Question: Use Java The starter code to do this following exercise is provided. I have created a google doc that includes the starter code here is
Use Java
The starter code to do this following exercise is provided. I have created a google doc that includes the starter code here is the link for the starter code: https://docs.google.com/document/d/1DIJRFqAiOWfR7-tc12LGl18KA6GVqqTihNyuq7AjIoo/edit
Postfix Calculator:
You will need to complete a postfix calculator. The input to the method will be a String. You can assume that all tokens will be separated by a space. Make sure to accommodate negative values. You should detect situations where there are not enough operands for an operator, or when there are extra operators, or missing operators. Throw an exception in these situations (IllegalArgumentException). You should support ^, *, /, +, - operators. You should fill in the evalPostfix() method that has been given to you in the starter code. An interaction with the program is given below. You will need to implement a menu that accepts inputs from the user until they are finished. (See output below).
Please Enter a valid postfix Expression: 4 5 6 + +
Calculation: 15.0
(E)valuate another or (Q)uit?E
Please Enter a valid postfix Expression: 4 5 6.22 - -
Calculation: 5.22
(E)valuate another or (Q)uit?E
Please Enter a valid postfix Expression: 1 2 * 3 * 3 / 5 ^
Calculation: 32.0
(E)valuate another or (Q)uit?Q
Thanks for evaluating!
Here is a second Set of output below:
Please Enter a valid postfix Expression: 3 2 4 + +
Calculation: 9.0
(E)valuate another or (Q)uit?e
Please Enter a valid postfix Expression: 8 9 / 7 12.2 - + 6 *
Calculation: -25.86666666666666
(E)valuate another or (Q)uit?q
Thanks for evaluating!
Infix Calculator:
In this assignment, you will implement the Infix calculation algorithm that was covered in class (See Stack slides, #22-24. (I have copied the slides to the end of this document for your reference). I have posted a starter code. You may create additional methods if you feel the need, but you may not change the method header of any of the given methods (i.e. return values or parameters).
The algorithm as given will not work with parenthesis. You will need to modify the algorithm slightly to work with parenthesis. A quick google search (hint: stack exchange) will give you a variation of our algorithm that also considers parenthesis. Here are the operators you must support in order of precedence.
- ( )
- ^ (power, i.e. 5 ^ 2)
- * / (multiplication and division)
- + - (addition and subtraction)
- $ (reference operator that has lowest precedence)
Note that you do not need to support {} or []. Your code should support multiple levels of parentheses.
You may assume that for a valid input, each token will be separated by a space. Here are examples of valid input:
- ( 1 + 2 ) + ( 3 + 4 ) * 5
- ( ( 1 + 2 ) + ( 3 + 4 ) ) * 5
- ( 2 * 1 ) ^ 10
You should treat values as doubles.
You should support numbers longer than a single digit.
If you are missing an operand or an operator or you have an extra operand or operator you should throw an IllegalArgumentException.
Tester:
Create a tester that tests all methods and error conditions as shown above. I will post a document that gives you some input and output examples. Create a PDF document that displays interaction with your program and tests various inputs, as well as testing error conditions. Note that since your inputs are all given from the console input, you wont actually create a tester, but instead, you will need to develop inputs to use with your program.
