Question: TRIUMF is Canada's particle accelerator centre and host to the largest cyclotron in the world, a machine capable of accelerating protons to energies of

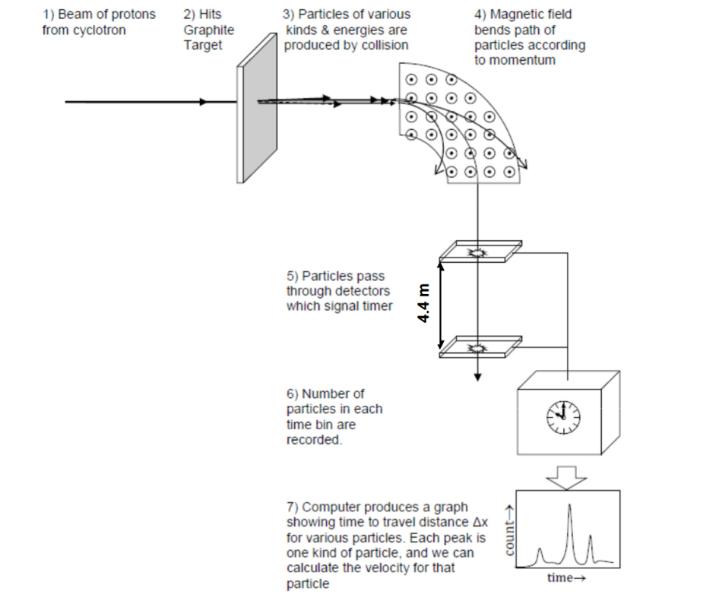

TRIUMF is Canada's particle accelerator centre and host to the largest cyclotron in the world, a machine capable of accelerating protons to energies of up to 520 MeV. Beams of these protons can be extracted from the accelerator and sent down a beamline, whereupon they can collide with a target. Depending on proton energy and the choice of target, a range of nuclear reactions can ensue and a range of outgoing particles can be observed. 1) Beam of protons from cyclotron 2) Hits Graphite Target 3) Particles of various kinds & energies are produced by collision 5) Particles pass through detectors which signal timer 6) Number of particles in each time bin are recorded. O 4.4 m 0000 OO 4) Magnetic field bends path of particles according to momentum OO 7) Computer produces a graph showing time to travel distance Ax for various particles. Each peak is one kind of particle, and we can calculate the velocity for that particle C Lill time- count- In some beamlines, a bending magnet can be used to steer particles (e.g. muons) with the same momentum into a time-of-flight detector of fixed length. Whilst the particles have equal momentum, with increasing mass comes decreasing velocity. Task a) Explain what a time-of-flight detector is used for and how it works. b) Deduce the velocities of the particles in the three groups shown in Figure 1. c) Estimate the uncertainty on these velocities, suggest what experimental factors may influence it, and consider which is likely to be more significant in practice. d) Determine the masses of these particles.
Step by Step Solution
3.50 Rating (150 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
The detailed ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


