Question: Using MATLAB The Problem: In an industrial process there are 3 storage tanks as shown in Figure 1. There are valves controlling the flow rates
Using MATLAB
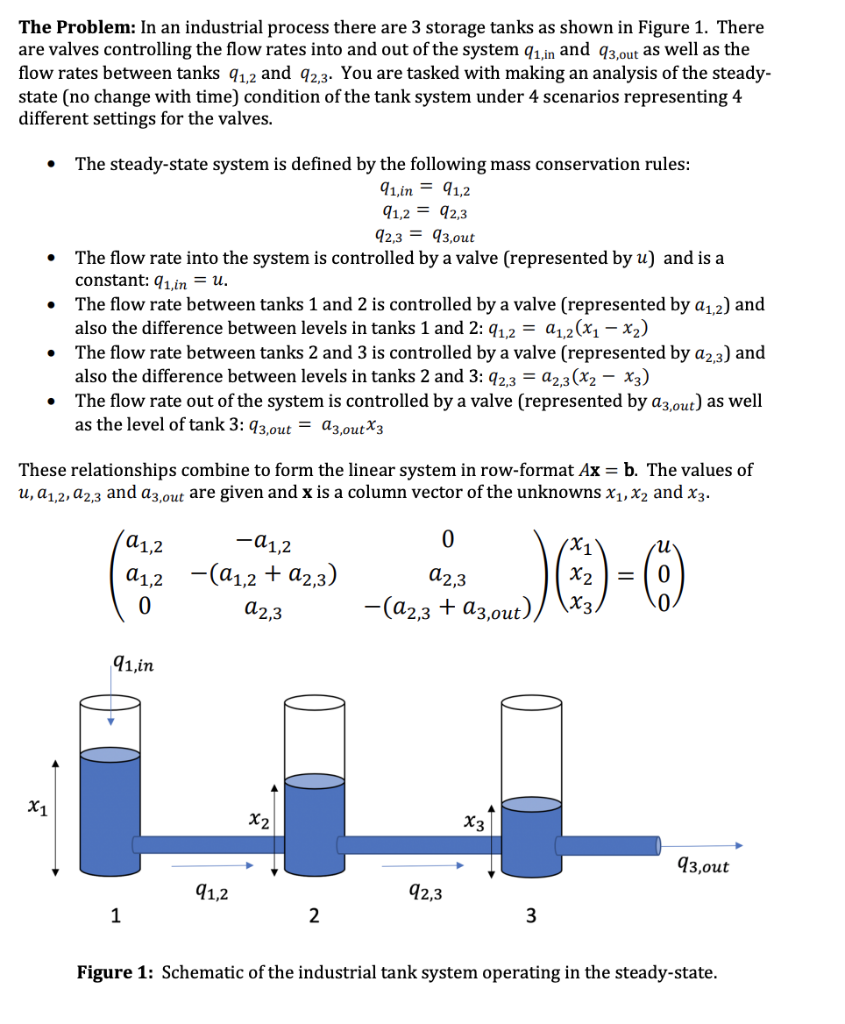

The Problem: In an industrial process there are 3 storage tanks as shown in Figure 1. There are valves controlling the flow rates into and out of the system q1in and q3,out as well as the flow rates between tanks q1,2 and q2.3. You are tasked with making an analysis of the steady- state (no change with time) condition of the tank system under 4 scenarios representing 4 different settings for the valves. The steady-state system is defined by the following mass conservation rules: . in 91,2 1,2 42,3 2,33,out The flow rate into the system is controlled by a valve (represented by u) and is a . The flow rate between tanks 1 and 2 is controlled by a valve (represented by a12) and . The flow rate between tanks 2 and 3 is controlled by a valve (represented by a2.3) and . The flow rate out of the system is controlled by a valve (represented by a3.out) as well constant: q1.in - u. also the difference between levels in tanks 1 and 2: q1.2-a1.2(x, - x2) also the difference between levels in tanks 2 and 3: q23- a2.3(x2- X3) as the level of tank 3: 93ta3,outX3 These relationships combine to form the linear system in row-format Ax- b. The values of u, a1,2, a2,3 and ag,out are given and x is a column vector of the unknowns x1,x2 and x3. 1,2 1,2 a1.2 -(a1,2 + a2.3) 2,3 2,3 1,in q3,out 2,3 2 Figure 1: Schematic of the industrial tank system operating in the steady-state Part 2: Solving a System of Equations Under Different Conditions (15 points) Below your code for Part 1, create a branch structure (if-elseif) to perform the following: If there is no inflow (u then the tanks will be empty. Set x - [0; 0; 0] and print the following message to screen: 1. 0) but all other valves are open (a1,2, a2.3 and a3,out 0), There is only the trivial solution: tanks are empty For example, the conditional expression for this part will be If there is nonzero inflow (u (a1,2, a2,3 or a3,out are zero), there is no solution and the valve settings are not compatible with the system. Set x = [NaN; NaN,NaN] (Hint: Do not put NaN in quotes) and print the following message to screen: 2. 0) but any one of the other three valves are closed There is no solution: open all valves. 3. If there is zero inflow (u - 0) but any one of the other three valves are closed (one or more of a1,2, a2.3 or a3,ou the other(s) may have an arbitrary depth. There are an infinite number of solutions, depending on how much fluid is in the system initially and its initial distribution between the 3 tanks. Set the solution x [0; 0; 0] and print the following message to screen: t is zero), then one (or more) of the tanks will be empty but There are an infinity of solutions: open all valves. If the inflow is non-zero (u non-zero), then the system has a unique, non-trivial equilibrium solution. Find the solution x using left-divide and print the following message to screen: 4. 