Question: + Trial 3 Trial Trial 2 initial ac 0.005 oool 0.00002 0.0015 0.005 0.oos 0.00002 0-00004 o-0015 0.00 15 0.00002 0.0015 o o.os [TO-] [H+
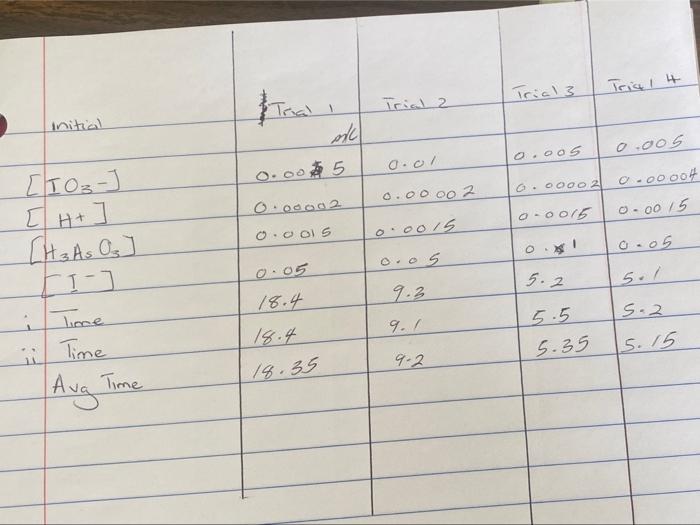

![[TO-] [H+ [H 3 As Oz JI) Time ii Time 0.05 18.4](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f8fd94d30ce_87666f8fd9478e70.jpg)
+ Trial 3 Trial Trial 2 initial ac 0.005 oool 0.00002 0.0015 0.005 0.oos 0.00002 0-00004 o-0015 0.00 15 0.00002 0.0015 o o.os [TO-] [H+ [H 3 As Oz JI) Time ii Time 0.05 18.4 5.2 5./ 9.3 5.2 9.1 19.4 5.5 5.35 15.15 9.2 18.35 Aug Time Rate Law Trial # Rate (M/s) initial [103] initial [1 '] initial [H] rate constant 1 2 3 4. Reaction order [103] = Reaction order [1] = _ Reaction order [H+ = Average k = Overall rate law: Calculate the initial rates for experiments 1, 2, 3 and 4 from A[H3ASO3]/At. (Note: A[H3A5O3) = 1/3 (initial concentration of H2AsO3). Give correct units. Determine the reaction orders with respect to the 10g. I and H+ ions. Determine the overall rate law for the reaction. Calculate the rate constant from all four experiments and determine the mean. Give correct units. Determine the rate constants at the two different temperatures used in the second part of the experiment. Make sure to calculate the rate for each reaction as you did in step 1 and use the rate law you found in step 4. Using the Arrhenius equation, k2 Ea (1 RT1 Ink +) Where R is 8.314 J/mol K, calculate the activation energy, Es, for the reaction
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


