Question: Use C program write a function ( void add_lists(Node *list1, Node *list2) ). The function add_lists should add the value of each node contained in
Use C program write a function ( void add_lists(Node *list1, Node *list2) ).
The function add_lists should add the value of each node contained in the same position in the lists together and store the result as the new value of list1's node at that position. If list1 is shorter than list2 or vice versa, than for nodes past the shorter of the two lists no addition needs to occur (and list1 should remain the same for these nodes). Use recursion to create this function (though not required, the function body can be created with 3 lines of code.
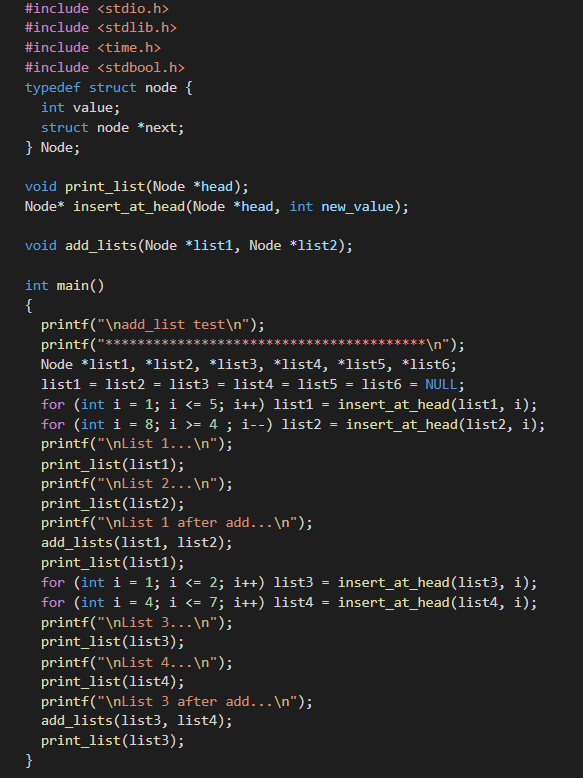
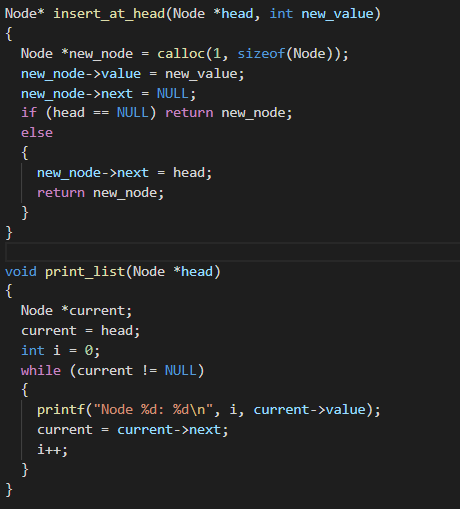
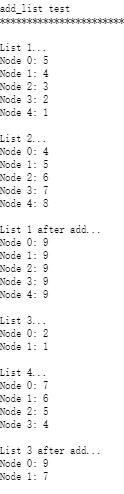
Here is the output
 plz use recursive
plz use recursive
#include #include #include #include typedef struct node { int value; struct node *next; } Node; void print_list(Node *head); Node* insert_at_head (Node *head, int new_value); void add_lists(Node *listi, Node *list2); int main() { printf(" add_list test "); printf(" ** "); Node *listi, *list2, *list3, *list4, *lists, *listi; list1 = list2 list3 = list4 list5 list6 NULL; for (int i = 1; i = 4; i--) list2 = insert_at_head(list2, i); printf(" List 1... "); print_list(list1); printf(" List 2... "); print_list(list2); printf(" List 1 after add... "); add_lists(listi, list2); print_list(list1); for (int i = 1; i value = new_value; new_node->next = NULL; if (head == NULL) return new_node; else { new_node->next = head; return new_node; } } void print_list(Node *head) { Node *current; current = head; int i = 0; while (current != NULL) { printf("Node %d: %d ", i, current->value); current = current->next; it; } } add_list test List 1... Node 0: 5 Node 1: 4 Node 2: 3 Node 3: 2 Node 4: 1 List 2... Node 0: 4 Node 1: 5 Node 2: 6 Node 3: 7 Node 4: 8 List 1 after add... Node 0: 9 Node 1: 9 Node 2: 9 Node 3: 9 Node 4: 9 List 3... Node 0: 2 Node 1: 1 List 4... Node 0: 7 Node 1: 6 Node 2: 5 Node 3: 4 List 3 after add... Node 0: 9 Node 1: 7


 plz use recursive
plz use recursive


