Question: W Input answers in supplied prelab google slides template. Answer 1 sentencefrdea for each part of the question. You do not necessarily need to include

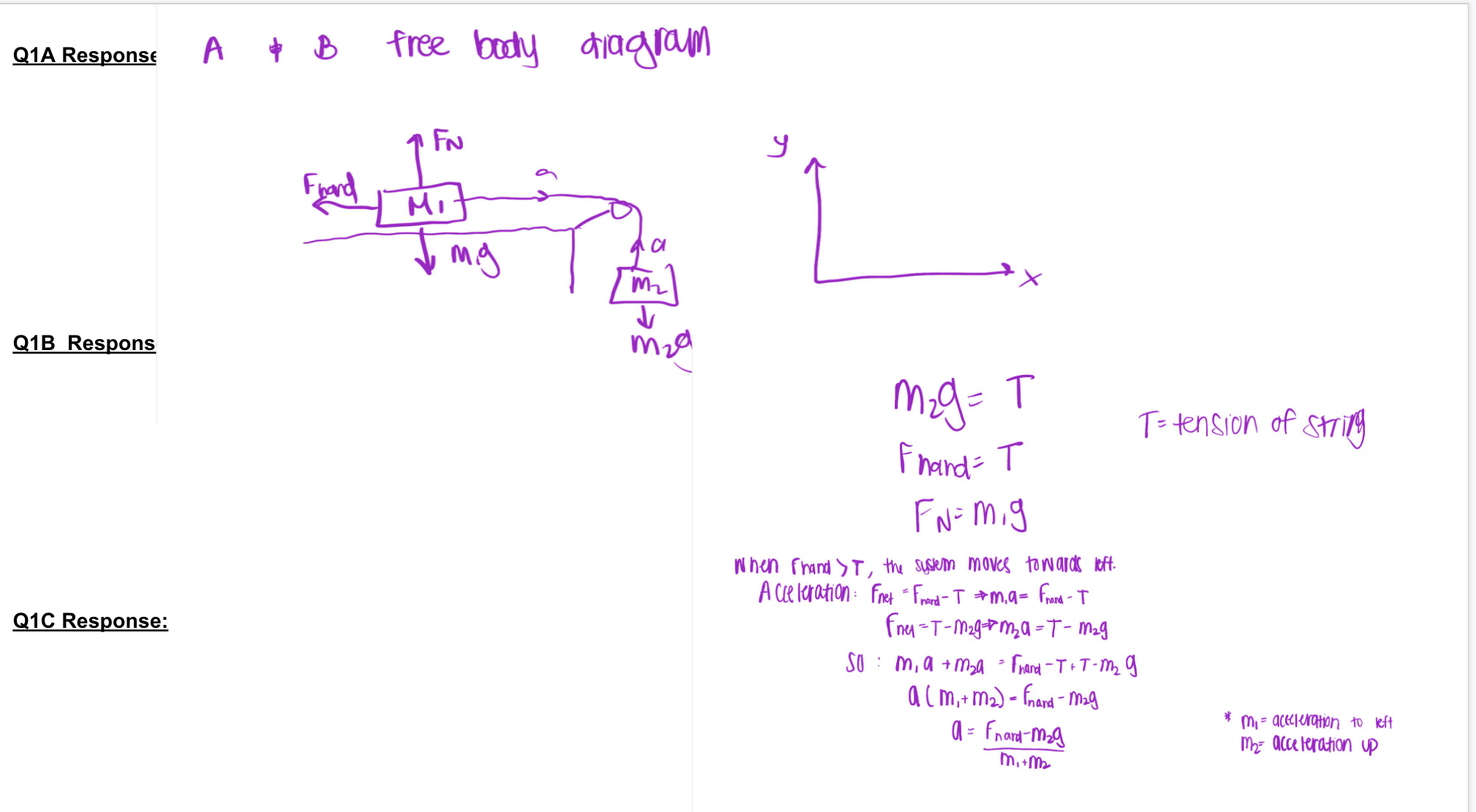
W Input answers in supplied prelab google slides template. Answer 1 sentencefrdea for each part of the question. You do not necessarily need to include complete sentences. Bullet points are ne. Setup; Cart on frictionless air track, holding cart still and letting it go to accelerate from external force from Tension in a Pulley System. a. As a continuation from slide 1b, draw the free body force diagram of the air cart (my), after you have released your hand's force on the car and it is allowed to accelerate. Keep your coordinate axes for n11 the same orientation as in slide 1. b. Draw the free body force diagram of the dangling mass (m;), after you have released your hands force on the cart, and it is accelerating. Again keep your coordinate axes for m; the same as you did in slide 1. 0. Write out on paper (and take a picture). or type out (if it's easier), the equations resulting from applying Newton's Second Law (ma = Fnet = all the component forces summed with proper signs for directions). Be clear about which equation corresponds to which object, and which direction. You need one equation for each dimension of each object. Pr-L Ii :Dlnln nEx rimn mrTnln r v.in lrin: a. Solve for the tension in the string when you are holding the cart and the system is at rest. (hint: focus on m2 free body diagram here). You can leave your answer in terms of mg and g. b. Conslder the tension in the string when you let go and the cart system is accelerating. Is the tension the same, greater than in part 3a, or less than in part 33? Justify your reasoning. 0. Describe how you can create a PASCO movie and accelerometer recording that captures information about the cart tension while you hold the cart still AND THEN release it to see the tension during acceleration (hint: the PASCO accelerometer is bolted to the top of the cart and the string over the pulley is attached to a tension sensor coming out of the accelerometer, see Figure 2 below). Figure 2: Image of the 3D PASCO accelerometer, with hook that serves as the 1D PASCO force sensor. Note the xy~z axes on the front. The force sensor is oriented along the -x direction. This sensor is bolted to the top of the air cart, with the string attached to the hook so that the PASCO force sensor can continuously measure Tension in the string. In 5AL Lab 5. you will make simultaneous measurements of PASCO x direction acceleration, PASCO force. and your PASCO movie recording. 1' J. '5 i E 0 U' m i D U n n 2 3. O : Q1A Response A + B free body diagram 1 FN Fhand MIT ma C X Q1B Respons mid mzg = T T= tension of string Fhand = T FN: mig when Fhand > T , the system moves towards left . Acceleration: Fnet = Frand- T # m. a= Frand- T Q1C Response: Foe = T- mag- # mza = T- mag SO : m, a + mza = Frand- T + T-mz g a (m, + m 2 ) = (nand - mag a = Fnard-mag * m, = acceleration to left my: acceleration up m. + mz
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


