Question: Use the contingency table below for the variables SEX and OTHSHELP (the extent to which respondents to the 2002 GSS believe that we should help
Use the contingency table below for the variables SEX and OTHSHELP (the extent to which respondents to the 2002 GSS believe that we should help others less fortunate than ourselves) to answer the next question(s)
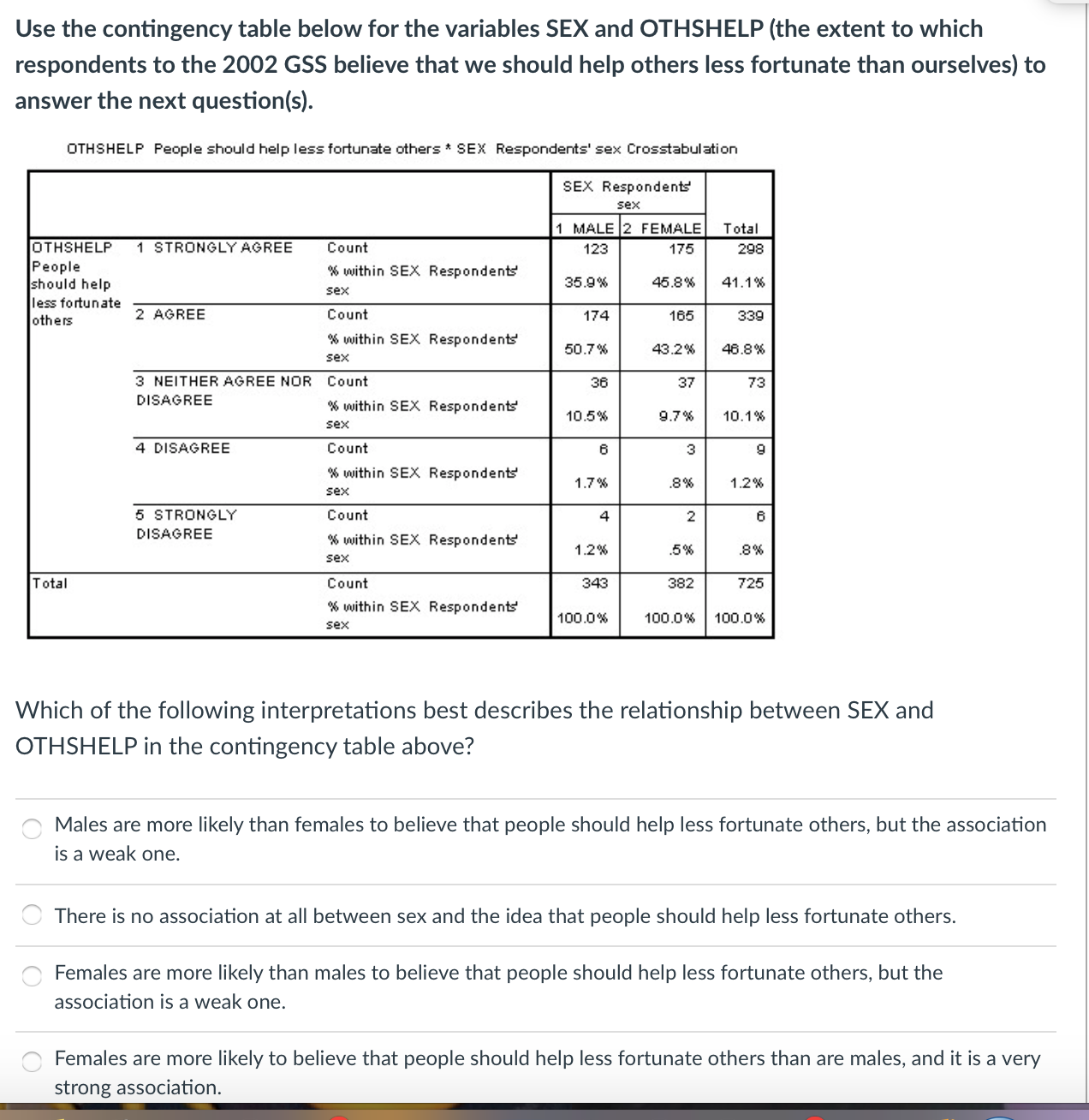
Use the contingency table below for the variables SEX and OTHSHELP (the extent to which respondents to the 2002 GSS believe that we should help others less fortunate than ourselves) to answer the next questionls). OTHSHELP People should help less fortunate other; * SEX Respondents' sax Crosstabulztion SEX Respondents' sex M2 FEMALE Total OTHSHELP 1 STRUHGLYAGREE Count 175 293 People 16within SEX. Fles ondenB' should help sex p 45-3\" 4141'" Iessforlunate others 2 AGREE Count 174 \"165 339 :rllln SEX. Respondents' 50.7% 43.2% 46.3% 3 NEITHER AGREE NDH Count 36 3? T3 DISAGREE - - :flthln SEX Respondent! 10.5% 91% 10.1% 4 DISAGREE Count 8 3 Q 16 within SEX. Respondents 1-7\" 3% 12% sex 5 STRONGLY Count 6 D'SAGREE as within sex Respondents .315 sex Count 343 382 1'25 within SEX Res ondents sax p 100.0% 100.0% 100.0% Which of the following interpretations best describes the relationship between SEX and OTHSHELP in the contingency table above? "f- Males are more likely than females to believe that people should help less fortunate others, but the association is a weak one. There is no association at all between sex and the idea that people should help less fortunate others. ff Females are more likely than males to believe that people should help less fortunate others, but the association is a weak one. \"f- Females are more likely to believe that peeple should help less fortunate others than are males, and it is a very strong association
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


