Question: unit 1 assignment 4 - compare inventory methods This assessment addresses the following course objective(s): Calculate appropriate inventory and deprecation entries. Account for various transactions
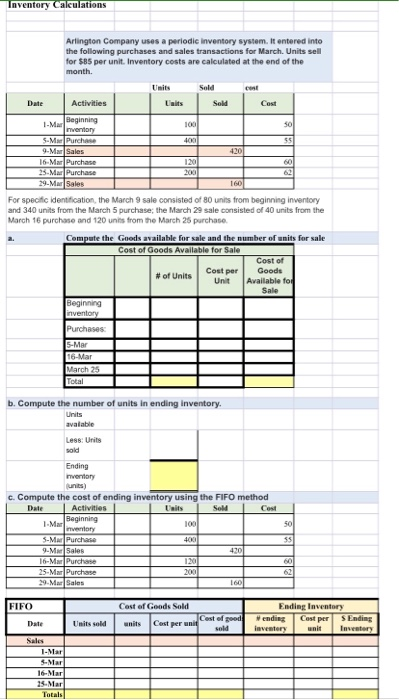
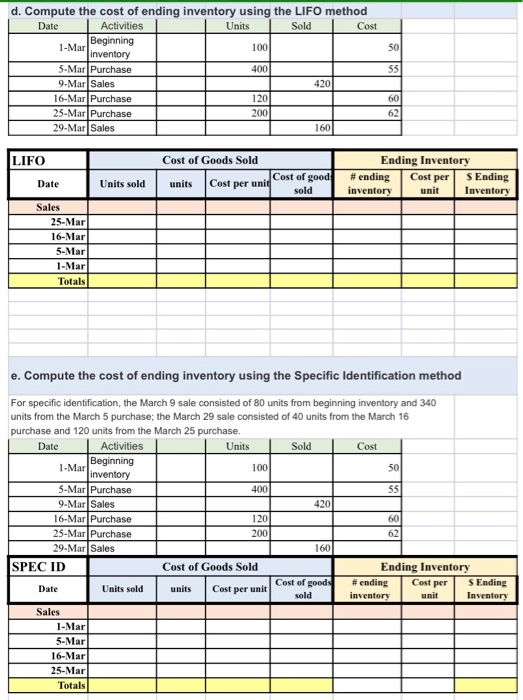
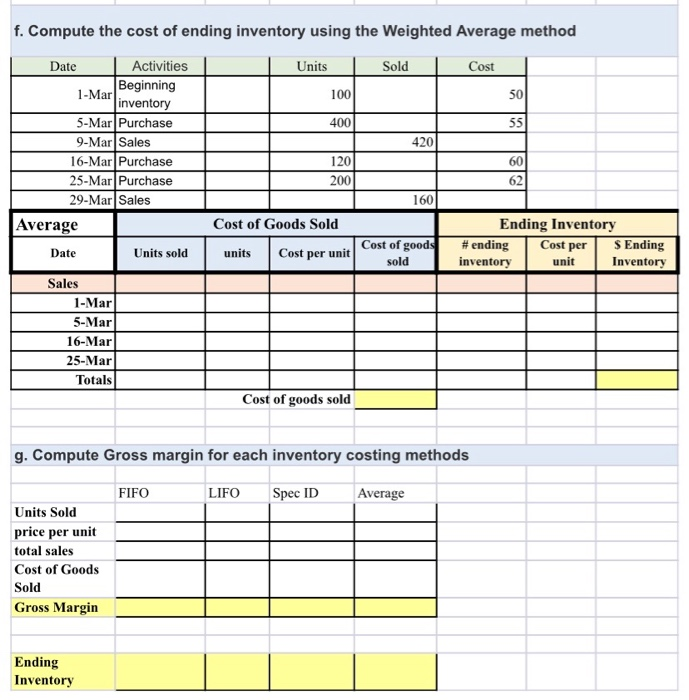
Inventory Calculations Arlington Company uses a periodic inventory system. It entered into the following purchases and sales transactions for March Units sell for $85 per unit. Inventory costs are calculated at the end of the month Solid Activities Maging 100 SM 400 Inventory Purchase Sales Purchase urchase 430 16. M M 201 200 For specific identication the March 9 sale consisted of from beginning inventory and 340 units from the March 5 purchase the March 29 sale consisted of 40 units from the March 16 purchase and 120 nitrom the March 25 purchase Compute the Goods available for sale and the number of units for sale Cost of Goods Available for Sale Cost of # of Units Cost per Goods Unit Available for Beginning Purchases 5-Mar 6 Mar March 25 Total b. Compute the number of units in ending inventory. Units avalable Less: Units Ending ventory unis) c. Compute the cost of ending inventory using the FIFO method Activities M ates 16V 25. M Purchase Mais FIFO Ending Inventory ending S Ending talls sold waits les per al Castelgood 16-Mar 1. Mar Beginning d. Compute the cost of ending inventory using the LIFO method Date Activities Units Sold Cost inventory 1001 5.Mar Purchase 4001 9-Mar Sales 1 420 16-Mar Purchase 120 25.Mar Purchase 200 29-Mar Sales 1 60 621 LIFO Cost of Goods Sold units Cost per unid Cost of good Ending Inventory #ending Cost per Cost S Ending inventory unit Inventory Date Units sold Sales 25-MarTTT 16-Mar S-Mar 1-Mar Totals e. Compute the cost of ending inventory using the Specific Identification method For specific identification, the March 9 sale consisted of 80 units from beginning inventory and 340 units from the March 5 purchase; the March 29 sale consisted of 40 units from the March 16 purchase and 120 units from the March 25 purchase. Date Activities Units Sold Cost Beginning 1-Mar 100 "inventory 5.Mar Purchase T 400 5 5 9.Mar Sales 420 16-Mar Purchase 120 60 25-Mar Purchase 2001 62 29-Mar Sales 160 SPEC ID Cost of Goods Sold Ending Inventory Units sold units Cost of goods Cost per unit Date ending Cost per S Ending sold inventory 1 unit aventer Sales 1-Mar S-Mar 16-Mar 25-Mar Totals f. Compute the cost of ending inventory using the Weighted Average method Units Sold Cost 100 50 400 Date Activities 1-Mar Beginning inventory 5-Mar Purchase 9-Mar Sales 16-Mar Purchase 25-Mar Purchase 29-Mar Sales Average 1201 2001 1601 Cost of Goods Sold Ending Inventory #ending Cost per S Ending inventory unit Inventory Date Units sold units Cost of goods sold Cost per unit Sales 1-Mar 5-Mar 16-Mar 25-Mar Totals Cost of goods sold g. Compute Gross margin for each inventory costing methods FIFO LIFO Spec ID Average Units Sold price per unit total sales Cost of Goods Sold Gross Margin Ending Inventory
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


