Question: Using short term futures if no long-term future can be found on market is a common strategy used by resource companies. What is the risk?
Using short term futures if no long-term future can be found on market is a common strategy used by resource companies. What is the risk? Read the case study on page 69 about Metallgesellschaft. Fill in the financial details.
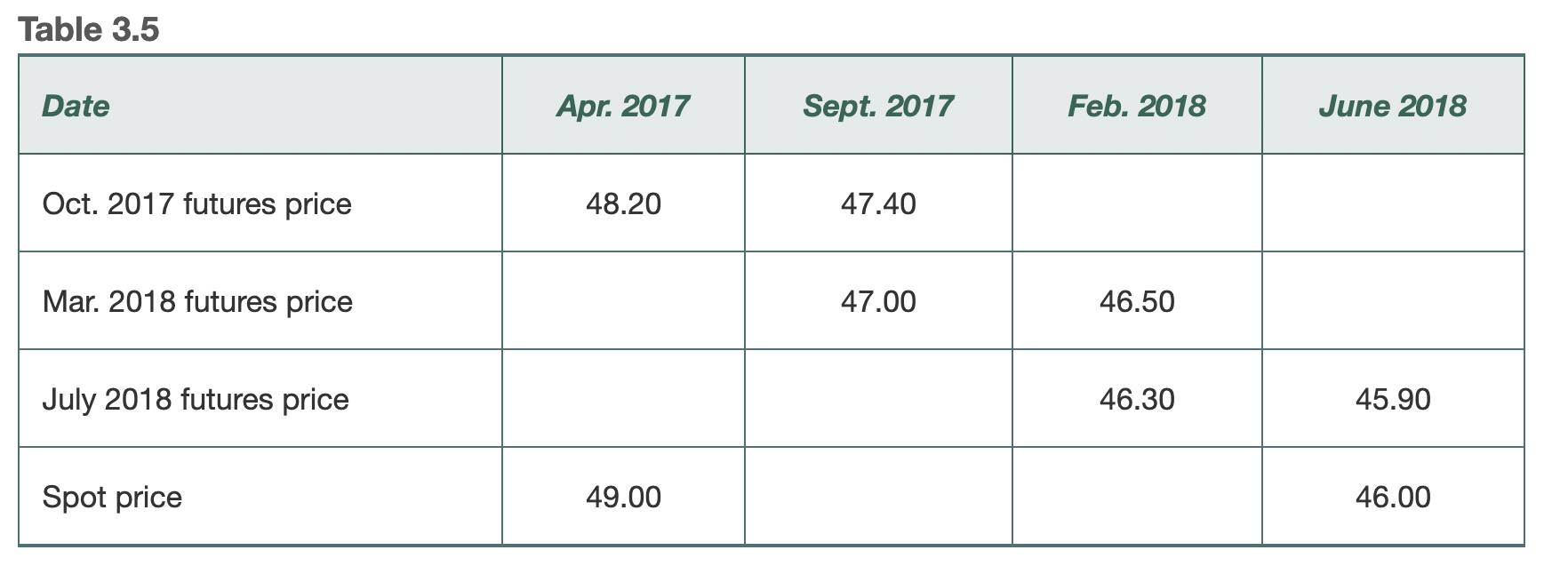

Table 3.5 Metallgesellschaft: Hedging Gone Awry Sometimes rolling hedges forward can lead to cash flow pressures. The problem was illustrated dramatically by the activities of a German company, Metallgesellschaft (MG), in the early 1990s. MG sold a huge volume of 5-to 10-year heating oil and gasoline fixed-price supply contracts to its customers at 6 to 8 cents above market prices. It hedged its exposure with long positions in short-dated futures contracts that were rolled forward. As it turned out, the price of oil fell and there were margin calls on the futures positions. Considerable short-term cash flow pressures were placed on MG. The members of MG who devised the hedging strategy argued that these short-term cash outflows were offset by positive cash flows that would ultimately be realized on the long-term fixed-price contracts. However, the company's senior management and its bankers became concerned about the huge cash drain. As a result, the company closed out all the hedge positions and agreed with its customers that the fixedprice contracts would be abandoned. The outcome was a loss to MG of $1.33 billion
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


