Question: Using C Language Our permutation needs to read 64-bytes (512 bits) from memory into variable, send the variables through the the mixing step multiple times,
Using C Language

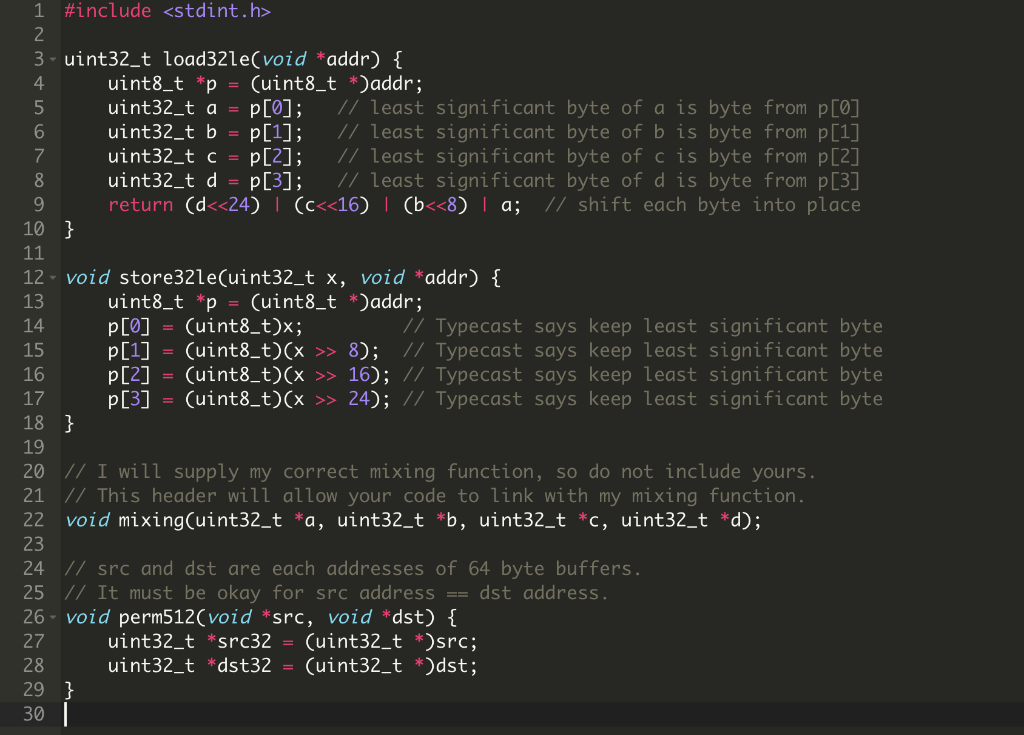
Our permutation needs to read 64-bytes (512 bits) from memory into variable, send the variables through the the mixing step multiple times, and then write the variables back out to memory. Here's the pseudocode. read 64 bytes into variables to, t1, ..., t15 doing little-endian reads. 10 times do: // Mix columns mixingto, t4, t8, t12) mixing(t1, t5, t9, t13) mixing(t2, t6, t10, t14) mixing(t3, t7, t11, t15) // Mix diagonals mixingto, t5, t10, t15) mixing(t1, t6, t11, t12) mixing(t2, t7, t8, t13) mixing(t3, t4, t9, t14) write 64 bytes from variables to, t1, ..., t15 doing little-endian writes. The comments about mixing columns and diagonals refers to an explanation given in lecture regarding this permutation. See that video for more explanation. 1 #include 2 3. uint32_t load321e(void *addr) { 4 uint8_t *p (uint8_t *)addr; 5 uint32_t a = p[0]; // least significant byte of a is byte from p[0] 6 uint32_t b = p[1]; // least significant byte of bis byte from p[1] 7 uint32_t c = p[2]; // least significant byte of cis byte from p[2] 8 uint32_t d = p[3]; // least significant byte of d is byte from p[3] 9 return (d> 8); // Typecast says keep least significant byte 16 p[2] = (uint8_t)(x >> 16); // Typecast says keep least significant byte 17 p[3] = (uint8_t)(x >> 24); // Typecast says keep least significant byte 18 } 19 20 // I will supply my correct mixing function, so do not include yours. 21 // This header will allow your code to link with my mixing function. 22 void mixing(uint32_t *a, uint32_t *b, uint32_t *c, uint32_t *d); 23 24 // src and dst are each addresses of 64 byte buffers. 25 // It must be okay for src address == dst address. 26 void perm512(void *src, void *dst) { 27 uint32_t *src32 (uint32_t *)src; 28 uint32_t *dst32 = (uint32_t *)dst; 29 } 30 | Our permutation needs to read 64-bytes (512 bits) from memory into variable, send the variables through the the mixing step multiple times, and then write the variables back out to memory. Here's the pseudocode. read 64 bytes into variables to, t1, ..., t15 doing little-endian reads. 10 times do: // Mix columns mixingto, t4, t8, t12) mixing(t1, t5, t9, t13) mixing(t2, t6, t10, t14) mixing(t3, t7, t11, t15) // Mix diagonals mixingto, t5, t10, t15) mixing(t1, t6, t11, t12) mixing(t2, t7, t8, t13) mixing(t3, t4, t9, t14) write 64 bytes from variables to, t1, ..., t15 doing little-endian writes. The comments about mixing columns and diagonals refers to an explanation given in lecture regarding this permutation. See that video for more explanation. 1 #include 2 3. uint32_t load321e(void *addr) { 4 uint8_t *p (uint8_t *)addr; 5 uint32_t a = p[0]; // least significant byte of a is byte from p[0] 6 uint32_t b = p[1]; // least significant byte of bis byte from p[1] 7 uint32_t c = p[2]; // least significant byte of cis byte from p[2] 8 uint32_t d = p[3]; // least significant byte of d is byte from p[3] 9 return (d> 8); // Typecast says keep least significant byte 16 p[2] = (uint8_t)(x >> 16); // Typecast says keep least significant byte 17 p[3] = (uint8_t)(x >> 24); // Typecast says keep least significant byte 18 } 19 20 // I will supply my correct mixing function, so do not include yours. 21 // This header will allow your code to link with my mixing function. 22 void mixing(uint32_t *a, uint32_t *b, uint32_t *c, uint32_t *d); 23 24 // src and dst are each addresses of 64 byte buffers. 25 // It must be okay for src address == dst address. 26 void perm512(void *src, void *dst) { 27 uint32_t *src32 (uint32_t *)src; 28 uint32_t *dst32 = (uint32_t *)dst; 29 } 30 |





