Question: Two forces are applied to a hook. B C F1 13/12 5 a F2 y A Values for the figure are given in the
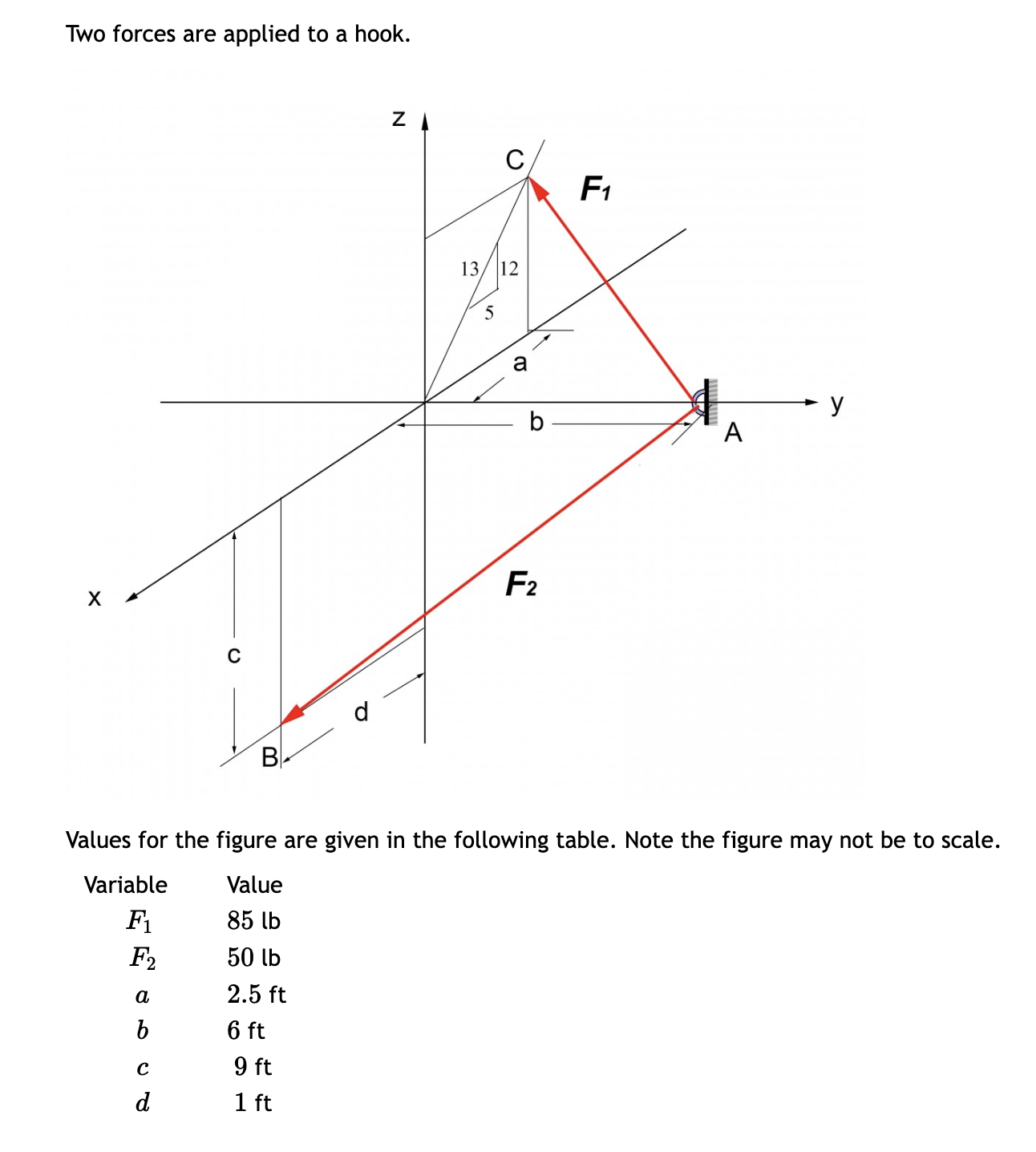

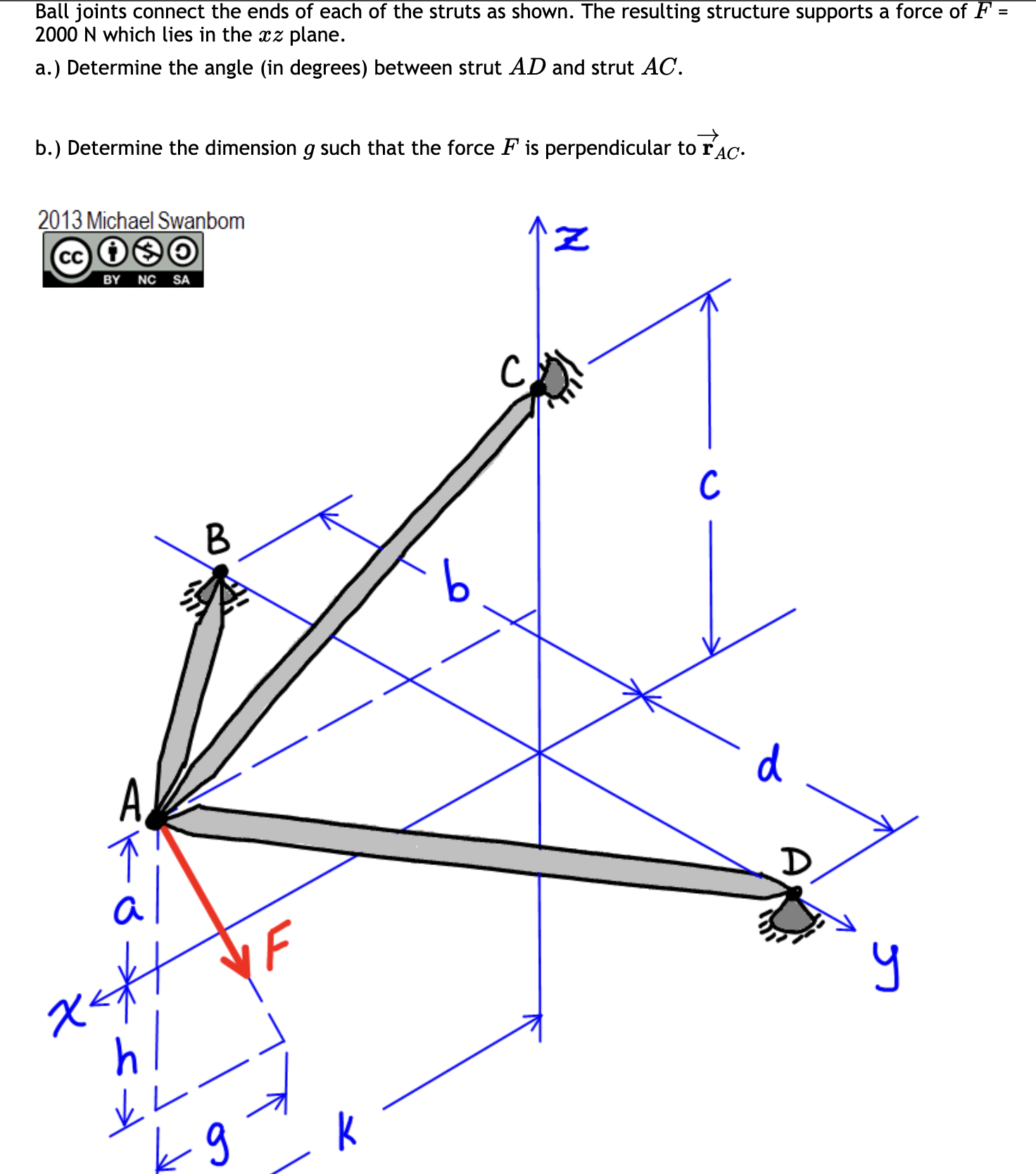
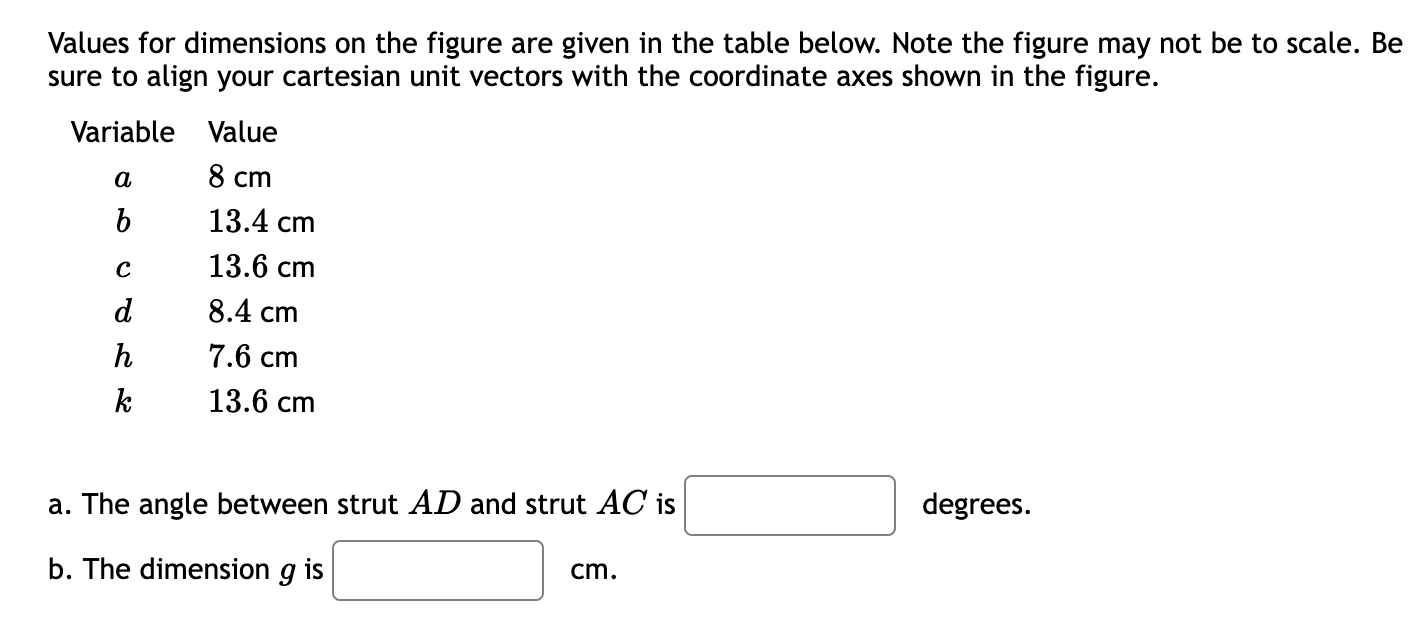
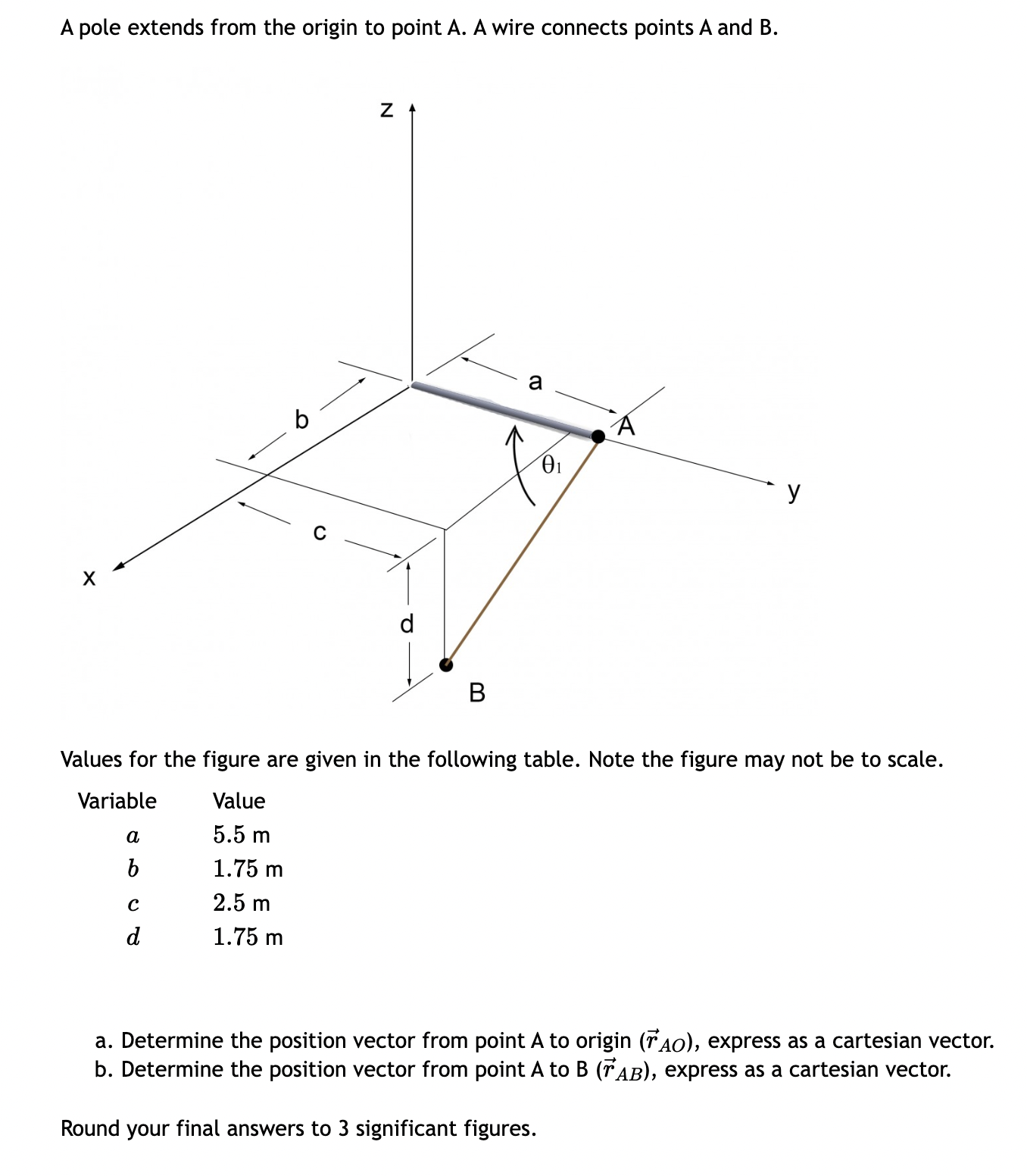
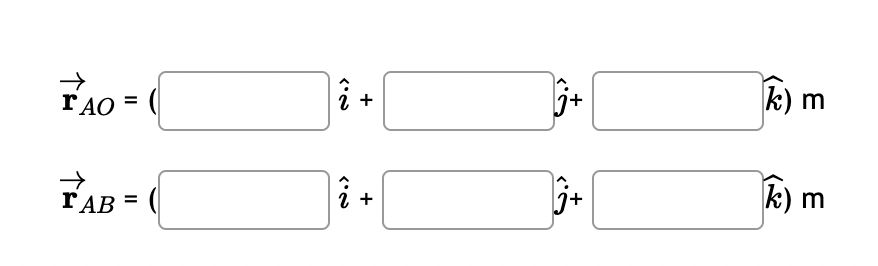
Two forces are applied to a hook. B C F1 13/12 5 a F2 y A Values for the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value F 85 lb F2 50 lb a b 2.5 ft 6 ft d 03 9 ft 1 ft Values for the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value 