Question: We consider the built-in iris data set in R. It consists of four numerical predictors and one categorical response: Sepal.Length: numeric Sepal. Width: numeric Petal.Length:
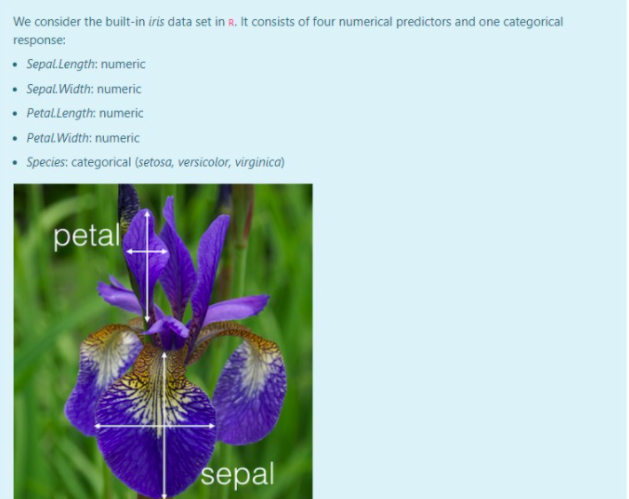
We consider the built-in iris data set in R. It consists of four numerical predictors and one categorical response: Sepal.Length: numeric Sepal. Width: numeric Petal.Length: numeric Petal. Width: numeric Species: categorical (setosa, versicolor, virginica) petal sepal sepal Sepal and petal of iris virginica. We build a decision tree model that predicts the Species of the plant by means of the numeric predictors with standard settings. > library(tree) > tree.model plot(tree.model) > text (tree.model) Compute the confusion matrix and the accuracy on the training set (Hint: Use the predict and table functions) Answer: We consider the built-in iris data set in R. It consists of four numerical predictors and one categorical response: Sepal.Length: numeric Sepal. Width: numeric Petal.Length: numeric Petal. Width: numeric Species: categorical (setosa, versicolor, virginica) petal sepal sepal Sepal and petal of iris virginica. We build a decision tree model that predicts the Species of the plant by means of the numeric predictors with standard settings. > library(tree) > tree.model plot(tree.model) > text (tree.model) Compute the confusion matrix and the accuracy on the training set (Hint: Use the predict and table functions)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


