Question: Using the attached documents, students will determine the best CPT code for each of the four patient cases. After reading the case, the students will
Using the attached documents, students will determine the best CPT code for each of the four patient cases. After reading the case, the students will select the best CPT code to use and provide a justification for their selection.
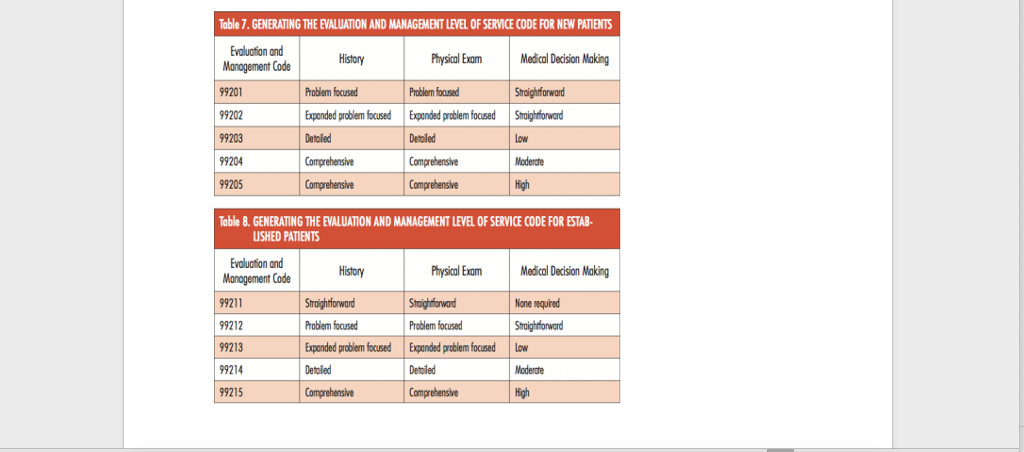


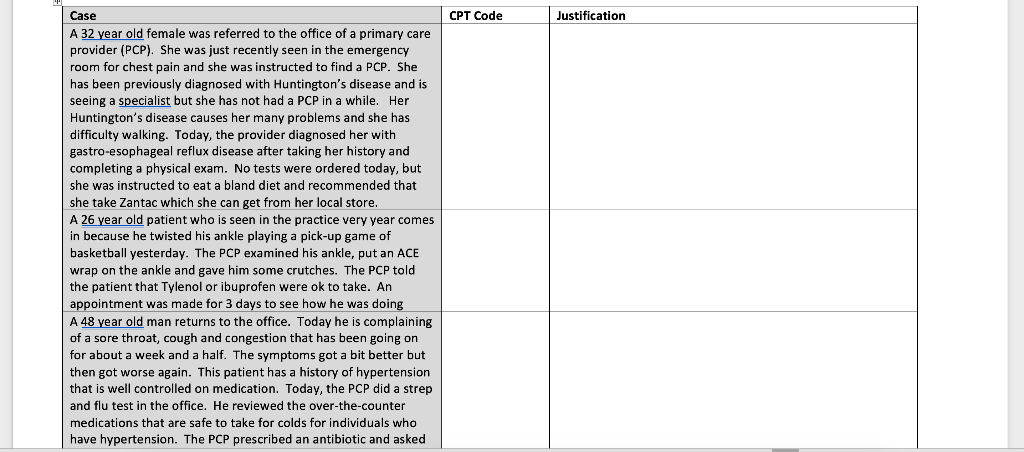
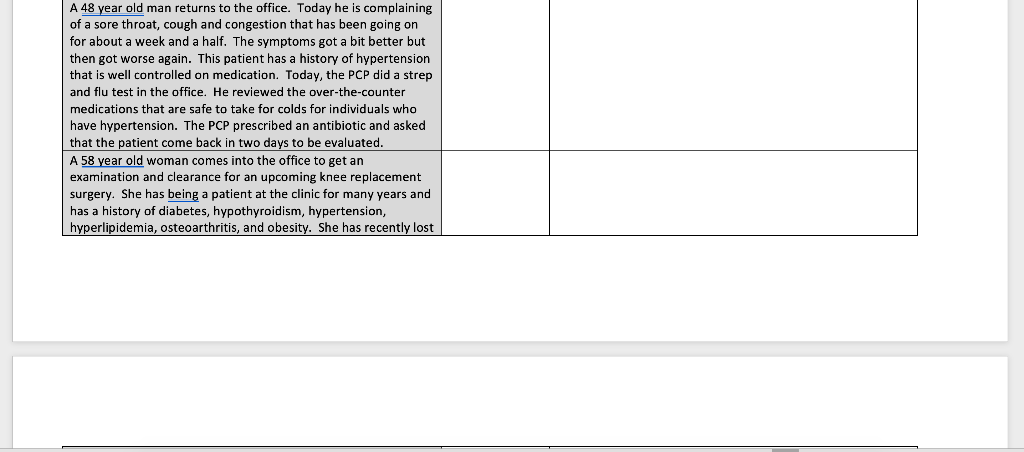

Table 7. GENERATING THE EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT LEVEL OF SERVICE CODE FOR NEW PATIENTS Evaluation and Management Code History Physical Exam Medical Decision Making 99201 Straightforward Straightforward 99202 Problem focused Problem focused Expanded problem focused Expanded problem focused Detoled Detailed Comprehensive Comprehensive Comprehensive Comprehensive 99203 99204 99205 Low Moderate High Table 8. GENERATING THE EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT LEVEL OF SERVICE CODE FOR ESTAB- USHED PATIENTS History Physical Exam Medical Decision Making Evolution and Management Code 99211 None required Straightforward 99212 Straightforward Straightforward Problem focused Problem focused Expanded problem focused Expanded problem focused Detailed Comprehensive Comprehensive 99213 99214 Low Detailed Moderute 99215 High For this assignment, students are going to evaluate the cases, then, using the graph above and the definitions provides to select the best billing CPT management and evaluation code for the case. Student will justify their selection in the last column. The justification must be cited and referenced (references can be listed at the end of the document). Students may type directly into the table to enter their CPT code selection and justification. Then the word document can be saved. The saved word document can then be uploaded to the assignment drop box Definitions New Patient: a patient who has not previously been seen in the practice Established Patient: a patient who is currently being treated at the practice Problem Focused: limited examination of one or two affected organ or body system that the patient is complaining about. (Ex: a patient who comes in only for a sprained ankle) Expanded Problem Focused: a limited examination of the affected organ or body system plus other systems that may be related. (Ex: a patient with a cold and cough) Detailed: an extensive examination of multiple body parts or systems (Ex: a patient with multiple diagnosis or one with one or more chronic diseases) Comprehensive: a complete examination of all body systems (Ex: a patient who is coming in for an annual physical) Straightforward: one or two diagnoses that are not complex and the patient is not very sick and the risk for the patient related to the problem is minimal. (Ex: a patient who has conjunctivitis) Low Complexity: more than two diagnosis that require some review of labs or diagnostic tests but the risk the problem for the patient is low (Ex: a patient who has strep throat) Moderate complexity: multiple diagnoses and diagnostics and labs must be reviewed and new prescriptions are written. The patient has a moderate risk to their health from their condition (Ex: a patient with diabetes who has pneumonia) High Complexity: extensive, complex diagnoses that affect the entire body that require significant testing and diagnostic studies and puts the patient at high risk of sickness or death. (Ex: a patient who is being evaluated for possible cancer or has a disease like multiple sclerosis) CPT Code Justification Case A 32 year old female was referred to the office of a primary care provider (PCP). She was just recently seen in the emergency room for chest pain and she was instructed to find a PCP. She has been previously diagnosed with Huntington's disease and is seeing a specialist but she has not had a PCP in a while. Her Huntington's disease causes her many problems and she has difficulty walking. Today, the provider diagnosed her with gastro-esophageal reflux disease after taking her history and completing