Question: Using Python 3 Construct Newton's Method Vs. Steepest Descent for a Function Newton's Method vs. Steepest Descent 15 points In the last question, you calculated
Using Python 3 Construct Newton's Method Vs. Steepest Descent for a Function
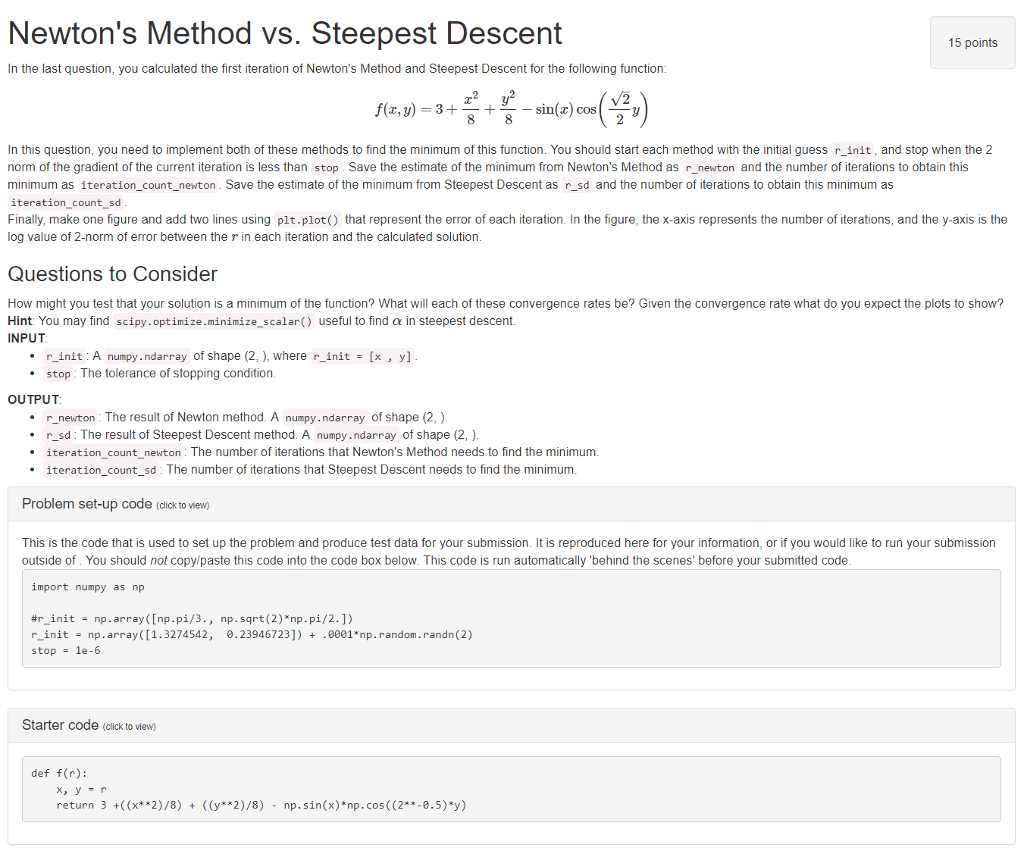
Newton's Method vs. Steepest Descent 15 points In the last question, you calculated the first iteration of Newton's Method and Steepest Descent for the following function f(z, y)-2+-+--sin(x) cos (-2-y In this question, you need to implement both of these methods to find the minimum of this function. You should start each method with the initial guess r_init, and stop when the 2 norm of the gradient of the current iteration is less than stop Save the estimate of the minimum from Newton's Method as r_newton and the number of iterations to obtain this minimum as iteration_count_newton. Save the estimate of the minimum from Steepest Descent as r_sd and the number of iterations to obtain this minimum as iteration count sd Finally, make one figure and add two lines using plt.plot() that represent the error of each iteration. In the figure, the x-axis represents the number of iterations, and the y-axis is the log value of 2-norm of error between the r in each iteration and the calculated solution Questions to Consider How might you test that your solution is a minimum of the function? What will each of these convergence rates be? Given the convergence rate what do you expect the plots to show? Hint You may find scipy.optimize.minimize-scalar() useful to find ? in steepest descent INPUT . r_init: A numpy.ndarray of shape (2,), where r_init - [x , y] Stop The tolerance of stopping condition OUTPUT r_newton: The result of Newton method. A numpy.ndarray of shape (2,) r_sd: The result of Steepest Descent method. A numpy.ndarray of shape (2,) iteration_count_newton The number of iterations that Newton's Method needs to find the minimum iteration_count_sd: The number of iterations that Steepest Descent needs to find the minimum Problem set-up code (click to view) This is the code that is used to set up the problem and produce test data for your submission. It is reproduced here for your information, or if you would like to run your submission outside of. You should not copylpaste this code into the code box below. This code is run automatically 'behind the scenes' before your submitted code import numpy as np #r-init - np.array([np.pl/3., np. sqrt (2)"np.pi/2.1) rinit np.array ([1.3274542, .23946723]) .0001*np.random.randn(2) stop1e-6 Starter code (click to view) def f(r): x, yr return 3 +((x**2)/8) ((y**2)/8)np.sin(x) np.cos( (2*-0.5)y) Newton's Method vs. Steepest Descent 15 points In the last question, you calculated the first iteration of Newton's Method and Steepest Descent for the following function f(z, y)-2+-+--sin(x) cos (-2-y In this question, you need to implement both of these methods to find the minimum of this function. You should start each method with the initial guess r_init, and stop when the 2 norm of the gradient of the current iteration is less than stop Save the estimate of the minimum from Newton's Method as r_newton and the number of iterations to obtain this minimum as iteration_count_newton. Save the estimate of the minimum from Steepest Descent as r_sd and the number of iterations to obtain this minimum as iteration count sd Finally, make one figure and add two lines using plt.plot() that represent the error of each iteration. In the figure, the x-axis represents the number of iterations, and the y-axis is the log value of 2-norm of error between the r in each iteration and the calculated solution Questions to Consider How might you test that your solution is a minimum of the function? What will each of these convergence rates be? Given the convergence rate what do you expect the plots to show? Hint You may find scipy.optimize.minimize-scalar() useful to find ? in steepest descent INPUT . r_init: A numpy.ndarray of shape (2,), where r_init - [x , y] Stop The tolerance of stopping condition OUTPUT r_newton: The result of Newton method. A numpy.ndarray of shape (2,) r_sd: The result of Steepest Descent method. A numpy.ndarray of shape (2,) iteration_count_newton The number of iterations that Newton's Method needs to find the minimum iteration_count_sd: The number of iterations that Steepest Descent needs to find the minimum Problem set-up code (click to view) This is the code that is used to set up the problem and produce test data for your submission. It is reproduced here for your information, or if you would like to run your submission outside of. You should not copylpaste this code into the code box below. This code is run automatically 'behind the scenes' before your submitted code import numpy as np #r-init - np.array([np.pl/3., np. sqrt (2)"np.pi/2.1) rinit np.array ([1.3274542, .23946723]) .0001*np.random.randn(2) stop1e-6 Starter code (click to view) def f(r): x, yr return 3 +((x**2)/8) ((y**2)/8)np.sin(x) np.cos( (2*-0.5)y)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


