Question: Using Java. This is my second time for posting question, please put all the methods and classes! Exercises - Requirements: 1. The main goal of
Using Java. This is my second time for posting question, please put all the methods and classes!
Exercises - Requirements:
1. The main goal of this assignment is to implement several recursive methods, each is built to manipulate binary tree data structures. Most of these methods are static and contained in a utility class named TreeFactory. You also need a node class similar to the BTNode class in the book (p 490) but it will be an utterly simplified version. As a warm-up exercise to this assignment it is recommended but not mandatory that in a separate project you implement and test all three traversal methods for binary trees we discussed in class. The warm-up exercise is not graded and do not submit it. 2. Add a class named BinaryNode to the project. This class supports the linked representations of binary trees. As for a template, look at the BTNode class specified and implemented in your book. However, for the BinaryNode class generic implementation not needed, the nodes will store integer values the standard methods will not be needed in this exercise except the constructor 3. Add a toString( ) method to the BinaryNode class. The method creates a String description of the tree. The method is analogous to the toString( ) method of HW 4.
The toString() method of HW4:
public String toString(int count){
String field1 = "";
String field2 = "";
if(data == null)
field1 = "data: dummy";
else
field1 = "data: " + data.toString();
if(link == null)
field2 = " \tlink: null in tail!";
else
field2 = " link:"+ link.toString(count + 1);
return field1 +" "+ field2;
}
4. Add the print( ) method we discussed in class to the BinaryNode class such that it displays a binary tree of linked representation to the console with indentation. See the slides #24 25 of Chapter 9.
The slides #24-25:
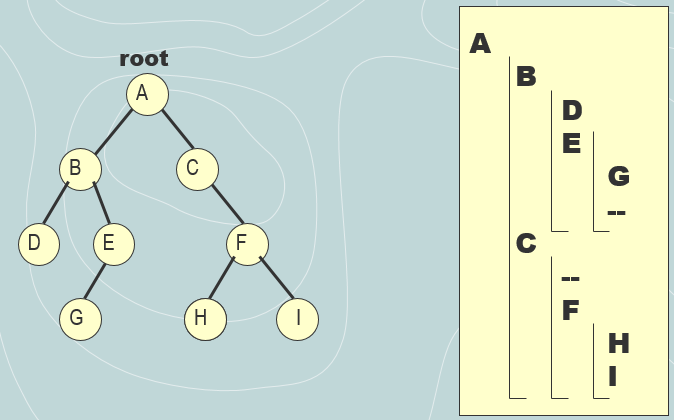

5. Add a class named TreeFactory to the project. All the methods in this class will be static. Following the descriptions below add the methods to the class. 6. powerOfTwo( ). Given any integer n>=0 the method computes recursively 2^n and returns the computed power. The parameter n is of type int, the return type is long. 7. findDepth( ). Given the root of a binary tree (the parameter of the method) the method computes recursively the depth of the tree and returns the depth value.
8. loadOverToArray ( ).
Given the root of a binary tree the method creates an array to represent the same tree.
The method loads over the data from the linked tree to the array and returns the array.
To make the array long enough for the tree, the method calls findDepth( ) and initializes the array to the size of the corresponding full binary tree. To get the size, use the powerOfTwo( ) method.
The method loads the data recursively (double recursion) . It takes two parameters, the root of the tree, and a sliding index for the entry element in the array where the load over operation begins
Hint: suppose index is the name of the parameter, then the array element at index is assigned the (relative) root data, and in the recursive call the parameter 2*index + 1 applies for the left child and 2*index + 2 for the right child 9. loadOverToLinked( ). This methods is NOT recursive!
Given the array representation of a binary tree the method creates a linked binary tree to represent the same data. The array is the parameter for the method
The method loads over the data from the array to the nodes of the linked tree and returns the root (return type BinaryNode)
It may help to declare and instantiate a parallel array of nodes.
Instantiate root with the data of index 0 and make root the 0 entry in the node array.
Run a for loop over the data array from index 1.
For k as current index instantiate a node with the data of index k.
Go back to the parent index from k.
If k is the left child from the parent index, assign the node as the left link of the parent node
Else assign the node as the right link of the parent node
Assign the node as the current index element of the node array 10. displayTree ( ). Given the root of a binary tree (the parameter) the method displays a linked tree arrangement of the data on the console. See a template in Figure1
8 4 12 2 6 10 14
1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15
Figure 1
Hints:
This method is not recursive
Determine the depth, call the findDepth( ) method
Call the loadOverToArray( ) method and follow the array order when printing
Create the spacing strings as you see it best (can be tricky)
A display not sharply accurate is acceptable, but the linked structure must be recognizable.
It is accepted if full binary trees are considered for display only. 11. BST_Builder( ). Given the depth N as a parameter, this method recursively builds a full binary search tree of depth N such that the nodes store the integers 1, 2, 3, , 2 N+1 1
Hints.
The method must return the root of the tree it built
The method shall be double recursive, a recursive call must apply (with decreased depth) to both the left link and right link of the current node
depth is naturally the control parameter and the base case is depth = = 0
it may be helpful to add another sliding parameter to the method, the top number stored in the root of the current sub-tree 12. Add an application class Test to the project, test and document all the methods in both classes BinaryNode and TreeFactory.
root
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


