Question: using the excel answer all the questions and i will thumbs up 8.4 A gear manufacturer is planning next week's production for four types of
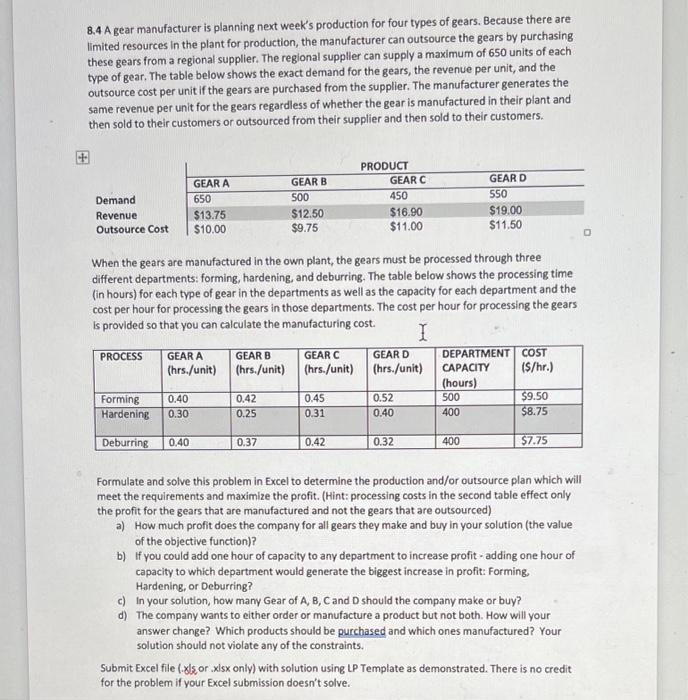
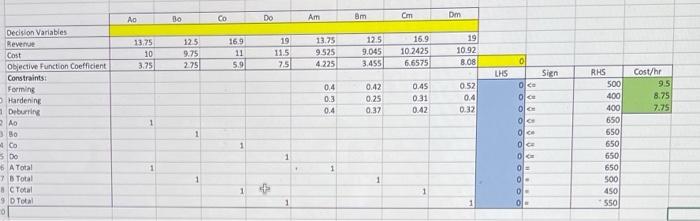
8.4 A gear manufacturer is planning next week's production for four types of gears. Because there are limited resources in the plant for production, the manufacturer can outsource the gears by purchasing these gears from a regional supplier. The regional supplier can supply a maximum of 650 units of each type of gear. The table below shows the exact demand for the gears, the revenue per unit, and the outsource cost per unit if the gears are purchased from the supplier. The manufacturer generates the same revenue per unit for the gears regardless of whether the gear is manufactured in their plant and then sold to their customers or outsourced from their supplier and then sold to their customers. Demand Revenue Outsource Cost GEAR A 650 $13.75 $10.00 GEAR B 500 $12.50 $9.75 PRODUCT GEAR C 450 $16.90 $11.00 GEARD 550 $19.00 $11.50 When the gears are manufactured in the own plant, the gears must be processed through three different departments: forming, hardening, and deburring. The table below shows the processing time (in hours) for each type of gear in the departments as well as the capacity for each department and the cost per hour for processing the gears in those departments. The cost per hour for processing the gears is provided so that you can calculate the manufacturing cost. I PROCESS GEAR A GEAR B GEAR C GEARD DEPARTMENT COST (hrs./unit) (hrs./unit) (hrs./unit) (hrs./unit) CAPACITY (S/hr.) (hours) Forming 0.40 0.42 0.45 0.52 500 $9.50 Hardening 0.30 0.25 0.31 0.40 400 $8.75 Deburring 0.40 0.37 0.42 0.32 400 $7.75 Formulate and solve this problem in Excel to determine the production and/or outsource plan which will meet the requirements and maximize the profit. (Hint: processing costs in the second table effect only the profit for the gears that are manufactured and not the gears that are outsourced) a) How much profit does the company for all gears they make and buy in your solution (the value of the objective function)? b) if you could add one hour of capacity to any department to increase profit -adding one hour of capacity to which department would generate the biggest increase in profit: Forming Hardening, or Deburring? c) in your solution, how many Gear of A, B, C and D should the company make or buy? d) The company wants to either order or manufacture a product but not both. How will your answer change? Which products should be purchased and which ones manufactured? Your solution should not violate any of the constraints. Submit Excel file (.xls or .xlsx only) with solution using LP Template as demonstrated. There is no credit for the problem if your Excel submission doesn't solve. Bo AD CO Do Dm Am Bm 8 15 13.75 10 3.75 125 9.75 2.75 169 11 5.9 19 11.5 7.51 13.75 9525 4.225 12.5 9.045 3.455 16.9 10.2425 6.6575 19 10.92 8.08 IN LHS 04 03 0.4 0.42 0.25 0.37 0.45 0:31 0.42 052 0.4 0.32 RHS 500 400 400 Cost/hr 95 8.75 7.75 Decision Variables Revenue Cost Objective Function Coefficient Constraints: Forming Hardening Deburring AD Bo Co 500 6 A Total 7 Total 8 Total 9 Total 1 