Question: ut References Mailings Review View Help Part 2 Yikes! He'll clearly have to complete more than 10 jobs. W.L. needs to be able to at
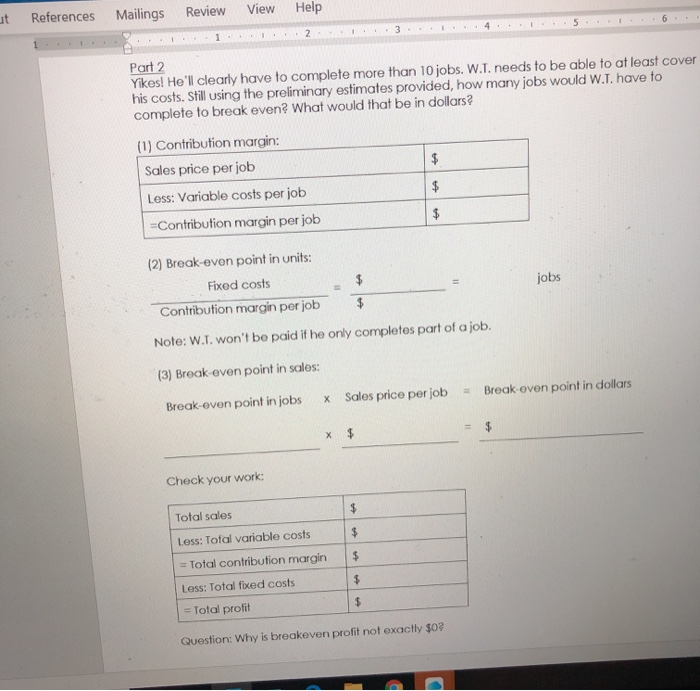

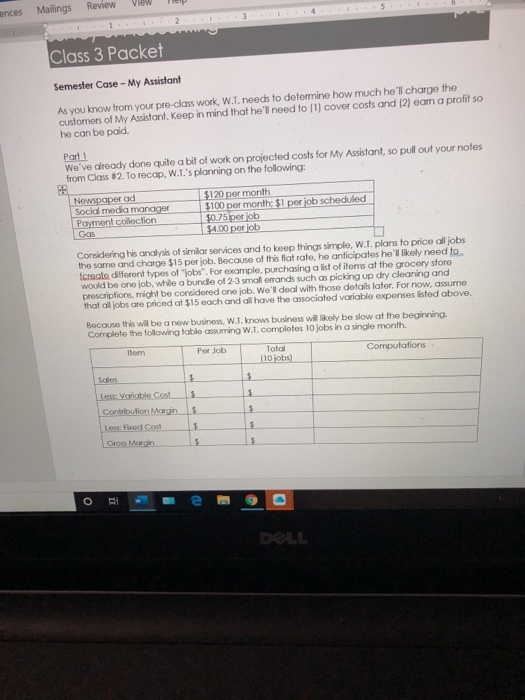
ut References Mailings Review View Help Part 2 Yikes! He'll clearly have to complete more than 10 jobs. W.L. needs to be able to at least cover his costs. Still using the preliminary estimates provided, how many jobs would W.T. have to complete to break even? What would that be in dollars? $ (1) Contribution margin: Sales price per job Less: Variable costs per job =Contribution margin per job jobs (2) Break-even point in units: Fixed costs Contribution margin per job Note: W.T. won't be paid if he only completes part of a job. (3) Break-even point in sales: Break-even point in jobs Sales price per job = Break oven point in dollars Check your work: Total sales Less: Total variable costs = Total contribution margin Less: Total fixed costs = Total profit Question: Why is breakeven profit not exactly 30% Survey of Accounung Class 3 Packet Semester Case - My Assistant As you know from your pre-class work, W.T. needs to determine how much he'll charg customers of My Assistant. Keep in mind that he'll need to (1) cover costs and (2) earr he can be paid. Part 1 We've already done quite a bit of work on projected costs for My Assistant, so pull ou from Class #2. To recap, W.T.'s planning on the following: Newspaper ad Social media manager Payment collection Gas $120 per month $100 per month; $1 per job scheduled $0.75 per job $4.00 per job Considering his analysis of similar services and to keep things simple, W.1. plans to pri the same and charge $15 per job. Because of this flat rate, he anticipates he'll likely fcreate different types of jobs". For example, purchasing a list of items at the grocer would be one job, while a bundle of 2-3 small errands such as picking up dry cleanin prescriptions, might be considered one job. We'll deal with those details later. For ng that all jobs are priced at $15 each and all have the associated variable expenses li I nnihusiness W.T. Knows business will likely be slow at the beg month View ences Review Me Mailings Class 3 Packet Semester Case - My Assistant As you know from your pre-class work, W.1. needs to determine how much he'll charge the customers of My Assistant. Keep in mind that he'll need to (1) cover costs and (2) eam a profit so he can be paid. Part 1 We've already done quite a bit of work on projected costs for My Assistant, so pull out your notes from Class 12. To recap, W..'s planning on the following: Newspaper ad Social media manager Payment collection Gas $120 per month $100 per month $1 per job scheduled $0.75 per ob $4.00 por job Considering his analysis of similar services and to keep things simple, W.1. plans to price all jobs the same and charge $15 por job. Because of this flat rate, he anticipates he'll likely need to Icreate different types of jobs". For example, purchasing a list of items at the grocery store would be ono job, while a bundle of 2-3 smallorands such as picking up dry cleaning and prescriptions might be considered one job. We'll deal with those details later. For now, assume that all jobs are priced at $15 each and all have the associated variable expenses listed above. Bocuse this will be a new business, W.Tknows business will likely be slow at the beginning Complete the following table assuming W.T. completes 10 jobs in a single month. Por Job Computations Total (10 jobs Low: Variable Cost Contribution Margin Less: Fixed Cost Gross Margin
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