0) and all valves are open (a1,2, a2.3 and a3,out are also The fluid depths are: Tank 1 = XX.XX Tank 2 = XX.XX Tank 3 -XX.XX The Problem: In an industrial process there are 3 storage tanks as shown in Figure 1. There are valves controlling the flow rates into and out of the system q1in and q3,out as well as the flow rates between tanks q1,2 and q2.3. You are tasked with making an analysis of the steady- state (no change with time) condition of the tank system under 4 scenarios representing 4 different settings for the valves. The steady-state system is defined by the following mass conservation rules: . in 91,2 1,2 42,3 2,33,out The flow rate into the system is controlled by a valve (represented by u) and is a . The flow rate between tanks 1 and 2 is controlled by a valve (represented by a12) and . The flow rate between tanks 2 and 3 is controlled by a valve (represented by a2.3) and . The flow rate out of the system is controlled by a valve (represented by a3.out) as well constant: q1.in - u. also the difference between levels in tanks 1 and 2: q1.2-a1.2(x, - x2) also the difference between levels in tanks 2 and 3: q23- a2.3(x2- X3) as the level of tank 3: 93ta3,outX3 These relationships combine to form the linear system in row-format Ax- b. The values of u, a1,2, a2,3 and ag,out are given and x is a column vector of the unknowns x1,x2 and x3. 1,2 1,2 a1.2 -(a1,2 + a2.3) 2,3 2,3 1,in q3,out 2,3 2 Figure 1: Schematic of the industrial tank system operating in the steady-state Part 2: Solving a System of Equations Under Different Conditions (15 points) Below your code for Part 1, create a branch structure (if-elseif) to perform the following: If there is no inflow (u then the tanks will be empty. Set x - [0; 0; 0] and print the following message to screen: 1. 0) but all other valves are open (a1,2, a2.3 and a3,out 0), There is only the trivial solution: tanks are empty For example, the conditional expression for this part will be If there is nonzero inflow (u (a1,2, a2,3 or a3,out are zero), there is no solution and the valve settings are not compatible with the system. Set x = [NaN; NaN,NaN] (Hint: Do not put NaN in quotes) and print the following message to screen: 2. 0) but any one of the other three valves are closed There is no solution: open all valves. 3. If there is zero inflow (u - 0) but any one of the other three valves are closed (one or more of a1,2, a2.3 or a3,ou the other(s) may have an arbitrary depth. There are an infinite number of solutions, depending on how much fluid is in the system initially and its initial distribution between the 3 tanks. Set the solution x [0; 0; 0] and print the following message to screen: t is zero), then one (or more) of the tanks will be empty but There are an infinity of solutions: open all valves. If the inflow is non-zero (u non-zero), then the system has a unique, non-trivial equilibrium solution. Find the solution x using left-divide and print the following message to screen: 4. 0) and all valves are open (a1,2, a2.3 and a3,out are also The fluid depths are: Tank 1 = XX.XX Tank 2 = XX.XX Tank 3 -XX.XX
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


