Question: Use MatLab to write a function called trapint.m that takes data sample locations and function samplings at those locations as inputs and returns an approximation
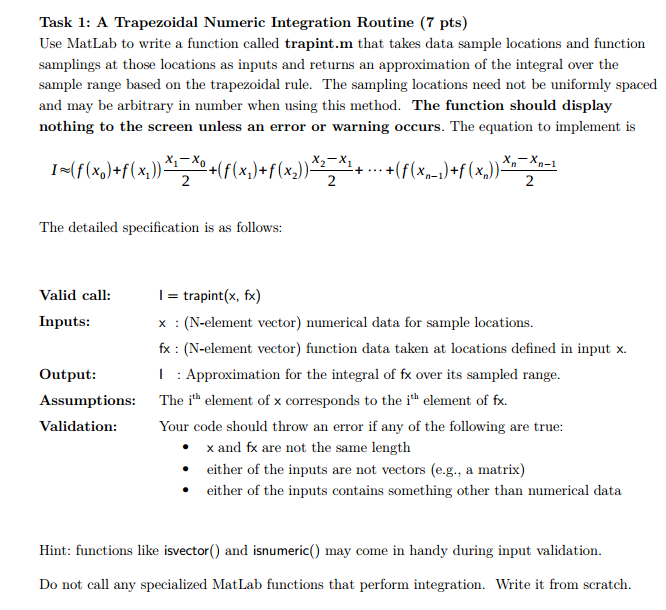
Use MatLab to write a function called trapint.m that takes data sample locations and function samplings at those locations as inputs and returns an approximation of the integral over the sample range based on the trapezoidal rule. The sampling locations need not be uniformly spaced and may be arbitrary in number when using this method. The function should display nothing to the screen unless an error or warning occurs. The equation to implement is I almosteqaulto (f(x_0) + (f(x_1)x_1 - x_0/2 + (f(x_1) + f (x_2))x_2 - x_1/2 + ... + (f(x_n - 1) + f(x_n))x_n - x_n - 1/2 The detailed specification is as follows: Valid call: I = trapint(x, fx) Inputs: x: (N-element vector) numerical data for sample locations. fx (N-element vector) function data taken at locations defined in input x. Output: I: Approximation for the integral of fx over its sampled range. Assumptions: The ith element of x corresponds to the ith element of fx. Validation: Your code should throw an error if any of the following are true: x and fx are not the same length either of the inputs are not vectors (e.g., a matrix) either of the inputs contains something other than numerical data Use MatLab to write a function called trapint.m that takes data sample locations and function samplings at those locations as inputs and returns an approximation of the integral over the sample range based on the trapezoidal rule. The sampling locations need not be uniformly spaced and may be arbitrary in number when using this method. The function should display nothing to the screen unless an error or warning occurs. The equation to implement is I almosteqaulto (f(x_0) + (f(x_1)x_1 - x_0/2 + (f(x_1) + f (x_2))x_2 - x_1/2 + ... + (f(x_n - 1) + f(x_n))x_n - x_n - 1/2 The detailed specification is as follows: Valid call: I = trapint(x, fx) Inputs: x: (N-element vector) numerical data for sample locations. fx (N-element vector) function data taken at locations defined in input x. Output: I: Approximation for the integral of fx over its sampled range. Assumptions: The ith element of x corresponds to the ith element of fx. Validation: Your code should throw an error if any of the following are true: x and fx are not the same length either of the inputs are not vectors (e.g., a matrix) either of the inputs contains something other than numerical data
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


