Question: Using #include typedef struct Node{ void* data; struct Node* next; struct Node* prev; } Node; typedef struct LList{ Node* first; Node* last; int size; int
Using
#include
typedef struct Node{
void* data;
struct Node* next;
struct Node* prev;
} Node;
typedef struct LList{
Node* first;
Node* last;
int size;
int itemSize;
char* type;
} LinkedList;
LinkedList* llist_initialize(int dataTypeSize, char* name) {
LinkedList* list = (LinkedList*) malloc(sizeof(LinkedList));
*list = (LinkedList) {
.first = NULL,
.last = NULL,
.size = 0,
.itemSize = dataTypeSize,
.type = name
};
return list;
}
bool llist_add_at(LinkedList* list, int index, void* element) {
if(list == NULL) {
return false;
}
if(!(0 size)) {
return false;
}
if(index == 0) {
return llist_add_first(list, element);
}
if(index == list->size) {
return llist_add_last(list, element);
}
Node* it = list->first;
while(--index > 0) {
it = it->next;
}
Node* node = (Node*) malloc(sizeof(Node));
*node = (Node) {
.data = element,
.next = it->next,
.prev = it,
};
it->next->prev = node;
it->next = node;
++list->size;
return true;
}
bool llist_add_first(LinkedList* list, void* element) {
if(list == NULL) {
return false;
}
Node* node = (Node*) malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(list->first == NULL) {
*node = (Node) {
.data = element,
.next = NULL,
.prev = NULL,
};
list->first = list->last = node;
} else {
*node = (Node) {
.data = element,
.next = list->first,
.prev = NULL,
};
list->first->prev = node;
list->first = node;
}
++list->size;
return true;
}
bool llist_add_last(LinkedList* list, void* element) {
if(list == NULL) {
return false;
}
Node* node = (Node*) malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(list->last == NULL) {
*node = (Node) {
.data = element,
.next = NULL,
.prev = NULL,
};
list->first = list->last = node;
} else {
*node = (Node) {
.data = element,
.next = NULL,
.prev = list->last,
};
list->last->next = node;
list->last = node;
}
++list->size;
return true;
}
void* llist_get(LinkedList* list, int index){
}
int llist_index_of(LinkedList* list, void* element){
}
void* llist_remove(LinkedList* list, void* element){
}
void* llist_remove_first(LinkedList* list) {
if(list == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
if(list->first == NULL) {
return NULL;
} else {
Node *temp = list->first;
void* ret = (void*)malloc(sizeof(temp->data));
ret = (temp->data);
if(list->first->next == NULL) {
list->first = list->last = NULL;
}
else {
list->first = list->first->next;
list->first->prev = NULL;
}
free(temp);
return ret;
}
}
void* llist_remove_last(LinkedList* list) {
if(list == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
if(list->last == NULL) {
return NULL;
} else {
Node *temp = list->last;
void* ret = (void*)malloc(sizeof(temp->data));
ret = (temp->data);
if(list->last->prev == NULL) {
list->first = list->last = NULL;
}
else {
list->last = list->last->prev;
list->last->next = NULL;
}
free(temp);
return ret;
}
}
bool llist_destroy(LinkedList* list) {
if(list == NULL) {
return true;
}
while(list->first != NULL) {
Node *temp = list->first;
if(list->first->next == NULL) {
list->first = list->last = NULL;
}
else {
list->first = list->first->next;
}
free(temp);
}
free(list);
list = NULL;
return true;
}
Complete functions
void* llist_get(LinkedList* list, int index){
}
int llist_index_of(LinkedList* list, void* element){
}
void* llist_remove(LinkedList* list, void* element){
}
C Programming
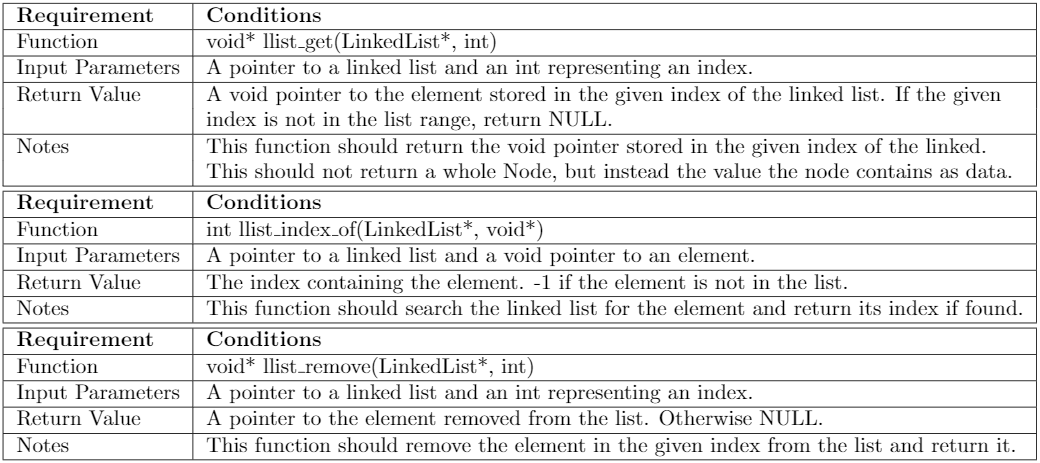
Requirement Function Input Parameters Return Value Notes Requirement Function Input Parameters Return Value Notes Requirement Function Input Parameters Return Value Notes Conditions void* llist_get(Linked List*, int) A pointer to a linked list and an int representing an index. A void pointer to the element stored in the given index of the linked list. If the given index is not in the list range, return NULL. This function should return the void pointer stored in the given index of the linked. This should not return a whole Node, but instead the value the node contains as data. Conditions int llist_index_of(Linked List*, void*) A pointer to a linked list and a void pointer to an element. The index containing the element. -1 if the element is not in the list. This function should search the linked list for the element and return its index if found. Conditions void* llist_remove(Linked List*, int) A pointer to a linked list and an int representing an index. A pointer to the element removed from the list. Otherwise NULL. This function should remove the element in the given index from the list and return it. Requirement Function Input Parameters Return Value Notes Requirement Function Input Parameters Return Value Notes Requirement Function Input Parameters Return Value Notes Conditions void* llist_get(Linked List*, int) A pointer to a linked list and an int representing an index. A void pointer to the element stored in the given index of the linked list. If the given index is not in the list range, return NULL. This function should return the void pointer stored in the given index of the linked. This should not return a whole Node, but instead the value the node contains as data. Conditions int llist_index_of(Linked List*, void*) A pointer to a linked list and a void pointer to an element. The index containing the element. -1 if the element is not in the list. This function should search the linked list for the element and return its index if found. Conditions void* llist_remove(Linked List*, int) A pointer to a linked list and an int representing an index. A pointer to the element removed from the list. Otherwise NULL. This function should remove the element in the given index from the list and return it
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


