Question: Using equations (15.4) and (15.5), show that Jo(x) = J2(x) at every maximum or %3D minimum of Ji(x), and Jo(r) = -J2(x) Computer plot
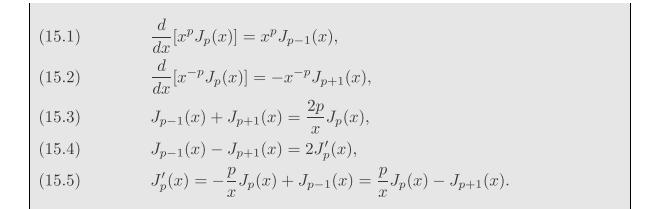
Using equations (15.4) and (15.5), show that Jo(x) = J2(x) at every maximum or %3D minimum of Ji(x), and Jo(r) = -J2(x) Computer plot Jo(x), Ji(x), and J2(a) on the same axes, and verify that these J{ (x) at every positive zero of J(x). results are true. (15.1) la" J,(r)] = r" Jp-1(x), dr d. [rPJp(x)] = --PJp+1(x), (15.2) dr Jp-1(x) + Jp+1(x) = "J,(x), Jp-1(x) Jp+1(a) = 2., (a), J,(x) = -J,(x) + Jp-1(r) = Jp(x) Jp+1(x). (15.3) (15.4) (15.5)
Step by Step Solution
3.49 Rating (172 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To solve the given problem we need to verify the relationships between Bessel functions J0x J1x and ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


