Question: We start by defining the independent set problem. Given a graph G = (V, E), we say a set of nods S V is independent
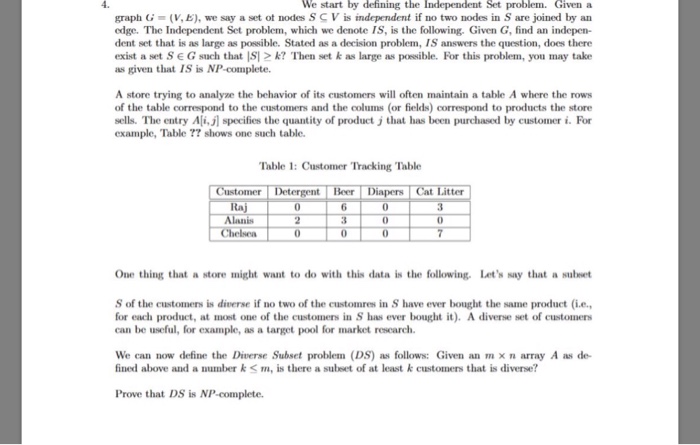
We start by defining the independent set problem. Given a graph G = (V, E), we say a set of nods S V is independent if no two nodes in S are joined by an edge. The Inexpedient Set problem, which we denote Is, answers the question, does there exist a set S G such that |S| greaterthanorequalto k? Then set k as large as possible. For this problem, you may take as given that IS is NP-complete. A store trying to analyze the behaviour of its customers will often maintain a table A where the rows of the table correspond to the customer* and the (or fields) correspond to products sells. The entry specifies quantity of product J that has been purchased by customer i. For example, Table ?? shows one such table. One thing that a store might want to do with this data is the following. Let's say that a subset S of the customers is diverse if no two of the customers in S have every bought the same product (i.e., of reach product, at most one of the customers in S has ever bought it). A diverse set of customers can be useful, for example, as a target pool for market research. We can now define the Diverse Subset problem (DS) as follows: Given an m times n array A as defined above and a number k lessthanorequalto m, is there a subset of at least k customers that is diverse? Prove that DS is NP-complete
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


