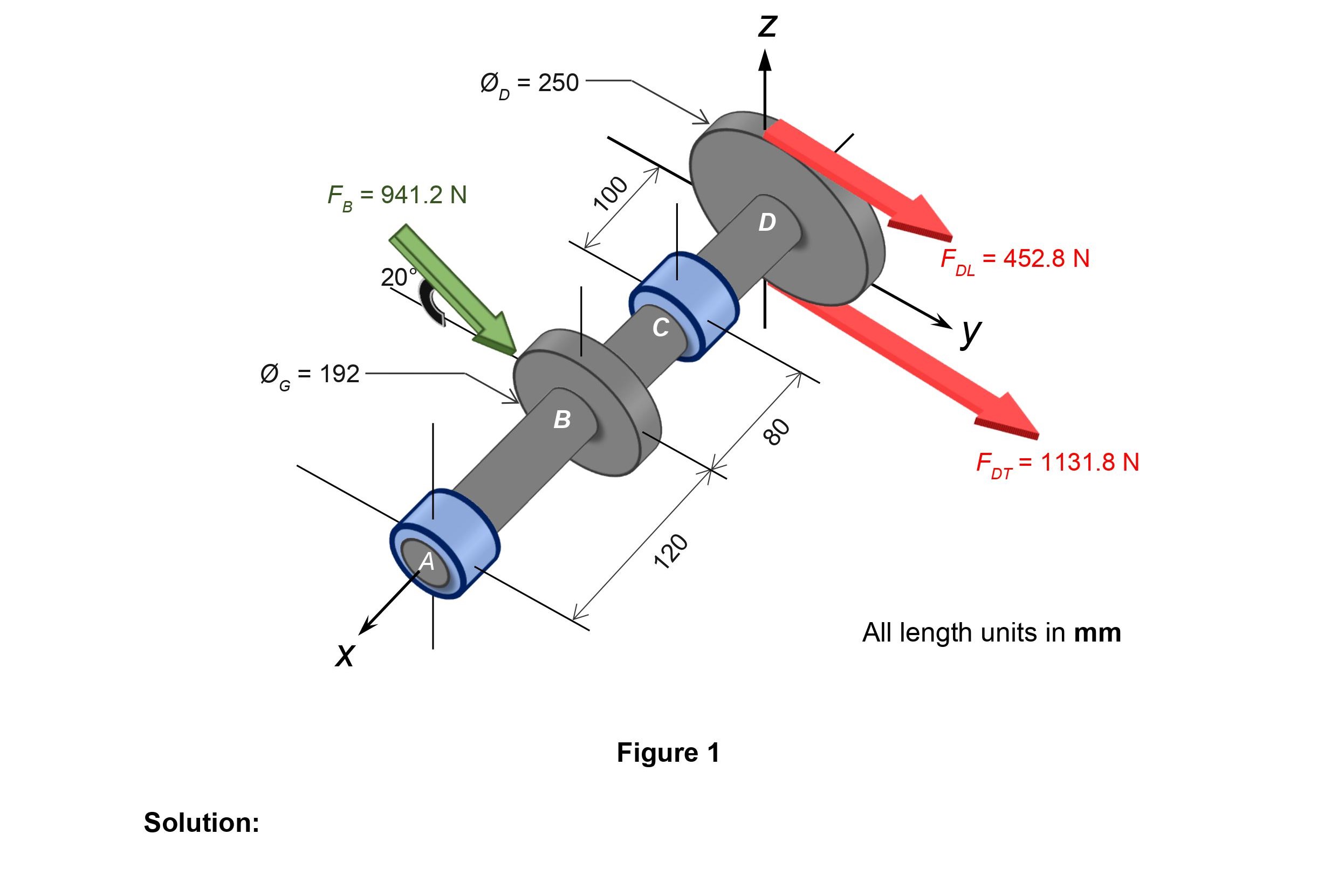
Topic Design from Failure Prevention Principle (Fatigue Loading Analysis) A power transmission shaft ABCD subjected to fatigue loading is to be designed with components as shown in Figure 1 by using two bearings at A and C as points of support, respectively. The engine power exerts onto the spur gear (192 mm diameter, weighs 8 kg) at B, a net force with magnitude FB = 941.2 N at 20 angle relative to x-y plane. The power-receiving pulley at D (250 mm diameter, weighs 10 kg) produces two tensional loads FDT = 1,131.8 N and FDL = 452.8 N on the tight and loose side of the belt, respectively. == The shaft material is expected to be machined from high-strength hot-rolled steel alloy with Sut 1,000 MPa and Sy = 770 MPa. All fillets and corners susceptible to stress concentrating effect are maintained at r = 3 mm with the resulting geometrical-dependent stress concentration factors in normal and shear directions of kt = 1.7 and kts = 1.35, respectively. The shaft reliability to fatigue load is targeted at 90% with safety factor for fatigue design, nf = 2 is specified to the system. Design a minimum required diameter for the shaft based on operational parameters as prescribed above following that of ASME-Elliptic criterion of fatigue loading. As shaft diameter is the unknown quantity, use a coefficient to modify the endurance limit due of size factor, kb = 0.8499. F = 941.2 N B 20 0 = 250 06 G = 192 B Solution: A 100 120 Figure 1 N D 08 FOL DL = 452.8 N y = 1131.8 N FDT= All length units in mm
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


