Question: Topic: DFS & Adjacency List The user should be able to enter both the number of nodes & the number of edges then the program
Topic: DFS & Adjacency List
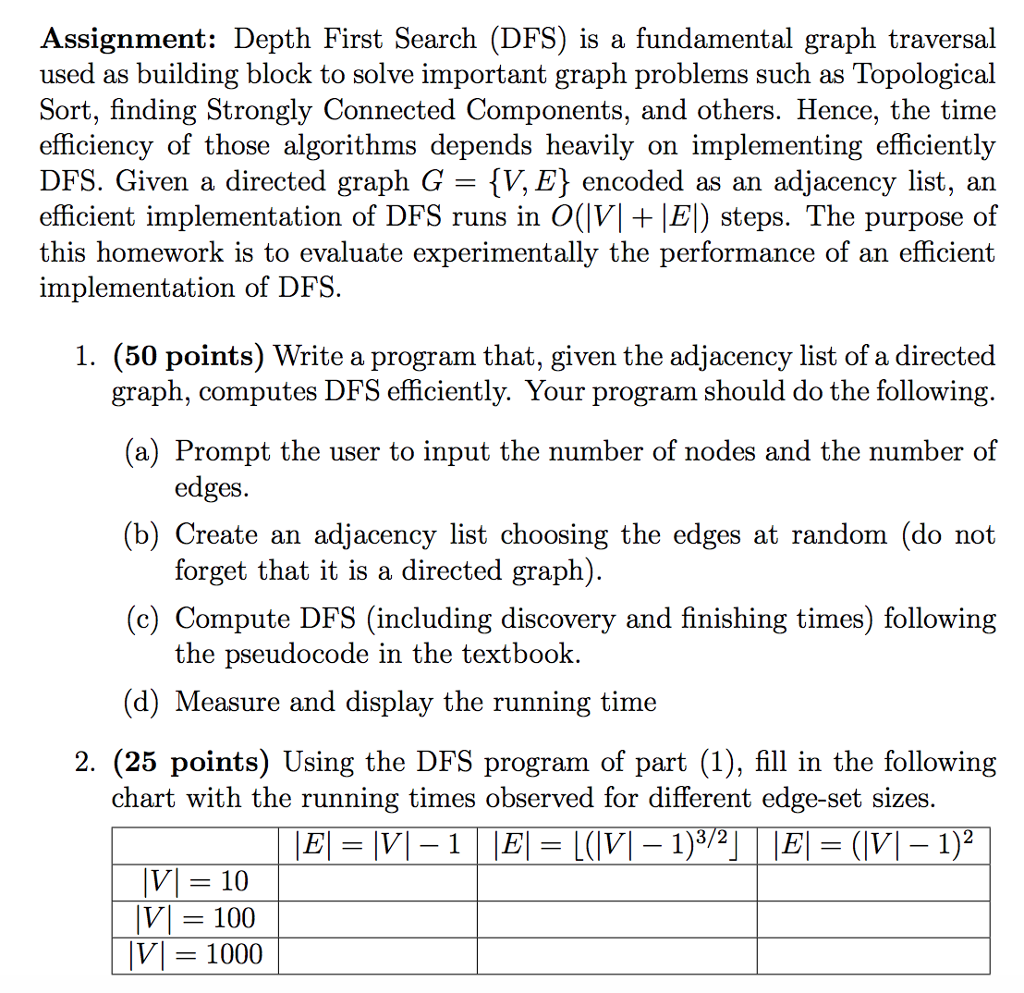
The user should be able to enter both the number of nodes & the number of edges then the program randomizes the edges, finds the discovery and finishing times.This program should also use an array of linked lists to keep the running time at O(V+E) time. My problem is trying to implement randomize edges 1(b). I can't implement that part properly which makes me a sitting duck.
I'm good on everything else it's just that part, any help would be appreciated. SHOULD BE IN JAVA.
Assignment: Depth First Search (DFS) is a fundamental graph traversal used as building block to solve important graph problems such as Topological Sort, finding Strongly Connected Components, and others. Hence, the time efficiency of those algorithms depends heavily on implementing efficiently DFS. Given a directed graph G - {V, E\ encoded as an adjacency list, an efficient implementation of DFS runs in O(VI +E) steps. The purpose of this homework is to evaluate experimentally the performance of an efficient implementation of DFS (50 points) Write a program that, given the adjacency list of a directed graph, computes DFS efficiently. Your program should do the following. 1 a) Prompt the user to input the number of nodes and the number of edges. (b) Create an adjacency list choosing the edges at random (do not forget that it is a directed graph) (c) Compute DFS (including discovery and finishing times) following the pseudocode in the textbook (d) Measure and display the running time 2. (25 points) Using the DFS program of part (1), fill in the following chart with the running times observed for different edge-set sizes. VI = 10 |V| 100 V 1000 Assignment: Depth First Search (DFS) is a fundamental graph traversal used as building block to solve important graph problems such as Topological Sort, finding Strongly Connected Components, and others. Hence, the time efficiency of those algorithms depends heavily on implementing efficiently DFS. Given a directed graph G - {V, E\ encoded as an adjacency list, an efficient implementation of DFS runs in O(VI +E) steps. The purpose of this homework is to evaluate experimentally the performance of an efficient implementation of DFS (50 points) Write a program that, given the adjacency list of a directed graph, computes DFS efficiently. Your program should do the following. 1 a) Prompt the user to input the number of nodes and the number of edges. (b) Create an adjacency list choosing the edges at random (do not forget that it is a directed graph) (c) Compute DFS (including discovery and finishing times) following the pseudocode in the textbook (d) Measure and display the running time 2. (25 points) Using the DFS program of part (1), fill in the following chart with the running times observed for different edge-set sizes. VI = 10 |V| 100 V 1000
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


