Question: + V X - C : 1 / 7 100% + 1 Problem 1. In our lectures, we have explored how to classify critical points
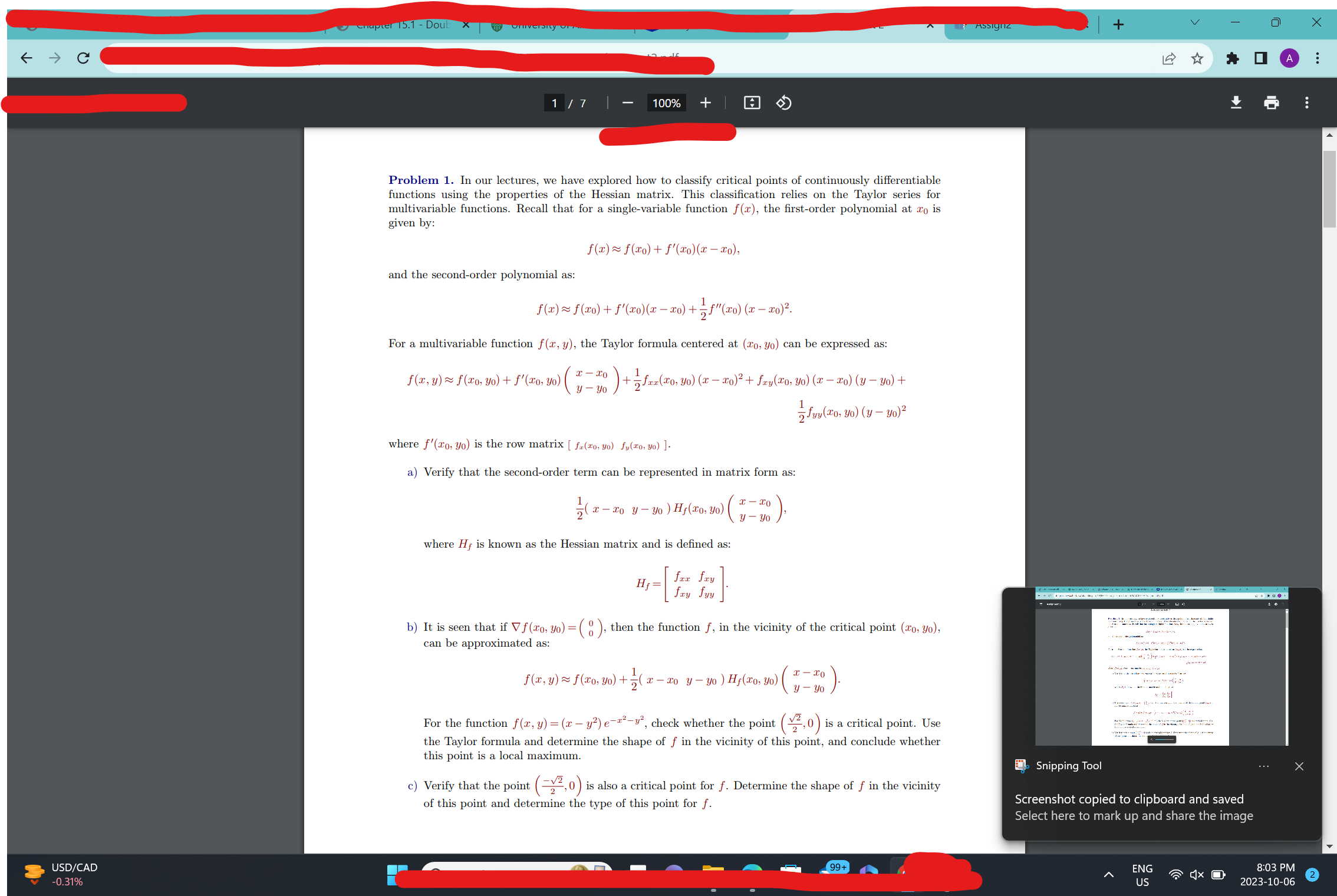
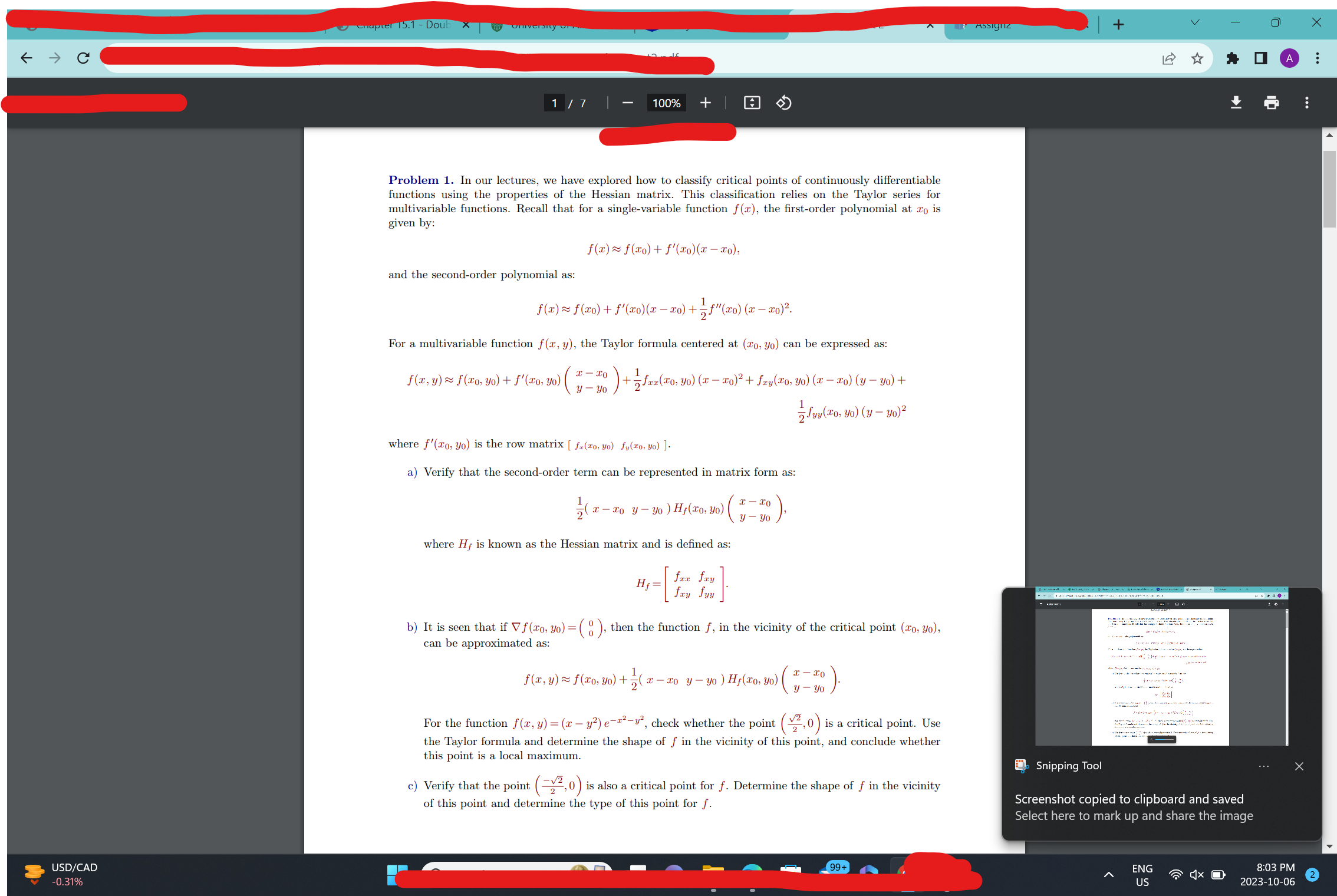
+ V X - C : 1 / 7 100% + 1 Problem 1. In our lectures, we have explored how to classify critical points of continuously differentiable functions using the properties of the Hessian matrix. This classification relies on the Taylor series for multivariable functions. Recall that for a single-variable function f(x), the first-order polynomial at To is given by: f(x) ~ f(xO) + f'(xO)(x - 20), and the second-order polynomial as: f(x) ~ f(20) + f'(20)(2 -20) + 28"(20) (x -20)2. For a multivariable function f(x, y), the Taylor formula centered at (To, yo) can be expressed as: f(x, y) ~ f(20, yo) + f'(20, 40) (7 70 +75xx(20, Vo) (x - 20)2 + fry(20, 30) (x - 20) ( - 90) + 7 fur ( 20, yo ) ( y - yo ) 2 where f'(To, yo) is the row matrix [ fa(zo, yo) fu(zo, vo) ]. a) Verify that the second-order term can be represented in matrix form as: 2 ( X - To y - yo ) H,(20, 30) 3 - 30 where Hf is known as the Hessian matrix and is defined as: b) It is seen that if Vf(To, yo) = (8 ), then the function f, in the vicinity of the critical point (To, yo), can be approximated as: f (x, y) ~ f (To, yo) + 2( x - 20 3 - yo ) H,(zo, VO) (X -20 For the function f(x, y) = (x - y?) e-2-y, check whether the point (22, 0 ) is a critical point. Use the Taylor formula and determine the shape of f in the vicinity of this point, and conclude whether this point is a local maximum. Snipping Tool ... c) Verify that the point (2 2,0 ) is also a critical point for f. Determine the shape of f in the vicinity of this point and determine the type of this point for f. Screenshot copied to clipboard and saved Select here to mark up and share the image USD/CAD 99+ ENG 8:03 PM 2 0.31% US 2023-10-06
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


