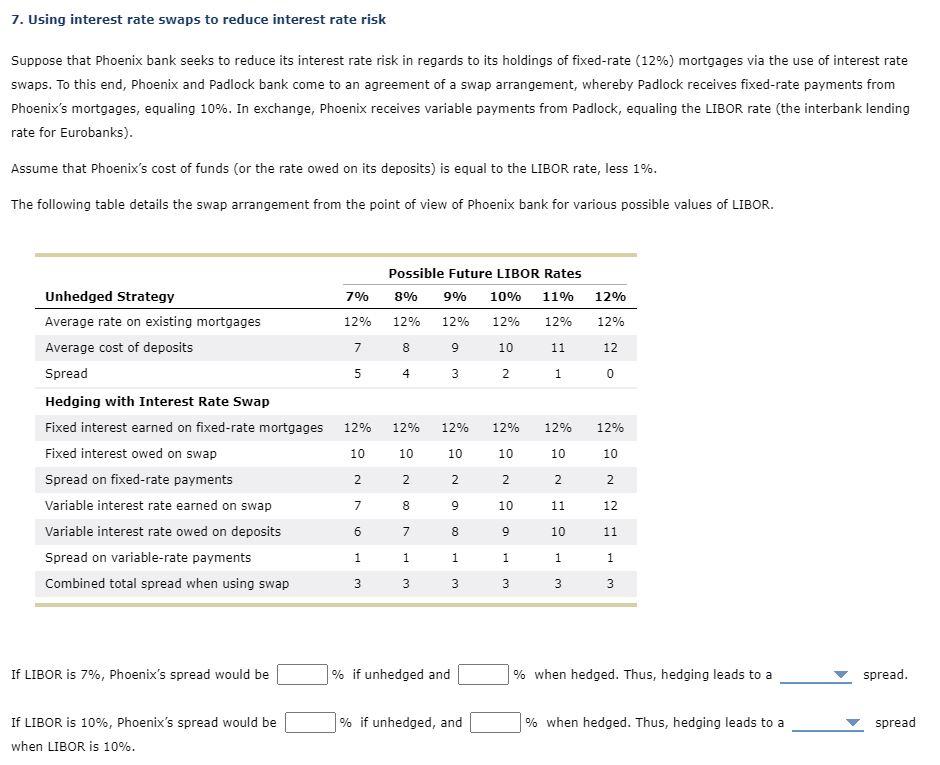
Question: Upvote for correct answer 7. Using interest rate swaps to reduce interest rate risk Suppose that Phoenix bank seeks to reduce its interest rate risk
 Upvote for correct answer
Upvote for correct answer
7. Using interest rate swaps to reduce interest rate risk Suppose that Phoenix bank seeks to reduce its interest rate risk in regards to its holdings of fixed-rate (12%) mortgages via the use of interest rate swaps. To this end, Phoenix and Padlock bank come to an agreement of a swap arrangement, whereby Padlock receives fixed-rate payments from Phoenix's mortgages, equaling 10%. In exchange, Phoenix receives variable payments from Padlock, equaling the LIBOR rate (the interbank lending rate for Eurobanks). Assume that Phoenix's cost of funds (or the rate owed on its deposits) is equal to the LIBOR rate, less 1%. The following table details the swap arrangement from the point of view of Phoenix bank for various possible values of LIBOR. Possible Future LIBOR Rates 8% 9% 10% 11% 7% 12% 12% 12% 12% 12% 12% 12% 7 8 9 10 11 12 5 4 4 3 2 1 0 12% 12% 12% 12% 12% 12% Unhedged Strategy Average rate on existing mortgages Average cost of deposits Spread Hedging with Interest Rate Swap Fixed interest earned on fixed-rate mortgages Fixed interest owed on swap Spread on fixed-rate payments Variable interest rate earned on swap Variable interest rate owed on deposits Spread on variable-rate payments Combined total spread when using swap 10 10 10 10 10 10 2 2 2 2 N 2 2 8 9 10 11 12 7 6 6 7 8 9 9 10 11 1 1 1 1 1 1 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 If LIBOR is 7%, Phoenix's spread would be % if unhedged and % when hedged. Thus, hedging leads to a spread. % if unhedged, and % when hedged. Thus, hedging leads to a spread If LIBOR is 10%, Phoenix's spread would be when LIBOR is 10%. 7. Using interest rate swaps to reduce interest rate risk Suppose that Phoenix bank seeks to reduce its interest rate risk in regards to its holdings of fixed-rate (12%) mortgages via the use of interest rate swaps. To this end, Phoenix and Padlock bank come to an agreement of a swap arrangement, whereby Padlock receives fixed-rate payments from Phoenix's mortgages, equaling 10%. In exchange, Phoenix receives variable payments from Padlock, equaling the LIBOR rate (the interbank lending rate for Eurobanks). Assume that Phoenix's cost of funds (or the rate owed on its deposits) is equal to the LIBOR rate, less 1%. The following table details the swap arrangement from the point of view of Phoenix bank for various possible values of LIBOR. Possible Future LIBOR Rates 8% 9% 10% 11% 7% 12% 12% 12% 12% 12% 12% 12% 7 8 9 10 11 12 5 4 4 3 2 1 0 12% 12% 12% 12% 12% 12% Unhedged Strategy Average rate on existing mortgages Average cost of deposits Spread Hedging with Interest Rate Swap Fixed interest earned on fixed-rate mortgages Fixed interest owed on swap Spread on fixed-rate payments Variable interest rate earned on swap Variable interest rate owed on deposits Spread on variable-rate payments Combined total spread when using swap 10 10 10 10 10 10 2 2 2 2 N 2 2 8 9 10 11 12 7 6 6 7 8 9 9 10 11 1 1 1 1 1 1 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 If LIBOR is 7%, Phoenix's spread would be % if unhedged and % when hedged. Thus, hedging leads to a spread. % if unhedged, and % when hedged. Thus, hedging leads to a spread If LIBOR is 10%, Phoenix's spread would be when LIBOR is 10%
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