6501 1 ol Sign Oce O OG OC ol OG OC 0 0 O O. 1 1 + 1 550 650 650 650 500 450 550 1 1 1 + 8.4 A gear manufacturer is planning next week's production for four types of gears. Because there are limited resources in the plant for production, the manufacturer can outsource the gears by purchasing these gears from a regional supplier. The regional supplier can supply a maximum of 650 units of each type of gear. The table below shows the exact demand for the gears, the revenue per unit, and the outsource cost per unit if the gears are purchased from the supplier. The manufacturer generates the same revenue per unit for the gears regardless of whether the gear is manufactured in their plant and then sold to their customers or outsourced from their supplier and then sold to their customers. Demand Revenue Outsource Cost GEAR A 650 $13.75 $10.00 GEAR B 500 $12.50 $9.75 PRODUCT GEAR C 450 $16.90 $11.00 GEARD 550 $19.00 $11.50 When the gears are manufactured in the own plant, the gears must be processed through three different departments: forming, hardening, and deburring. The table below shows the processing time (in hours) for each type of gear in the departments as well as the capacity for each department and the cost per hour for processing the gears in those departments. The cost per hour for processing the gears is provided so that you can calculate the manufacturing cost. I PROCESS GEAR A GEAR B GEAR C GEARD DEPARTMENT COST (hrs./unit) (hrs./unit) (hrs./unit) (hrs./unit) CAPACITY (S/hr.) (hours) Forming 0.40 0.42 0.45 0.52 500 $9.50 Hardening 0.30 0.25 0.31 0.40 400 $8.75 Deburring 0.40 0.37 0.42 0.32 400 $7.75 Formulate and solve this problem in Excel to determine the production and/or outsource plan which will meet the requirements and maximize the profit. (Hint: processing costs in the second table effect only the profit for the gears that are manufactured and not the gears that are outsourced) a) How much profit does the company for all gears they make and buy in your solution (the value of the objective function)? b) if you could add one hour of capacity to any department to increase profit -adding one hour of capacity to which department would generate the biggest increase in profit: Forming Hardening, or Deburring? c) in your solution, how many Gear of A, B, C and D should the company make or buy? d) The company wants to either order or manufacture a product but not both. How will your answer change? Which products should be purchased and which ones manufactured? Your solution should not violate any of the constraints. Submit Excel file (.xls or .xlsx only) with solution using LP Template as demonstrated. There is no credit for the problem if your Excel submission doesn't solve. Bo AD CO Do Dm Am Bm 8 15 13.75 10 3.75 125 9.75 2.75 169 11 5.9 19 11.5 7.51 13.75 9525 4.225 12.5 9.045 3.455 16.9 10.2425 6.6575 19 10.92 8.08 IN LHS 04 03 0.4 0.42 0.25 0.37 0.45 0:31 0.42 052 0.4 0.32 RHS 500 400 400 Cost/hr 95 8.75 7.75 Decision Variables Revenue Cost Objective Function Coefficient Constraints: Forming Hardening Deburring AD Bo Co 500 6 A Total 7 Total 8 Total 9 Total 1 6501 1 ol Sign Oce O OG OC ol OG OC 0 0 O O. 1 1 + 1 550 650 650 650 500 450 550 1 1 1 +
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


