Question: b. The same loop invariant can be used to prove the correctness of both SortA and SortB. State, but do not prove, this invariant. Loop
 b. The same loop invariant can be used to prove the correctness of both SortA and SortB. State, but do not prove, this invariant.
b. The same loop invariant can be used to prove the correctness of both SortA and SortB. State, but do not prove, this invariant.
Loop Invariant: After the tth iteration of the outer loop...
c. Suppose your above loop invariant is true for all values of t greater than or equal to 0 (you do not need to include the proof). How can you show SortA is correct based on this loop invariant being true?


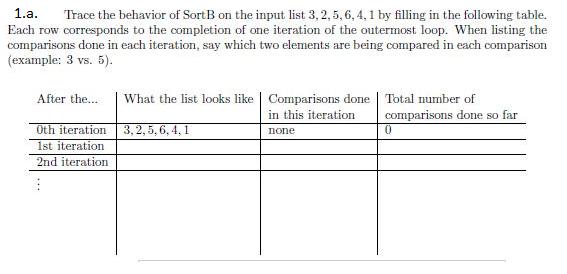
1.a. Trace the behavior of SortB on the input list 3, 2, 5, 6, 4, 1 by filling in the following table. Each row corresponds to the completion of one iteration of the outermost loop. When listing the comparisons done in each iteration, say which two elements are being compared in each comparison (example: 3 vs. 5). After the... Oth iteration 1st iteration 2nd iteration What the list looks like Comparisons done in this iteration. 3,2,5, 6, 4,1 none Total number of comparisons done so far 0
Step by Step Solution
3.44 Rating (163 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1a Trace the behavior of Sort B on the input list 3 2 5 6 4 1 by filling in the following table Each ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


