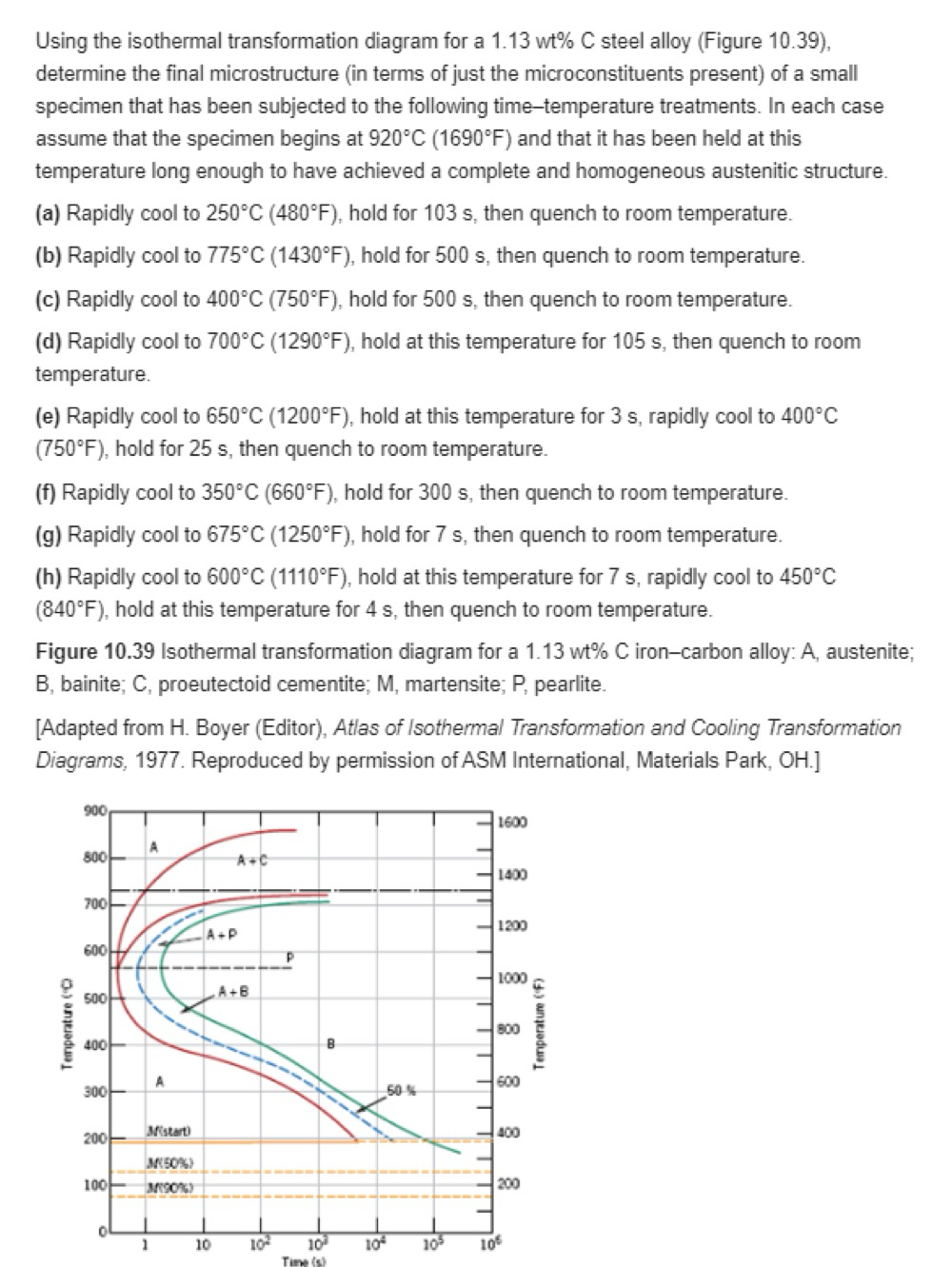
Question: Using the isothermal transformation diagram for a 1 . 1 3 w t % C steel alloy ( Figure 1 0 . 3 9 )
Using the isothermal transformation diagram for a steel alloy Figure determine the final microstructure in terms of just the microconstituents present of a small specimen that has been subjected to the following timetemperature treatments. In each case assume that the specimen begins at and that it has been held at this temperature long enough to have achieved a complete and homogeneous austenitic structure.
a Rapidly cool to hold for s then quench to room temperature.
b Rapidly cool to hold for s then quench to room temperature.
c Rapidly cool to hold for s then quench to room temperature.
d Rapidly cool to hold at this temperature for s then quench to room temperature.
e Rapidly cool to hold at this temperature for s rapidly cool to hold for s then quench to room temperature.
f Rapidly cool to hold for s then quench to room temperature.
g Rapidly cool to hold for s then quench to room temperature.
h Rapidly cool to hold at this temperature for s rapidly cool to hold at this temperature for s then quench to room temperature.
Figure Isothermal transformation diagram for a ironcarbon alloy: A austenite; bainite; C proeutectoid cementite; martensite; pearlite.
Adapted from H Boyer Editor Atlas of Isothermal Transformation and Cooling Transformation Diagrams, Reproduced by permission of ASM International, Materials Park, OH
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