Here is the images of the slide (#22-24):
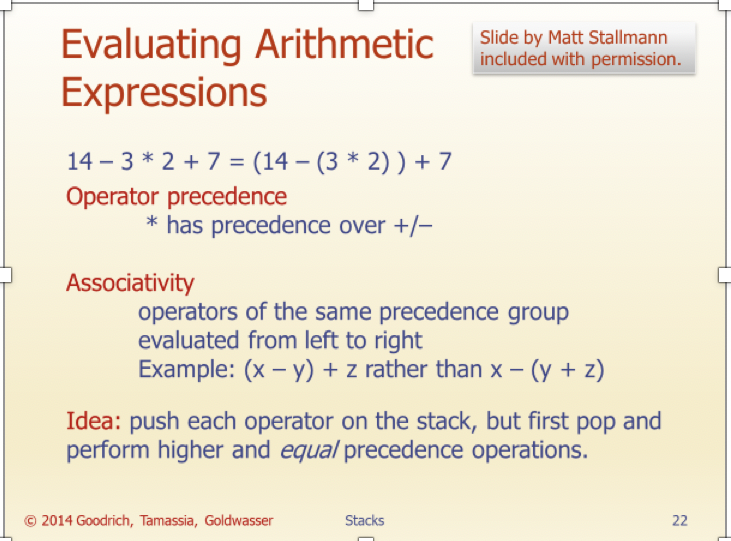
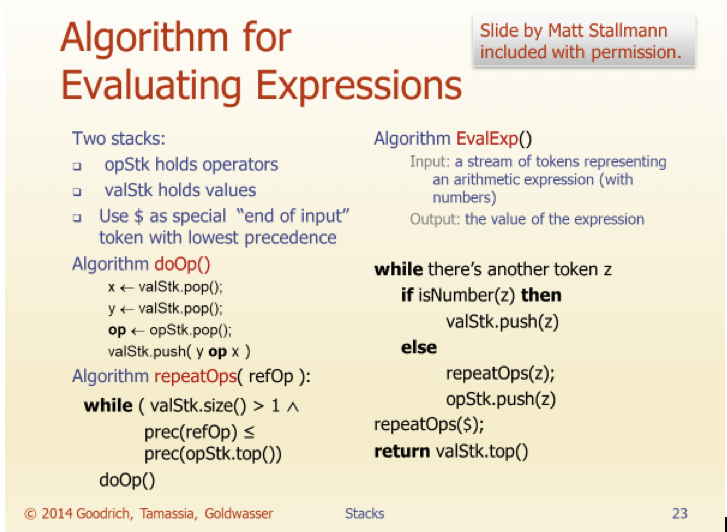
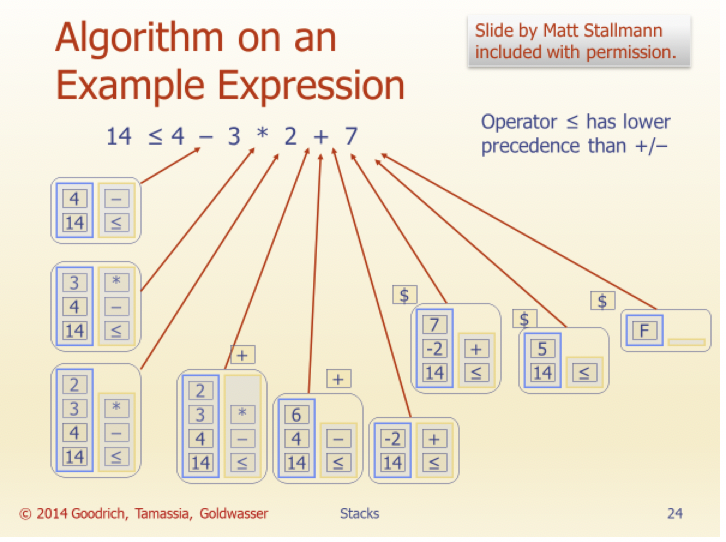
Slide by Matt Stallmann included with permission. Evaluating Arithmetic Expressions 14 - 3* 2 + 7 = (14 (3 * 2)) + 7 Operator precedence * has precedence over +/- Associativity operators of the same precedence group evaluated from left to right Example: (x - y) + z rather than x - (y + z) Idea: push each operator on the stack, but first pop and perform higher and equal precedence operations. 2014 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser Stacks Slide by Matt Stallmann included with permission. Algorithm for Evaluating Expressions Two stacks: Algorithm EvalExpo opStk holds operators Input: a stream of tokens representing an arithmetic expression (with valStk holds values numbers) . Use $ as special "end of input" Output: the value of the expression token with lowest precedence Algorithm doop while there's another token z X+ valStk.pop(); if isNumber(z) then y valStk.pop(); op opStk.pop(); valStk.push(z) valStk.push( y op ) else Algorithm repeatOps( refop): repeatOps(z); while ( valStk.size() >14 opStk.push(z) prec(refop) repeatOps($); prec(opStk.topO) return valStk.top() doop 2014 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser Stacks Slide by Matt Stallmann included with permission. Algorithm on an Example Expression 14 54,- 3 * 2 + 7 Operator 14 opStk.push(z) prec(refop) repeatOps($); prec(opStk.topO) return valStk.top() doop 2014 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser Stacks Slide by Matt Stallmann included with permission. Algorithm on an Example Expression 14 54,- 3 * 2 + 7 Operator
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


