Question: Question 4 Ellis Ltd uses an operating costing system and produces two products. The same conversion cost is charged to all products passing through a
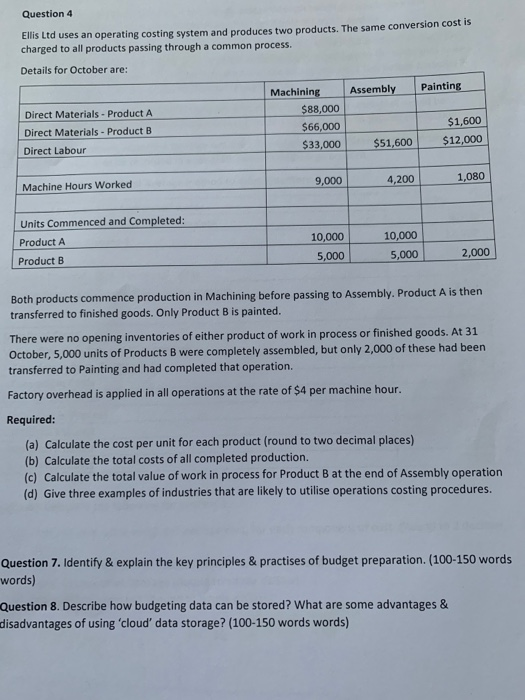
Question 4 Ellis Ltd uses an operating costing system and produces two products. The same conversion cost is charged to all products passing through a common process. Details for October are: Machining Assembly Painting Direct Materials - Product A $88,000 Direct Materials - Product B $66,000 $1,600 Direct Labour $51,600 $12,000 - 9,000 4,200 Machine Hours Worked 1,080 Units Commenced and Completed: Product A Product B 10,000 5,000 10,000 5,000 2,000 Both products commence production in Machining before passing to Assembly. Product A is then transferred to finished goods. Only Product B is painted. There were no opening inventories of either product of work in process or finished goods. At 31 October, 5,000 units of Products B were completely assembled, but only 2,000 of these had been transferred to Painting and had completed that operation. Factory overhead is applied in all operations at the rate of $4 per machine hour. Required: (a) Calculate the cost per unit for each product (round to two decimal places) (b) Calculate the total costs of all completed production. (c) Calculate the total value of work in process for Product B at the end of Assembly operation (d) Give three examples of industries that are likely to utilise operations costing procedures. Question 7. Identify & explain the key principles & practises of budget preparation. (100-150 words words) Question 8. Describe how budgeting data can be stored? What are some advantages & disadvantages of using 'cloud' data storage? (100-150 words words)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


