Question: USE ONLY THESE FUNCTIONS: empty = 'empty' def is_link(s): s is a linked list if it is empty or a (first, rest) pair. return s
USE ONLY THESE FUNCTIONS:
empty = 'empty'
def is_link(s): """s is a linked list if it is empty or a (first, rest) pair.""" return s == empty or (len(s) == 2 and is_link(s[1]))
def link(first, rest): """Construct a linked list from its first element and the rest.""" assert is_link(rest), "rest must be a linked list." return [first, rest]
def first(s): """Return the first element of a linked list s.""" assert is_link(s), "first only applies to linked lists." assert s != empty, "empty linked list has no first element." return s[0]
def rest(s): """Return the rest of the elements of a linked list s.""" assert is_link(s), "rest only applies to linked lists." assert s != empty, "empty linked list has no rest." return s[1]
# define length def len_link(s): """Return the length of linked list s.""" length = 0 while s != empty: s, length = rest(s), length + 1 return length
# getitem def getitem(s, i): """Return the element at index i of linked list s.""" while i > 0: s, i = rest(s), i - 1 return first(s)
 IN CASE YOU NEED TO KNOW WHAT PUSH/POP DOES:
IN CASE YOU NEED TO KNOW WHAT PUSH/POP DOES: 
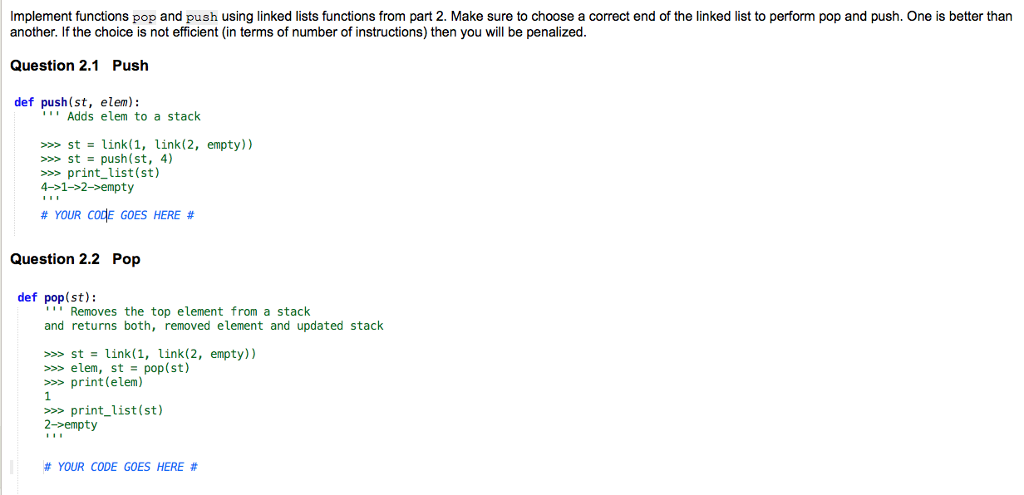
Implement functions pop and push using linked lists functions from part 2. Make sure to choose a correct end of the linked list to perform pop and push. One is better than another. If the choice is not efficient (in terms of number of instructions) then you will be penalized. Question 2.1 Push def push(st, elem): Adds elem to a stack st-link(1, ink(2, empty)) st push(st, 4) >s> print_list(st.) 4->1->2-empty #YOUR codE GOES HERE # Question 2.2 Pop def pop(st): Removes the top element from a stack and returns both, removed element and updated stack >>> st link(1, link(2, empty)) >elem, stpop (st) >print(elem) print_list(st) 2->empty # YOUR CODE GOES HERE # Implement functions pop and push using linked lists functions from part 2. Make sure to choose a correct end of the linked list to perform pop and push. One is better than another. If the choice is not efficient (in terms of number of instructions) then you will be penalized. Question 2.1 Push def push(st, elem): Adds elem to a stack st-link(1, ink(2, empty)) st push(st, 4) >s> print_list(st.) 4->1->2-empty #YOUR codE GOES HERE # Question 2.2 Pop def pop(st): Removes the top element from a stack and returns both, removed element and updated stack >>> st link(1, link(2, empty)) >elem, stpop (st) >print(elem) print_list(st) 2->empty # YOUR CODE GOES HERE #
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


