Question: We have learned that p V = n R T is used to describe an ideal gas. One way to model non - ideal gas
We have learned that is used to describe an ideal gas. One way to model non
ideal gas is to use van der Waals equation where a and are
constants. Such a gas is called van der Waals gas. For mol monatomic van der Waals gas
the molar energy is given by where is the molar volume at
temperature and is the constant in the van der Waals equation. Initially mol
monatomic van der Waals gas is at the temperature and occupies a volume The gas
is allowed to expand adiabatically into a vacuum so that it occupies a total volume
What is the final temperature of the gas?
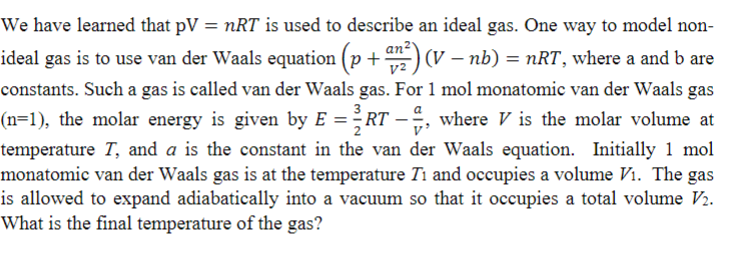
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


