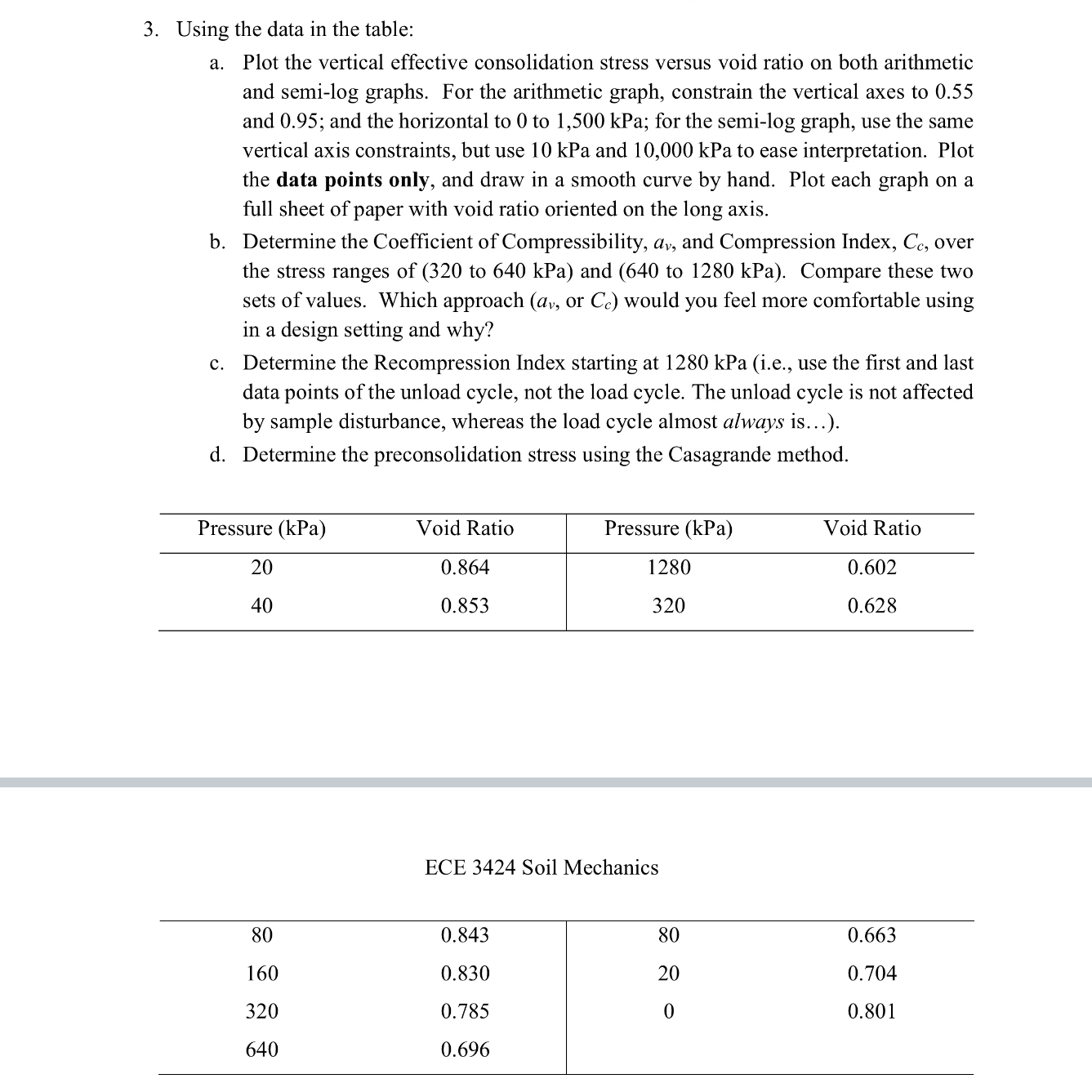
Question: Using the data in the table: a . Plot the vertical effective consolidation stress versus void ratio on both arithmetic and semi - log graphs.
Using the data in the table:
a Plot the vertical effective consolidation stress versus void ratio on both arithmetic and semilog graphs. For the arithmetic graph, constrain the vertical axes to and ; and the horizontal to to kPa; for the semilog graph, use the same vertical axis constraints, but use kPa and kPa to ease interpretation. Plot the data points only, and draw in a smooth curve by hand. Plot each graph on a full sheet of paper with void ratio oriented on the long axis.
b Determine the Coefficient of Compressibility, and Compression Index, over the stress ranges of to kPa and to kPa Compare these two sets of values. Which approach or would you feel more comfortable using in a design setting and why?
c Determine the Recompression Index starting at kPa ie use the first and last data points of the unload cycle, not the load cycle. The unload cycle is not affected by sample disturbance, whereas the load cycle almost always is
d Determine the preconsolidation stress using the Casagrande method.
tablePressure kPaVoid Ratio,Pressure kPaVoid Ratio
ECE Soil Mechanics
table
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


