Question: Use the description and code given in the picture to First find the scaling law for the end to end disrance and radius gyration of
Use the description and code given in the picture to First find the scaling law for the end to end disrance and radius gyration of 3D random walk polymer as a function of polymer length. What is the code to plot the average end to end distance and end-to-end distance together with the corresponding analytical functions describing their scaling behaviour.
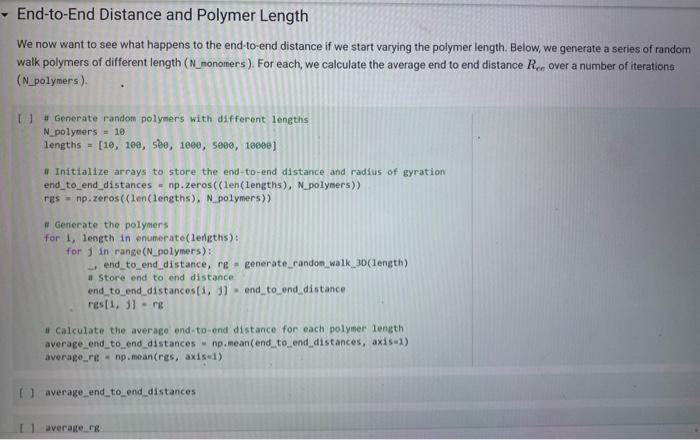
End-to-End Distance and Polymer Length We now want to see what happens to the end-to-end distance if we start varying the polymer length. Below, we generate a series of random walk polymers of different length (N_monomers). For each, we calculate the average end to end distance Rce over a number of iterations (N_polymers). [ ] a Generate random polymers with different lengths N_polyners =10 lengths =[10,100,500,1000,5000,10900] if Initialize arpays to store the end-to-end distance and radius of gyration end_to_end_distances = np.zeros((len(lengths), N_polymers)) res = np.zeros((len(lengths), N_polymers )) I Generate the polymers for 1 , length in enumerate(lengths): for j in range ( N_polymers): -. end_to_end_distance, rg= generate_randon_walk_30(1ength) it store end to end distance end_to_end_distances [1,1]= end_to_end_distance res [1,1]=rg II Calculate the average end-to-end distance for each polywer length average_end_to_end_distances =np.mean(end_to_end_distances, axis=1 ) average_rit = np,mean(res,axis=1) I I average_end_to_end distances
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


