Question: undefined 224 Part II Market Analysis APPENDIX 6.2 Estimating an Experience Curve Coefficient and the Percent Experience Curve Variables Unit Cost at Time 1 Unit
undefined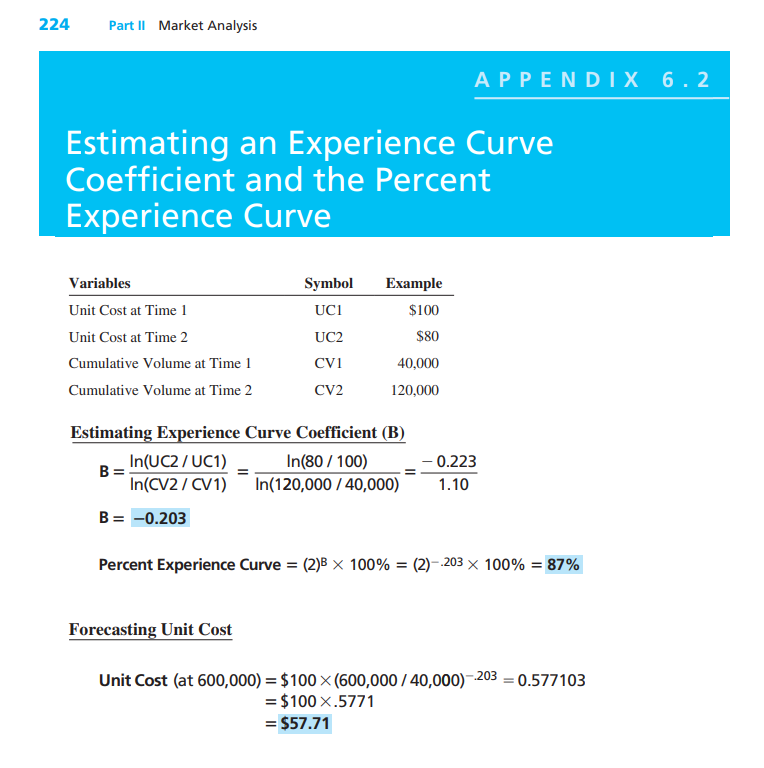
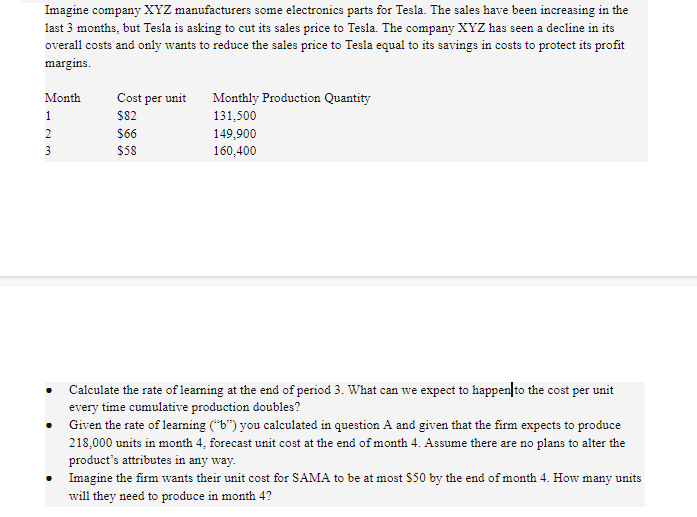
224 Part II Market Analysis APPENDIX 6.2 Estimating an Experience Curve Coefficient and the Percent Experience Curve Variables Unit Cost at Time 1 Unit Cost at Time 2 Cumulative Volume at Time! Cumulative Volume at Time 2 Symbol UCI UC2 cvi CV2 Example $100 $80 40,000 120,000 = Estimating Experience Curve Coefficient (B) In(UC2 / UC1) In(80 / 100) B In(CV2 / CV1) In(120,000 / 40,000) B= -0.203 -0.223 1.10 Percent Experience Curve = (2)B 100% = (2)-.203 100% = 87% Forecasting Unit Cost Unit Cost (at 600,000) = $100 (600,000 / 40,000)-203 = 0.577103 = $100 X.5771 = $57.71 Imagine company XYZ manufacturers some electronics parts for Tesla. The sales have been increasing in the last 3 months, but Tesla is asking to cut its sales price to Tesla. The company XYZ has seen a decline in its overall costs and only wants to reduce the sales price to Tesla equal to its savings in costs to protect its profit margins. Month 1 2 Cost per unit $82 $66 $58 Monthly Production Quantity 131,500 149.900 160,400 3 Calculate the rate of learning at the end of period 3. What can we expect to happen to the cost per unit every time cumulative production doubles? Given the rate of learning ("6") you calculated in question A and given that the firm expects to produce 218.000 units in month 4. forecast unit cost at the end of month 4. Assume there are no plans to alter the product's attributes in any way. Imagine the firm wants their unit cost for SAMA to be at most $50 by the end of month 4. How many units will they need to produce in month 4? 224 Part II Market Analysis APPENDIX 6.2 Estimating an Experience Curve Coefficient and the Percent Experience Curve Variables Unit Cost at Time 1 Unit Cost at Time 2 Cumulative Volume at Time! Cumulative Volume at Time 2 Symbol UCI UC2 cvi CV2 Example $100 $80 40,000 120,000 = Estimating Experience Curve Coefficient (B) In(UC2 / UC1) In(80 / 100) B In(CV2 / CV1) In(120,000 / 40,000) B= -0.203 -0.223 1.10 Percent Experience Curve = (2)B 100% = (2)-.203 100% = 87% Forecasting Unit Cost Unit Cost (at 600,000) = $100 (600,000 / 40,000)-203 = 0.577103 = $100 X.5771 = $57.71 Imagine company XYZ manufacturers some electronics parts for Tesla. The sales have been increasing in the last 3 months, but Tesla is asking to cut its sales price to Tesla. The company XYZ has seen a decline in its overall costs and only wants to reduce the sales price to Tesla equal to its savings in costs to protect its profit margins. Month 1 2 Cost per unit $82 $66 $58 Monthly Production Quantity 131,500 149.900 160,400 3 Calculate the rate of learning at the end of period 3. What can we expect to happen to the cost per unit every time cumulative production doubles? Given the rate of learning ("6") you calculated in question A and given that the firm expects to produce 218.000 units in month 4. forecast unit cost at the end of month 4. Assume there are no plans to alter the product's attributes in any way. Imagine the firm wants their unit cost for SAMA to be at most $50 by the end of month 4. How many units will they need to produce in month 4
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


