Question: Under the assumptions of the BSM model, consider a binary option on a non-dividend paying stock with a strike price of $40 per share and
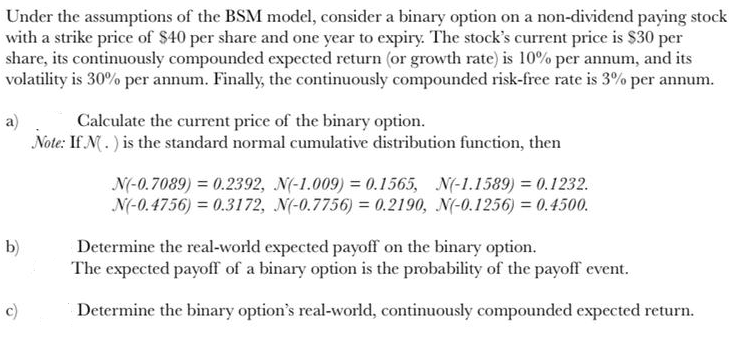
Under the assumptions of the BSM model, consider a binary option on a non-dividend paying stock with a strike price of $40 per share and one year to expiry. The stock's current price is $30 per share, its continuously compounded expected return (or growth rate) is 10% per annum, and its volatility is 30% per annum. Finally, the continuously compounded risk-free rate is 3% per annum. a Calculate the current price of the binary option. Note: If N. ) is the standard normal cumulative distribution function, then N(-0.7089) = 0.2392, N(-1.009) = 0.1565, N(-1.1589) = 0.1232. N(-0.4756) = 0.3172, N(-0.7756) = 0.2190, N(-0.1256) = 0.4500. b) Determine the real-world expected payoff on the binary option, The expected payoff of a binary option is the probability of the payoff event. Determine the binary option's real-world, continuously compounded expected return. Under the assumptions of the BSM model, consider a binary option on a non-dividend paying stock with a strike price of $40 per share and one year to expiry. The stock's current price is $30 per share, its continuously compounded expected return (or growth rate) is 10% per annum, and its volatility is 30% per annum. Finally, the continuously compounded risk-free rate is 3% per annum. a Calculate the current price of the binary option. Note: If N. ) is the standard normal cumulative distribution function, then N(-0.7089) = 0.2392, N(-1.009) = 0.1565, N(-1.1589) = 0.1232. N(-0.4756) = 0.3172, N(-0.7756) = 0.2190, N(-0.1256) = 0.4500. b) Determine the real-world expected payoff on the binary option, The expected payoff of a binary option is the probability of the payoff event. Determine the binary option's real-world, continuously compounded expected return
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


