Question: Tutorial Exercise A 1 . 5 0 - k g iron horseshoe initially at 6 4 0 C is dropped into a bucket containing 2
Tutorial Exercise
A iron horseshoe initially at is dropped into a bucket containing kg of water at What is the final temperature of the waterhorseshoe system? Ignore the heat capacity of the container and assume a negligible amount of water boils away.
Step
The water will gain the energy lost by the iron. Using the expressions for the quantity of heat exchanged by the two materials, the change in water temperature can be found. The specific heat of iron is and the specific heat of water is
We assume that the waterhorseshoe system is thermally isolated insulated from the environment for the short time required for the horseshoe to cool off and the water to warm up Then the total energy input from the surroundings is zero, as expressed by the equation
The energy transferred between a sample of mass of a material and its surroundings with a temperature change is given by
Substituting the expressions for iron and water into the energy equation, we have
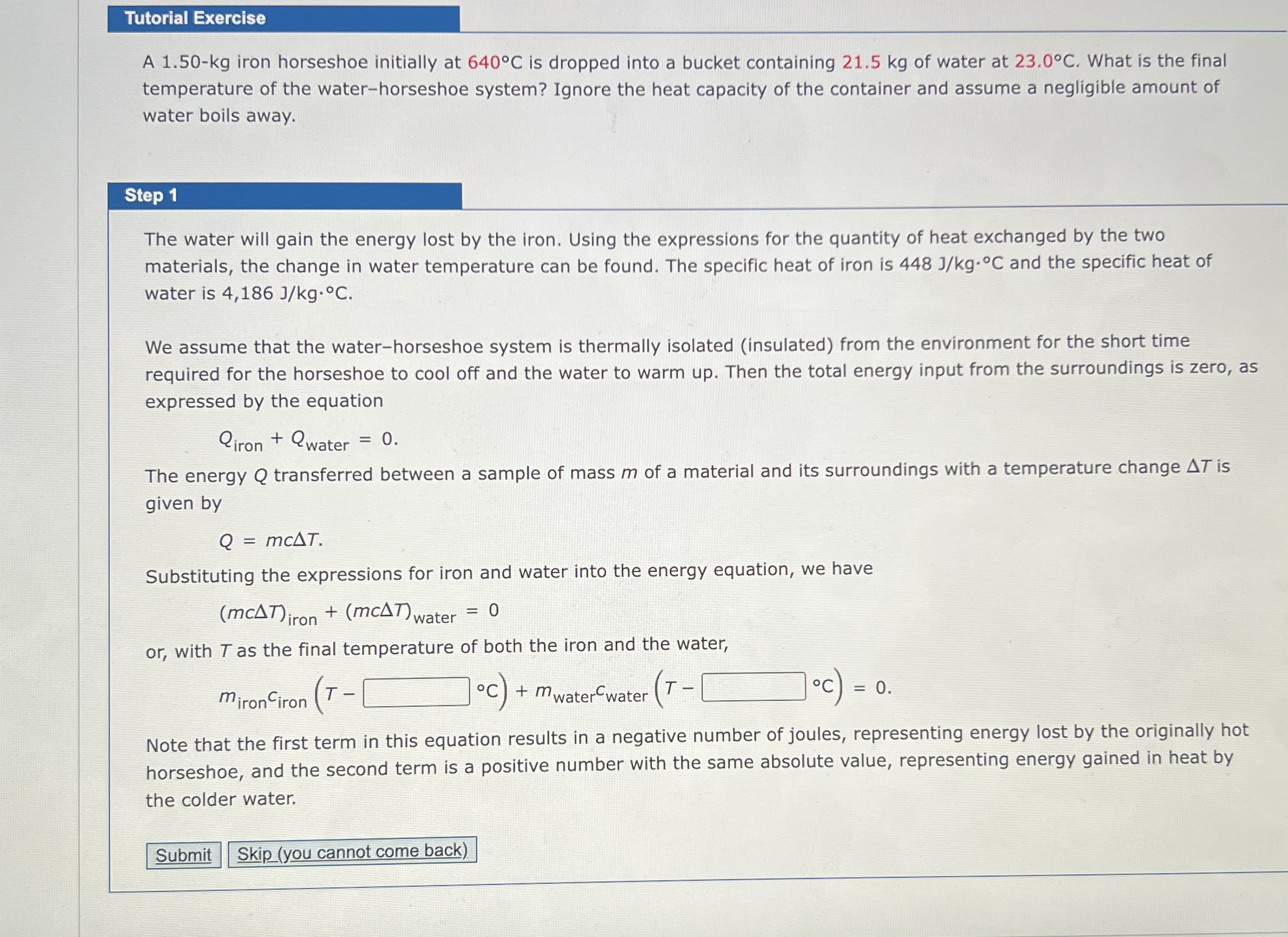
or with as the final temperature of both the iron and the water,
Note that the first term in this equation results in a negative number of joules, representing energy lost by the originally hot horseshoe, and the second term is a positive number with the same absolute value, representing energy gained in heat by the colder water.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


