Question: Use the modular arithmetic rules : Definition 0.2 Let ZN = {a ZN |gcd(a, n) = 1} (i.e., set of integers co-prime with N). Let
Use the modular arithmetic rules :
Definition 0.2
Let ZN = {a ZN |gcd(a, n) = 1} (i.e., set of integers co-prime with N). Let x denote the order of ZN . Then, without loss of generality, if a ZN : ay mod N = ay mod x mod N where y 0.
Example of how to apply the definition: Find 450 mod 9. Here N = 9, So, ZN = Z9 = {1, 2, 4, 5, 7, 8}, and so, x = |Z9|= 6. y = 50. 450 mod 9 = 450 mod 6 mod 9 = 42 mod 9 = 16 mod 9 = 7
| QUESTIONS |
A)
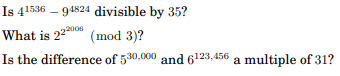
B)

Is 4153694824 divisible by 35 ? What is 222006(mod3)? Is the difference of 530,000 and 6123,456 a multiple of 31 ? Consider the problem of computing xy for given integers x and y : we want the whole answer, not modulo a third integer. We know two algorithms for doing this: the iterative algorithm which performs y1 multiplications by x; and the recursive algorithm based on the binary expansion of y. Compare the time requirements of these two algorithms, assuming that the time to multiply an n-bit number by an m-bit number is O(mn)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


