Question: Tuple.h// #ifndef TUPLE_H #define TUPLE_H // A Tuple represents a sequence of items of type int in the range MINVALUE to MAXVALUE. // The number
Tuple.h//
#ifndef TUPLE_H #define TUPLE_H
// A Tuple represents a sequence of items of type int in the range MINVALUE to MAXVALUE. // The number of item in any Tuple is equal to SIZE where SIZE is a static constant. // The items are accessed by position where the first position is 1 and the last position is SIZE. class Tuple { public: static const int SIZE = 8; // SIZE could be any positive value. Don't assume that SIZE is always 5. static const int MINVALUE = 1, MAXVALUE = 100; // range of legal items. private: int items[SIZE]; // items[0] holds the first item, items[1] holds second item and so on.
public: Tuple(int init = MINVALUE); // initialize the tuple object with all items equal to init.
// Return the nth item for any n in the range {1...SIZE}. // Remember: The nth item is stored at index n-1, NOT index n. // For n SIZE, return the last item. int get(int n) const;
// Assuming v in range {MINVALUE...MAXVALUE} and n in range {1...SIZE} // set(n,v) sets the nth item to v. // For n in range and v MAXVALUE, set(n,v) is equivalent to set(n,MAXVALUE). // For n out of range set(n,v) does nothing, regardless of what v is. void set(int n, int v);
// Rotate item forward by the given amount. For example, if amount = 3 // then fourth will get the original value of first, first will get the original value of second // second will get the original value of third and third will get the original value of fourth. // If amount is a multiple of SIZE or negative then rotate will do nothing. // If amount is bigger than SIZE, then rotate by amount % SIZE. void rotate(int amount);
void reverse(); // reverse the order of elements e.g. {10,14,5,87} --> {87,5,14,10}.
void print() const; // print values in braces, separated by commas e.g. {10,20,30,40}, then print endl.
double getAverage() const; // return the average of all items in the Tuple.
void sort(); // arrange the value in ascending order. Use bubblesort or selection sort.
bool equal(const Tuple& t) const; // return true iff the two Tuples contain the same sequence of values.
// Return true iff the current object and t contain the same multiset ("bag") of items. // That means, for any value v, if v occurs k times in one object // then v must also occur k times in the other object. // Hint: Create a sorted version of each Tuple and compare for equality. bool equalBags(const Tuple& t) const;
};
#endif
MAIN//
#include
using namespace std;
void testSet() { cout
void testSort() { cout 1; i--) t.set(i-1, t.get(i) + 1); t.print(); t.sort(); t.print(); t.set(1,Tuple::MAXVALUE); t.print(); t.sort(); t.print(); cout
void testReverse() { cout
void testRotate() { cout
int main() { testSet(); testSort(); testReverse(); testRotate(); return 0; }
TUPLE.CPP (FILL IN THE BLANKS BASED ON INSTRUCTIONS IN TUPLE.H)
#include "Tuple.h" #include
Tuple::Tuple(int init) {
}
int Tuple::get(int n) const {
}
void Tuple::set(int position, int value) {
}
void Tuple::rotate(int amount) {
}
void Tuple::reverse() {
}
void Tuple::print() const {
}
double Tuple::getAverage() const {
}
void Tuple::sort() {
}
bool Tuple::equal(const Tuple& t) const {
}
bool Tuple::equalBags(const Tuple& t) const {
}
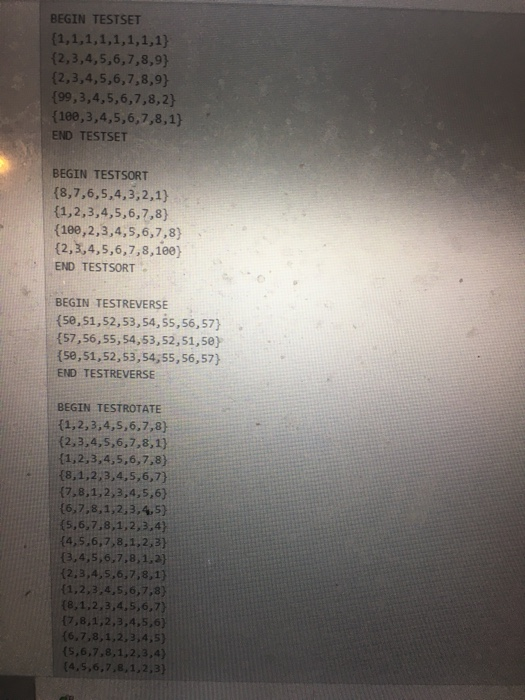
BEGIN TESTSET {1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1) {2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9) {2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9) {99,3,4,5,6,7,8,2} {100,3,4,5,6,7,8,1} END TESTSET BEGIN TESTSORT {8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1) {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8} {100,2,3,4,5,6,7,8) {2,3,4,5,6,7,8,100) END TESTSORT BEGIN TESTREVERSE {50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57} {57,56,55,54,53,52,51,50) {50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57} END TESTREVERSE BEGIN TESTROTATE {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8} {2,3,4,5,6,7,8,1} {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8) {8,1,2,3,4,5,6,7) {7,8,1,2,3,4,5,6} {6,7,8,1,2,3,4,5) {5,6,7,8,1,2,3,4} {4,5,6,7,8,1,2,3) 13,4,5,6,7,8,1,2} 12,3,4,5,6,7,8,1) {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8) {8,1,2,3,4,5,6,7} {7,8,1,2,3,4,5,6) {6,7,8,1,2,3,4,5) 15,6,7,8,1,2,3,4) (4,5,6,7,8,1,2,3)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