a physical exam. No tests were ordered today, but she was instructed to eat a bland diet recommended that she take Zantac which she can get from her local store. A 26 year old patient who is seen in the practice very year comes in because he twisted his ankle playing a pick-up game of basketball yesterday. The PCP examined his ankle, put an ACE wrap on the ankle and gave him some crutches. The PCP told the patient that Tylenol or ibuprofen were ok to take. An appointment was made for 3 days to see how he was doing A 48 year old man returns to the office. Today he is complaining of a sore throat, cough and congestion that has been going on for about a week and a half. The symptoms got a bit better but then got worse again. This patient has a history of hypertension that is well controlled on medication. Today, the PCP did a strep and flu test in the office. He reviewed the over-the-counter medications that are safe to take for colds for individuals who have hypertension. The PCP prescribed an antibiotic and asked A 48 year old man returns to the office. Today he is complaining of a sore throat, cough and congestion that has been going on for about a week and a half. The symptoms got a bit better but then got worse again. This patient has a history of hypertension that is well controlled on medication. Today, the PCP did a strep and flu test in the office. He reviewed the over-the-counter medications that are safe to take for colds for individuals who have hypertension. The PCP prescribed an antibiotic and asked that the patient come back in two days to be evaluated. A 58 year old woman comes into the office to get an examination and clearance for an upcoming knee replacement surgery. She has being a patient at the clinic for many years and has a history of diabetes, hypothyroidism, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, osteoarthritis, and obesity. She has recently lost 50 pounds in preparation for the surgery. The PCP reviewed a recent chest x-ray, ECG diagnostic studies. She also reviewed the results of labs including CBC, Electrolytes, thyroid studies, and a lipid panel. The PCP examined her from head to toe. At the end of the visit, the PCP gave the patient clearance for surgery and documented this extensively for the surgeon. References: Table 7. GENERATING THE EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT LEVEL OF SERVICE CODE FOR NEW PATIENTS Evaluation and Management Code History Physical Exam Medical Decision Making 99201 Straightforward Straightforward 99202 Problem focused Problem focused Expanded problem focused Expanded problem focused Detoled Detailed Comprehensive Comprehensive Comprehensive Comprehensive 99203 99204 99205 Low Moderate High Table 8. GENERATING THE EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT LEVEL OF SERVICE CODE FOR ESTAB- USHED PATIENTS History Physical Exam Medical Decision Making Evolution and Management Code 99211 None required Straightforward 99212 Straightforward Straightforward Problem focused Problem focused Expanded problem focused Expanded problem focused Detailed Comprehensive Comprehensive 99213 99214 Low Detailed Moderute 99215 High For this assignment, students are going to evaluate the cases, then, using the graph above and the definitions provides to select the best billing CPT management and evaluation code for the case. Student will justify their selection in the last column. The justification must be cited and referenced (references can be listed at the end of the document). Students may type directly into the table to enter their CPT code selection and justification. Then the word document can be saved. The saved word document can then be uploaded to the assignment drop box Definitions New Patient: a patient who has not previously been seen in the practice Established Patient: a patient who is currently being treated at the practice Problem Focused: limited examination of one or two affected organ or body system that the patient is complaining about. (Ex: a patient who comes in only for a sprained ankle) Expanded Problem Focused: a limited examination of the affected organ or body system plus other systems that may be related. (Ex: a patient with a cold and cough) Detailed: an extensive examination of multiple body parts or systems (Ex: a patient with multiple diagnosis or one with one or more chronic diseases) Comprehensive: a complete examination of all body systems (Ex: a patient who is coming in for an annual physical) Straightforward: one or two diagnoses that are not complex and the patient is not very sick and the risk for the patient related to the problem is minimal. (Ex: a patient who has conjunctivitis) Low Complexity: more than two diagnosis that require some review of labs or diagnostic tests but the risk the problem for the patient is low (Ex: a patient who has strep throat) Moderate complexity: multiple diagnoses and diagnostics and labs must be reviewed and new prescriptions are written. The patient has a moderate risk to their health from their condition (Ex: a patient with diabetes who has pneumonia) High Complexity: extensive, complex diagnoses that affect the entire body that require significant testing and diagnostic studies and puts the patient at high risk of sickness or death. (Ex: a patient who is being evaluated for possible cancer or has a disease like multiple sclerosis) CPT Code Justification Case A 32 year old female was referred to the office of a primary care provider (PCP). She was just recently seen in the emergency room for chest pain and she was instructed to find a PCP. She has been previously diagnosed with Huntington's disease and is seeing a specialist but she has not had a PCP in a while. Her Huntington's disease causes her many problems and she has difficulty walking. Today, the provider diagnosed her with gastro-esophageal reflux disease after taking her history and completing a physical exam. No tests were ordered today, but she was instructed to eat a bland diet recommended that she take Zantac which she can get from her local store. A 26 year old patient who is seen in the practice very year comes in because he twisted his ankle playing a pick-up game of basketball yesterday. The PCP examined his ankle, put an ACE wrap on the ankle and gave him some crutches. The PCP told the patient that Tylenol or ibuprofen were ok to take. An appointment was made for 3 days to see how he was doing A 48 year old man returns to the office. Today he is complaining of a sore throat, cough and congestion that has been going on for about a week and a half. The symptoms got a bit better but then got worse again. This patient has a history of hypertension that is well controlled on medication. Today, the PCP did a strep and flu test in the office. He reviewed the over-the-counter medications that are safe to take for colds for individuals who have hypertension. The PCP prescribed an antibiotic and asked A 48 year old man returns to the office. Today he is complaining of a sore throat, cough and congestion that has been going on for about a week and a half. The symptoms got a bit better but then got worse again. This patient has a history of hypertension that is well controlled on medication. Today, the PCP did a strep and flu test in the office. He reviewed the over-the-counter medications that are safe to take for colds for individuals who have hypertension. The PCP prescribed an antibiotic and asked that the patient come back in two days to be evaluated. A 58 year old woman comes into the office to get an examination and clearance for an upcoming knee replacement surgery. She has being a patient at the clinic for many years and has a history of diabetes, hypothyroidism, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, osteoarthritis, and obesity. She has recently lost 50 pounds in preparation for the surgery. The PCP reviewed a recent chest x-ray, ECG diagnostic studies. She also reviewed the results of labs including CBC, Electrolytes, thyroid studies, and a lipid panel. The PCP examined her from head to toe. At the end of the visit, the PCP gave the patient clearance for surgery and documented this extensively for the surgeon. References
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


