Question: USING SQL DATA DEFINITION LANGUAGE TO CREATE TABLES, ALTER TABLES, INSERT RECORDS For this lab, ALL of the tasks will be done with SQL by
USING SQL DATA DEFINITION LANGUAGE TO CREATE TABLES, ALTER TABLES, INSERT RECORDS
For this lab, ALL of the tasks will be done with SQL by creating SQL Scripts (queries) in the NEW SQL QUERY window.
Make sure you save the script files for each query that you run. Use the details in the figure below to create additional tables within your SQL server account.
Relation Attribute Data type Constraints REGION RegionID Integer Primary Key RegionName VARCHAR2(50) COUNTRY CountryID Integer Primary Key CountryName VARCHAR2(50) RegionID Integer Must match attribute in Region relation (FK) EMPLOYEE EmpID Integer EmpLastName VARCHAR2(50) EmpFirstName VARCHAR2(50) CountryMgr? VARCHAR2(1) Allowed values are Y or N COUNTRY MGR CMID Integer Must match EmpID (FK) CountryID Integer Must match CountryID (FK)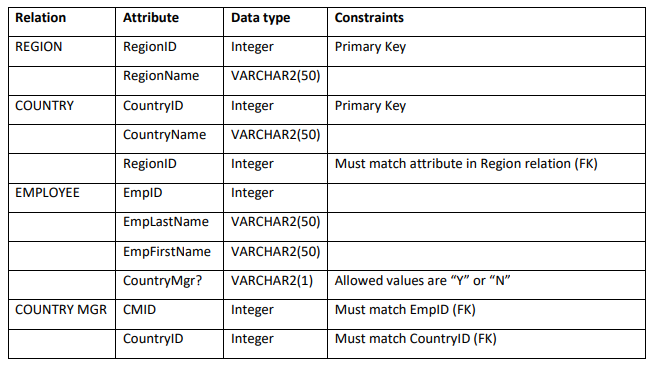
1. Use SQL statements Create the tables REGION, COUNTRY, EMPLOYEE and COUNTRY MANAGER as per the specifications in the figure above. [see figure 6-6 on page 254 of course text for examples of SQL CREATE statements). Make sure you include the ON UPDATE CASCADE clause in your create statements where necessary (wherever you create a FOREIGN KEY CONSTRAINT)
2. Use SQL statement to insert FIVE records into each of the four tables created in 1. Above (see pages 257-258 of course text for examples of INSERT statements).
3. Use the ALTER TABLE command to change the structure of the ORDER, PAYMENT, PRODUCT tables that you created in lab 3 (page 36 of the course text) by: a. adding correct FOREIGN KEY fields into those tables (the PK of the table on one-side of the relationship becomes an FK in the table on the many-side of the relationship), and b. adding FOREIGN KEY CONSTRAINTS to those tables.
4. Use the ALTER TABLE command to add FOREIGN KEY constraints in the structure of the ORDERLINE (also called the ORDEREDPRODUCT) table that you created in lab 3.
5. Use the SQL COMMENTS to add comments into your SQL scripts: a. Your name should be at the top of each script b. Comment at the top of each code block explaining what the code-block does 6. Save ALL the SQL Scripts that contain your SQL code and submit them to CANVAS. I will suggest that your FILENAMES for each script match the TASK that you are trying to achieve with the script
Attribute RegionlD Region Name VARCHAR2(50) CountrylD CountryName VARCHAR2(50) RegionID EmpID EmpLastName VARCHAR2(50) EmpFirstName VARCHAR2(50) CountryMgr? VARCHAR2(1) Allowed values are "Y" or "N" Relation Data type Constraints REGION Integer Primary Key COUNTRY Integer Primary Key Integer Must match attribute in Region relation (FK) EMPLOYEE Integer COUNTRY MGRCMID Integer Must match EmpID (FK) CountrylD Integer Must match CountrylD (FK)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