85 lb 50 lb 2.5 ft F F2 b 9 ft d 1 ft 6 ft a. Write each force (F1, F2) as cartesian vectors. > b. Find the resultant force FR, express as a cartesian vector c. Find the magnitude of the resultant force FR d. Determine the coordinate direction angles of the resultant force FR i. ii. B iii. Y Round your final answers to 3 significant digits/figures. TE = F2 = ( FR= FR= = ( II 2 + k) lb 2 + + k) lb + + k) lb lb degrees B = ( degrees Y = ( degrees Ball joints connect the ends of each of the struts as shown. The resulting structure supports a force of F = 2000 N which lies in the xz plane. a.) Determine the angle (in degrees) between strut AD and strut AC. r b.) Determine the dimension g such that the force F is perpendicular to TAC. 2013 Michael Swanbom cc 10 BY NC SA B Z C A al x4*1 h g F k d D y Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the table below. Note the figure may not be to scale. Be sure to align your cartesian unit vectors with the coordinate axes shown in the figure. Variable Value a 8 cm b 13.4 cm 13.6 cm d 8.4 cm h 7.6 cm k 13.6 cm a. The angle between strut AD and strut AC is b. The dimension g is cm. degrees. A pole extends from the origin to point A. A wire connects points A and B. C Z a A 01 B Values for the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable a Value 5.5 m b 1.75 m 2.5 m d 1.75 m a. Determine the position vector from point A to origin (AO), express as a cartesian vector. b. Determine the position vector from point A to B (TAB), express as a cartesian vector. Round your final answers to 3 significant figures. 1 AO = ( 2 + + AB = 2 + k) m k) m
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


