Question: Using Python please. ## Directions For this project, you will need to implement a filtering inference task on an HMM. These are described in Section
Using Python please.
## Directions
For this project, you will need to implement a filtering inference task on an HMM. These are described in Section 15.2 of the text.
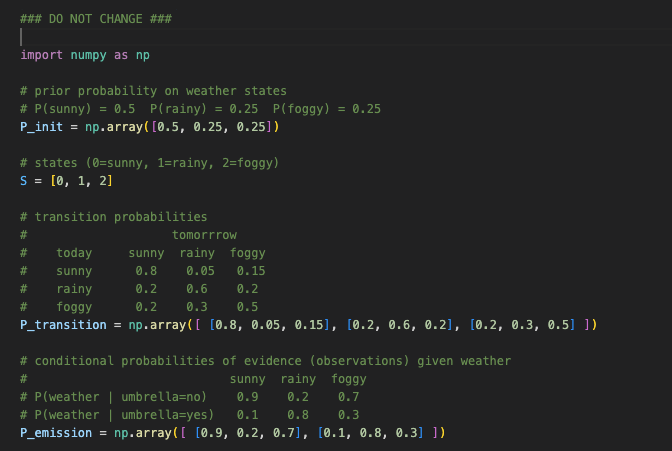
Denote the hidden states of the HMM by `S(t)` and the observations (evidence) by `E(t)`. In the weather problem from the HMM Tutorial, X(t) would be either sunny, rainy, or foggy, and `E(t)` is yes or no to indicate if an umbrella was observed. We will use this model with prior probabilities P(sunny) = 0.5, P(rainy) = 0.25, P(foggy) = 0.25. The remaining probilities you need are specified below in the emisssion (`P_emission`) and transition matrices (`P_transition`).
## Probability Definitions
Below you will find:
- `P_init`: The initial probabilities of the weather state, whether sunny (0), rainy (1) or foggy (2)
- `P_transition`: The transition probabilities or the probability that one weather state one day transitions to another weather state
- `P_emission`: The 'emission' probabilities or the probabilities that an observation is made, conditioned on the underlying state.
### [Question - State Transitions]
- If today is sunny what is the most likely forecast for the next two days if you have no umbrella observations to work with?
### [Question - Emission probabilities ]
If on the first day you see no umbrella, what is the probability that it is rainy, foggy or sunny (Hint: remember the importance of overall probability of each state)?
What is the most likely weather (hidden state)?

P_state_day0_given_umbrella =[## YOUR CODE HERE \#\#\#] print " "The most likely weather on the first day is ..." \#\#\# Your Code Here) \#\# please enter your answer in the print statement
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


